iOS already features a system-wide translation characteristic that permits customers to simply translate textual content into numerous languages. With the discharge of iOS 17.4 (and iOS 18), now you can leverage the brand new Translation API to combine this highly effective translation functionality into your apps.
Apple offers two choices for builders to make the most of the Translation API. The quickest and easiest technique is to make use of the .translationPresentation modifier, which shows a translation overlay in your app. For a extra versatile answer, you may straight name the Translation API to construct a customized translation characteristic.
On this tutorial, we are going to discover each approaches and information you thru their implementation utilizing a SwiftUI demo app. Please observe that you will want Xcode 16 to observe alongside.
Utilizing the translationPresentation Modifier
Let’s begin with the easy method: the .translationPresentation modifier. In Safari, customers can spotlight any textual content to entry the interpretation possibility, which then shows a translation overlay with the translated textual content.
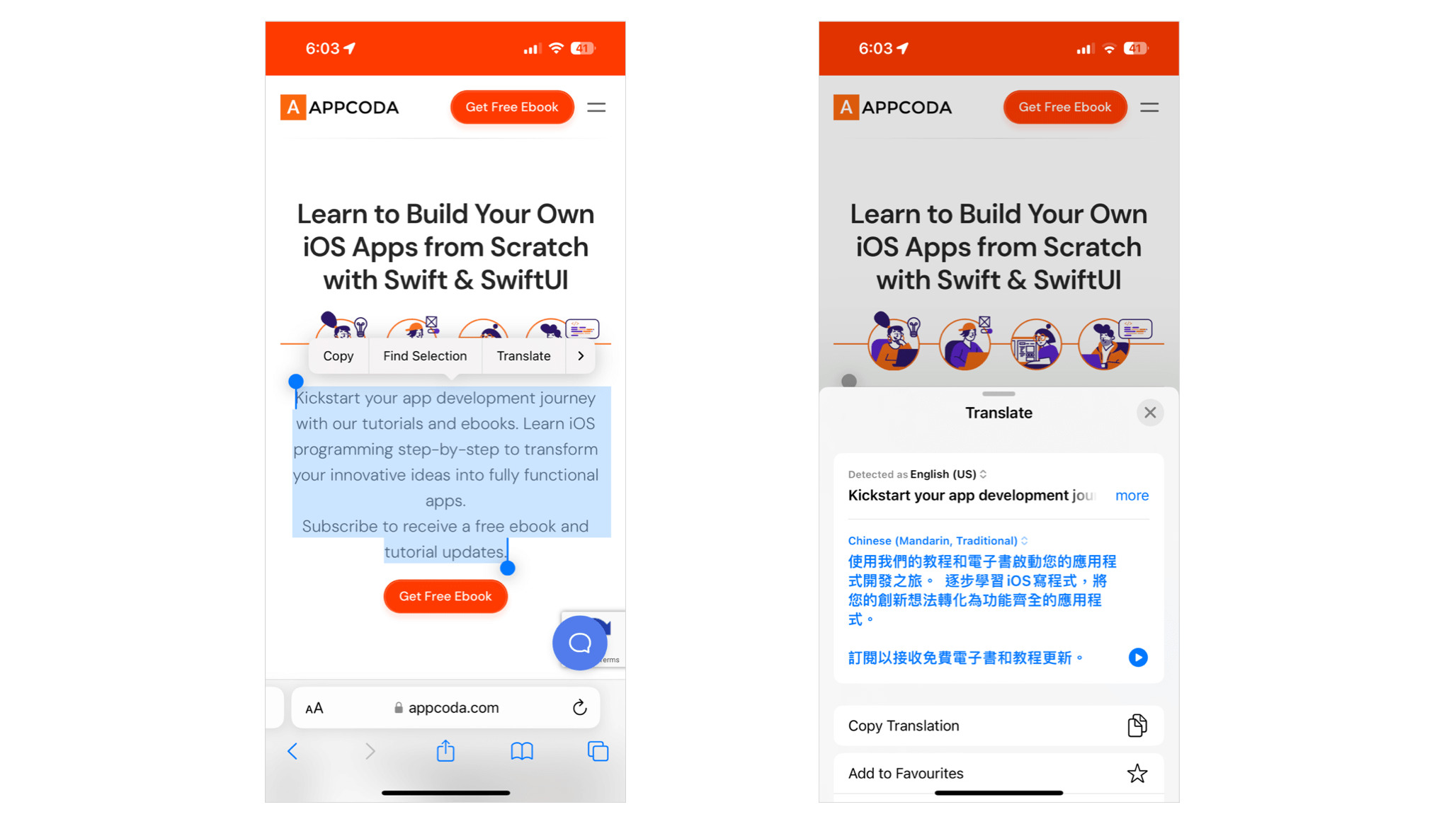
If you wish to carry this translation overlay to your app, all you want is to import the Translation bundle and use the .translationPresentation modifier. Check out the next pattern code:
import SwiftUI
import Translation
struct ContentView: View {
@State non-public var showTranslation = false
@State non-public var sampleText = article
