A workforce of researchers has reviewed a singular technique for reforming the constructions of ultra-small nanomaterials. These nanomaterials, referred to as metallic nanoclusters, bridge the hole between the metallic atom and the majority metallic, making them extremely helpful in each primary and utilized analysis. Steel nanoclusters have the potential for wide-ranging functions within the biomedical fields.
The workforce’s assessment paper is printed within the journal Polyoxometalates.
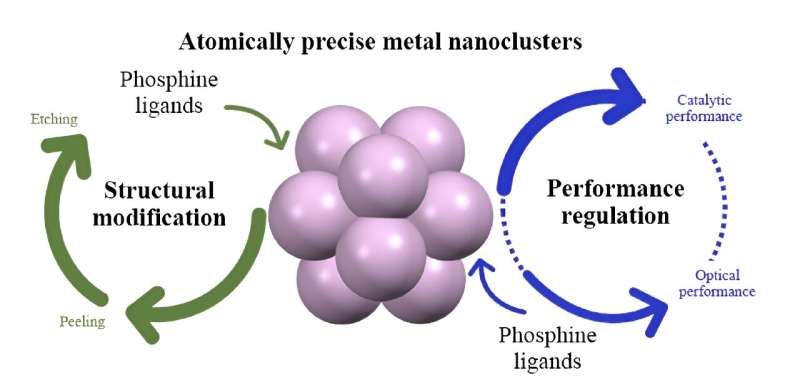
The workforce investigated the phosphine-LEIST response. This technique exhibits benefits in metallic nanoclusters’ structural modification and property modulation. “The tactic we reviewed is ready to modulate the atomically exact construction of metallic nanoclusters and regulate their corresponding efficiency,” stated Man-Bo Li, a professor at Anhui College, China.
Due to their exceptional measurement traits and exact constructions, metallic nanoclusters function bridges between nanoparticles and molecules. They supply scientists with a superb platform for learning nanomaterials’ construction and property modulation on the atomic degree.
In recent times, scientists working within the discipline of metallic nanocluster chemistry have steadily targeted extra on the impact of peripheral ligands on metallic nanoclusters. Ligands are atoms or molecules that bind on to the metallic ion.
Scientists have progressively realized that natural ligands’ spatial construction and bonding mode can considerably influence the properties of metallic nanoclusters when it comes to topology and digital construction, solubility, stability, and associated functions. So ligand engineering is turning into a vital department of metallic nanocluster chemistry.
Beforehand, nanocluster synthesis was achieved by metallic doping and direct synthesis strategies. Out of the direct synthesis technique, scientists derived the ligand-exchange-induced measurement/construction transformation (LEIST). Many nanoclusters have been synthesized utilizing the LEIST technique. With LEIST, scientists have gained a deeper understanding of the transformation phenomenon in metallic nanoclusters and broader software prospects.
The workforce examined the phosphine ligand-induced structural transformations and the corresponding catalytic and optical efficiency regulation of metallic nanoclusters. They needed to resolve the contradiction between the steadiness and exercise of metallic nanoclusters.
“The final word objective is getting ready ultra-stable and extremely lively metallic nanoclusters for sensible functions. Probably the most thrilling software can be catalysis as a result of metallic nanoclusters possess exact constructions, considerable floor activation websites, and recycling functionality. They’re perfect industrial catalysts, combining some great benefits of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts,” stated Li.
In recent times, scientists have proposed new potential makes use of for phosphine-protected metallic nanoclusters by utilizing the LEIST technique for phosphine ligands. Phosphine ligands can rework metallic nanoclusters’ construction in a top-down evolutionary course of that “peels” and “etches” for various template nanoclusters.
Phosphine ligands will also be used with different synthesis strategies. Over time, researchers have found increasingly phosphine ligands with totally different practical properties. Researchers are utilizing these to change the prevailing metallic nanocluster constructions. Phosphine ligands supply promising potential for the structural modification of metallic nanoclusters.
The workforce’s work highlights the crucial significance of growing a greater variety of functionalized phosphine ligands. “As increasingly phosphine ligands are designed and synthesized, the functions of metallic nanoclusters in varied fields can be considerably expanded,” stated Li.
Of their assessment, the workforce targeted on the phosphine-induced structural transformations of metallic nanoclusters and their ensuing efficiency regulation. They highlighted phosphine ligand-induced nanocluster transformations. They summarized the various achievements of structural modification by the phosphine-LEIST technique utilizing phosphines.
Additionally they mentioned the synergistic methodology of phosphine-induced structural modification mixed with different artificial strategies. Lastly, they summarized the potential function of phosphine ligand engineering in modulating metallic nanoclusters’ properties, akin to optical and catalytic actions.
Via their assessment, the workforce decided that the phosphine-induced transformations of atomically exact metallic nanoclusters maintain nice promise as analysis subjects and deserve additional exploration in growing and making use of these metallic nanoclusters.
Extra info:
Wenwen Fei et al, Structural modification and efficiency regulation of atomically exact metallic nanoclusters by phosphine, Polyoxometalates (2023). DOI: 10.26599/POM.2023.9140043
Offered by
Tsinghua College Press
Quotation:
Workforce critiques phosphine ligand-induced structural transformation of metallic nanoclusters (2023, December 7)
retrieved 7 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-team-phosphine-ligand-induced-metal-nanoclusters.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


