Jan 04, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) A analysis group consisting of members of the Egyptian Petroleum Analysis Institute and the Useful Supplies Engineering Laboratory on the Toyohashi College of Know-how, has developed a novel high-performance photoelectrode by establishing a zinc oxide nanopagoda array with a singular form on a clear electrode and making use of silver nanoparticles to its floor.
The findings have been revealed in Electrochemistry Communications (“Ag nanoparticles embellished ZnO nanopagodas for photoelectrochemical utility”).
Key Takeaways
Improvement of a singular high-performance photoelectrode utilizing zinc oxide nanopagoda arrays and silver nanoparticles for environment friendly daylight absorption and enhanced photoelectrochemical properties.
The zinc oxide nanopagoda displays minimal crystal defects, excessive electron conductivity, and step buildings enabling excessive floor chemical response exercise.
Introduction of silver nanoparticles improves seen mild absorption, enhancing photocurrent by roughly 1.5 instances, useful for photoelectrochemical water splitting.
The distinctive construction of zinc oxide nanopagoda effectively captures ultraviolet rays, contributing to improved photoelectrochemical properties.
Ongoing analysis focuses on structural management and floor ornament of zinc oxide nanopagodas to extend sturdiness and optimize hydrogen manufacturing from water splitting.
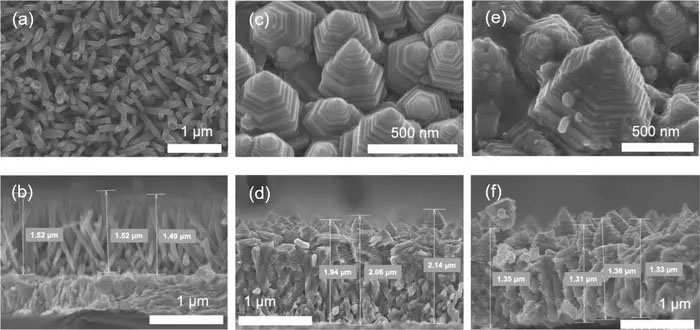
(a)(b): zinc oxide nanorod array, (c)(d): zinc oxide nanopagoda array, (e)(f): silver-nanoparticle-decorated zinc oxide nanopagoda array. The higher row contains floor photos, and the decrease row contains corresponding cross-sectional photos. (Picture: Toyohashi College of Know-how)
The Analysis
The zinc oxide nanopagoda is characterised by having many step buildings, because it includes stacks of otherwise sized hexagonal prisms. As well as, it displays only a few crystal defects and wonderful electron conductivity. By adorning its floor with silver nanoparticles, the zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode good points seen mild absorption properties, enabling it to perform underneath daylight irradiation.
Photoelectrochemical water splitting utilizing daylight is anticipated for use as a know-how to provide clear vitality within the type of hydrogen. As key supplies for this know-how, photoelectrodes will need to have low overpotential towards water splitting reactions, along with excessive photo voltaic absorption and cost switch efficiencies. For sensible applicability, this know-how can’t use uncommon metals as main supplies, and the fabrication course of have to be industrialized; nonetheless, supplies that fulfill these necessities haven’t but been developed.
Accordingly, the analysis group solely targeted on the zinc oxide nanopagoda array, as such arrays are cheap to provide, function excessive electron conductivity, and should not weak to uncooked materials depletion. Initially, zinc oxide nanopagoda arrays had been thought of troublesome to manufacture with good reproducibility. Led by Marwa Abouelela – a third-year doctoral pupil who can be the lead creator of this paper – the group first optimized the synthesis course of to make sure excessive reproducibility.
When the photoelectrochemical properties of the obtained photoelectrode had been evaluated, a comparatively massive photocurrent was noticed to emerge underneath pseudo-sunlight irradiation. Along with the excessive cost switch effectivity related to low defect density and excessive floor chemical response exercise in lots of steps, an electromagnetic area evaluation has revealed that the nanopagoda’s distinctive nanostructure can effectively seize ultraviolet rays contained within the incident mild.
To make sure the efficient utilization of seen mild, which accounts for 55% of daylight, the analysis group additional improved the photoelectrochemical properties by adorning the zinc oxide nanopagoda floor with silver nanoparticles that exhibit localized floor plasmon resonance, rising the photocurrent by roughly 1.5-fold.
The motion spectrum of the photocurrent worth signifies that this enchancment is primarily attributed to the recent electron switch brought on by seen mild absorption by the localized floor plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles. By optimizing the applying of silver nanoparticles, it turned doable to solely enhance the photoelectrochemical properties whereas stopping antagonistic results on the properties of the nanopagoda itself.
Improvement background
Affiliate Professor Go Kawamura, one of many corresponding authors, acknowledged the next: “Zinc oxide nanopagodas had been thought of for utility solely to electron gun emitters, using their excessive cost switch effectivity. Nevertheless, as a result of the construction has many steps, our preliminary concept was that it’s extremely lively towards floor chemical reactions and could also be appropriate for catalyzing photoelectrochemical reactions.
Having succeeded in fabricating the nanopagoda, we aimed to enhance the effectivity of daylight utilization by making use of silver nanoparticles that exhibit localized floor plasmon resonance, and evaluated the impact by electromagnetic area evaluation; nonetheless, it was discovered that the zinc oxide nanopagoda captures incident mild, particularly ultraviolet rays, into its inside. Though this was utterly surprising, it was a lucky discovery, as this property contributes to the development of photoelectrochemical properties.”
Future outlook
At the moment, Marwa and college students of the identical laboratory are main an investigation into the impact of exact structural management of zinc oxide nanopagodas, in addition to floor ornament with different supplies, on the photoelectrochemical properties of mentioned pagodas. As a result of zinc oxide is vulnerable to photocorrosion, it can’t face up to long-term daylight irradiation by itself, main us to deal with bettering sturdiness by way of floor ornament. Upon attaining each excessive photoelectrochemical properties and sturdiness, we plan to hold out water splitting hydrogen manufacturing in an actual surroundings (decomposition of river water or seawater by daylight) and extract actual issues.
 (a)(b): zinc oxide nanorod array, (c)(d): zinc oxide nanopagoda array, (e)(f): silver-nanoparticle-decorated zinc oxide nanopagoda array. The higher row contains floor photos, and the decrease row contains corresponding cross-sectional photos. (Picture: Toyohashi College of Know-how)
(a)(b): zinc oxide nanorod array, (c)(d): zinc oxide nanopagoda array, (e)(f): silver-nanoparticle-decorated zinc oxide nanopagoda array. The higher row contains floor photos, and the decrease row contains corresponding cross-sectional photos. (Picture: Toyohashi College of Know-how)