var physique: some View {
VStack {
Textual content(sampleText)
.font(.system(.physique, design: .rounded))
Button("Translate") {
showTranslation.toggle()
}
.controlSize(.extraLarge)
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
}
.padding()
.translationPresentation(isPresented: $showTranslation, textual content: article)
}
}The app shows some pattern textual content in English with a Translate button positioned under it.
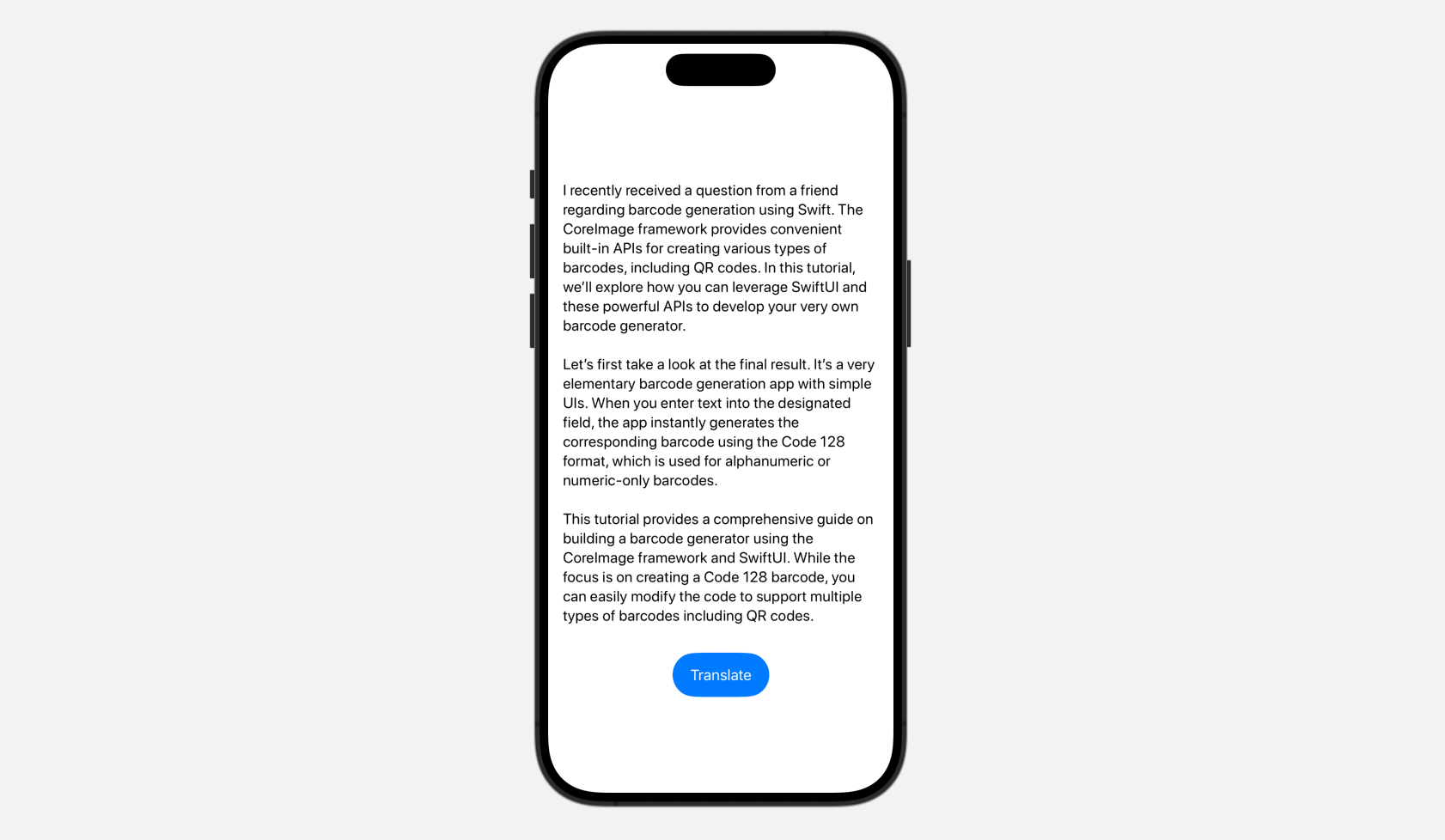
Now, whenever you faucet the “Translate” button, a translation overlay seems, displaying the translated textual content in your required language. Apart from iOS, the Translation API additionally works on each iPadOS and macOS. At the moment, this translation characteristic can’t be examined in Xcode Preview; you will need to deploy the app onto an actual machine for testing.
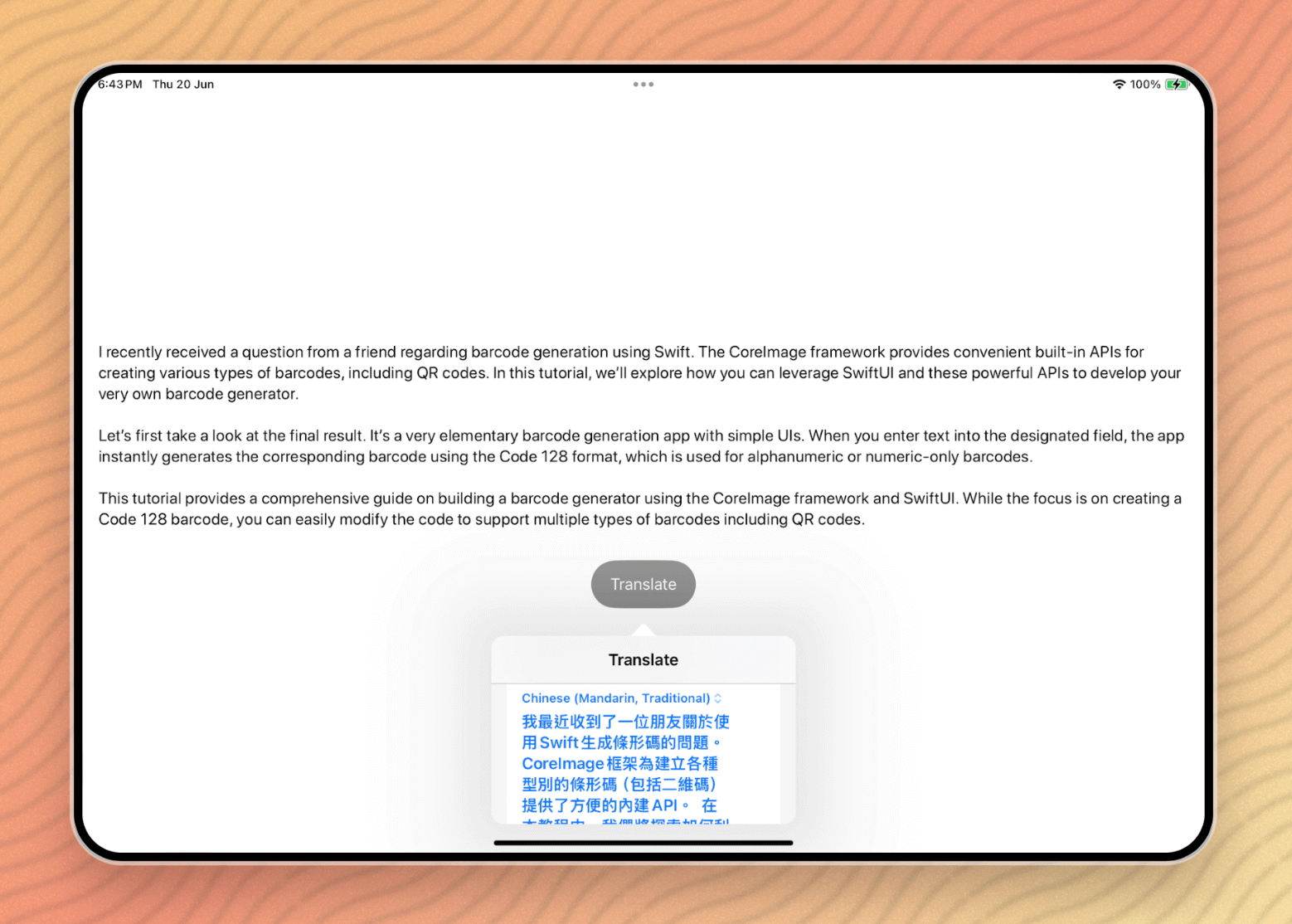
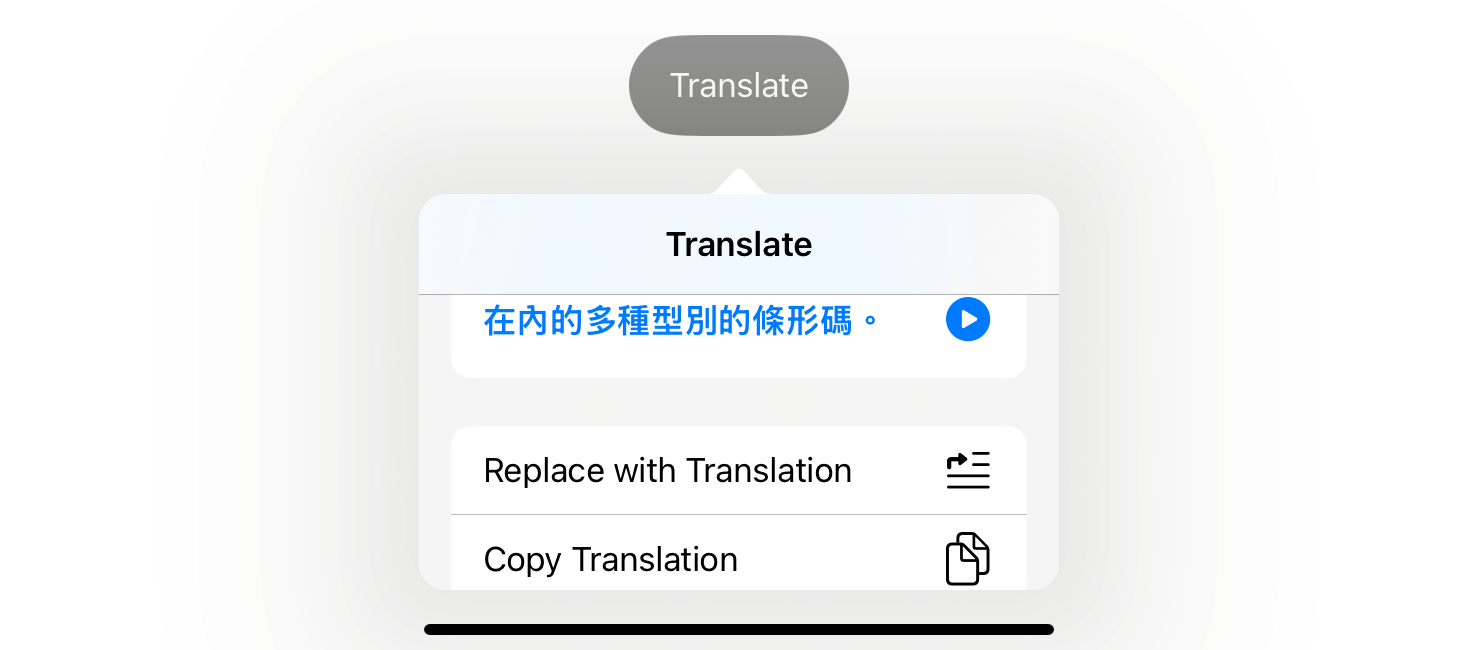
The .translationPresentation modifier means that you can specify an non-compulsory motion to be carried out when customers faucet the “Change with Translation” button. As an illustration, if you wish to change the unique textual content with the translated textual content when the button is tapped, you may outline this motion like this:
.translationPresentation(isPresented: $showTranslation, textual content: article) { translatedText in
sampleText = translatedText
}When you specify the motion within the modifier, you will notice the “Change with Translation” possibility within the translation overlay.
Working with the Translation API
For better management over translations, you should utilize the Translation API straight as a substitute of counting on the interpretation overlay. As an illustration, in case your app shows a listing of article excerpts and also you need to provide translation assist, the interpretation overlay won’t be supreme as a result of customers must choose every excerpt individually for translation.
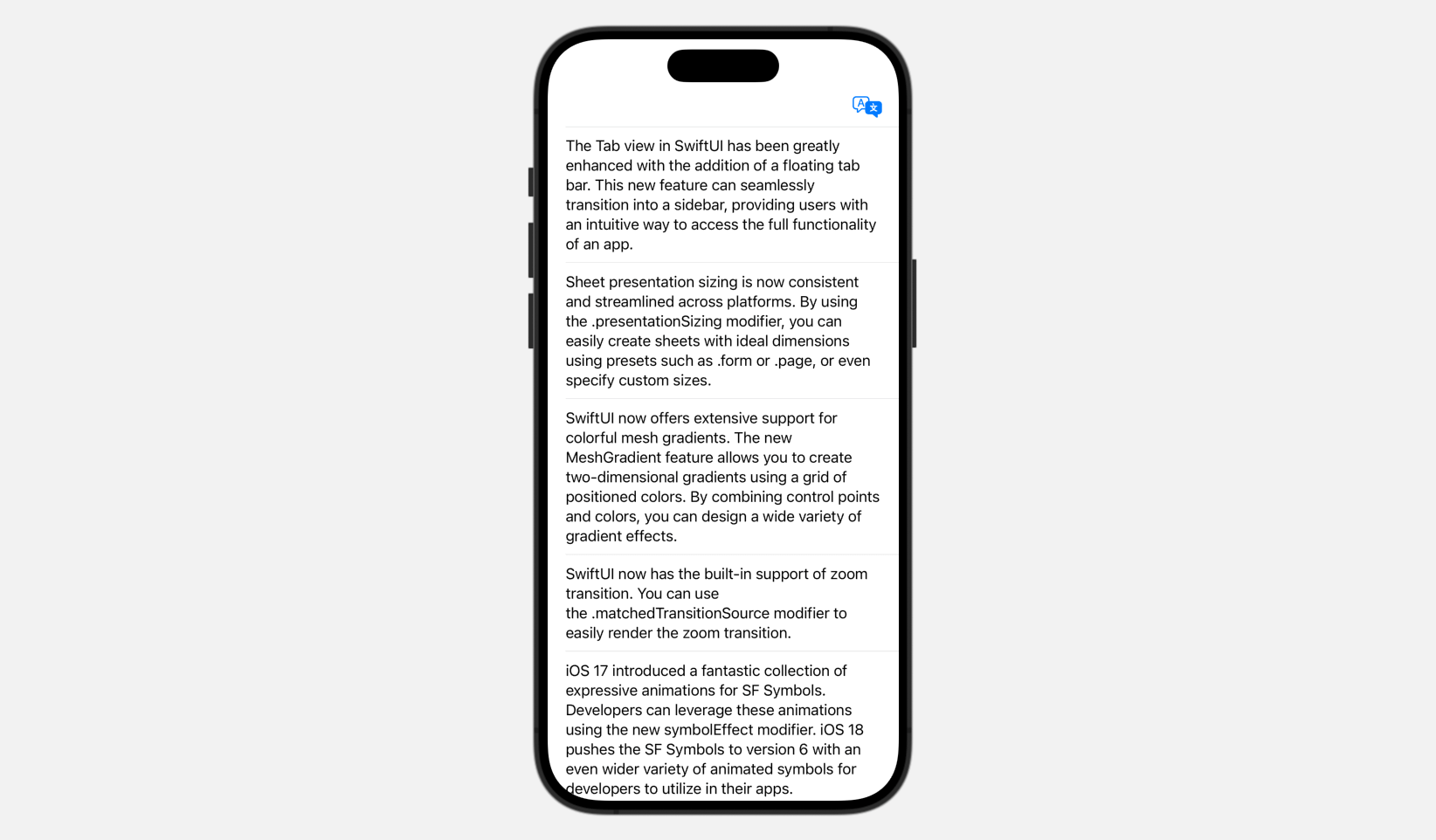
A extra environment friendly answer is to carry out a batch translation of all of the article excerpts when customers faucet the “Translate” button. Let’s create a easy demo to see find out how to work with the Translation API and deal with batch translations.
Under is the pattern code for creating the UI above:
struct BatchTranslationDemo: View {
@State non-public var articles = sampleArticles
var physique: some View {
NavigationStack {
Record(articles) { article in
VStack {
Textual content(article.textual content)
if article.translatedText != "" {
Textual content(article.translatedText)
.body(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .main)
.padding()
.background(Colour(.systemGray4))
}
}
}
.listStyle(.plain)
.toolbar {
Button {
} label: {
Label("Translate", systemImage: "translate")
.labelStyle(.iconOnly)
}
}
}
}
}To carry out a batch translation, you first must outline a translation configuration that specifies each supply and goal languages. Within the code, you may declare a state variable to carry the configuration like under:
@State non-public var configuration: TranslationSession.Configuration?After which, within the closure of the toolbar’s Button, we are able to instantiate the configuration:
Button {
if configuration == nil {
configuration = TranslationSession.Configuration(supply: .init(identifier: "en-US"), goal: .init(identifier: "zh-Hant-TW"))
return
}
configuration?.invalidate()
} label: {
Label("Translate", systemImage: "translate")
.labelStyle(.iconOnly)
}We specify English because the supply language and Conventional Chinese language because the goal language. If you don’t specify the languages, the Translation API will mechanically create a default configuration, with iOS figuring out the supply and goal languages for you.
To carry out translation, you connect the .translationTask modifier to the checklist view:
Record(articles) { article in
.
.
.
}
.translationTask(configuration) { session in
let requests = articles.map { TranslationSession.Request(sourceText: $0.textual content, clientIdentifier: $0.id.uuidString) }
if let responses = attempt? await session.translations(from: requests) {
responses.forEach { response in
updateTranslation(response: response)
}
}
}This modifier initiates a translation process utilizing the desired configuration. At any time when the configuration modifications and isn’t nil, the interpretation process is executed. Inside the closure, we put together a set of translation requests and use the session’s translations(from:) technique to carry out a batch translation.
If the interpretation process succeeds, it returns an array of translation responses containing the translated textual content. We then move this translated textual content to the updateTranslation technique to show it on display.
func updateTranslation(response: TranslationSession.Response) {
guard let index = articles.firstIndex(the place: { $0.id.uuidString == response.clientIdentifier }) else {
return
}
articles[index].translatedText = response.targetText
}Let’s deploy the app to an actual machine for testing. I examined the app on my iPad Air. Once you faucet the “Translate” button, the app ought to show extra article excerpts in Conventional Chinese language.

Abstract
With the brand new Translation API launched in iOS 17.4 (and iOS 18), builders can now simply combine highly effective translation options into their apps. This tutorial covers two main strategies for using the API: the easy method utilizing the .translationPresentation modifier for displaying a translation overlay, and a extra versatile method utilizing the Translation API straight for customized translation options.
We exhibit each approaches on this tutorial. As illustrated within the demo, you may simply add translation capabilities with just some strains of code. Given the simplicity and energy of this API, there’s no motive to not embody translation performance in your apps.


