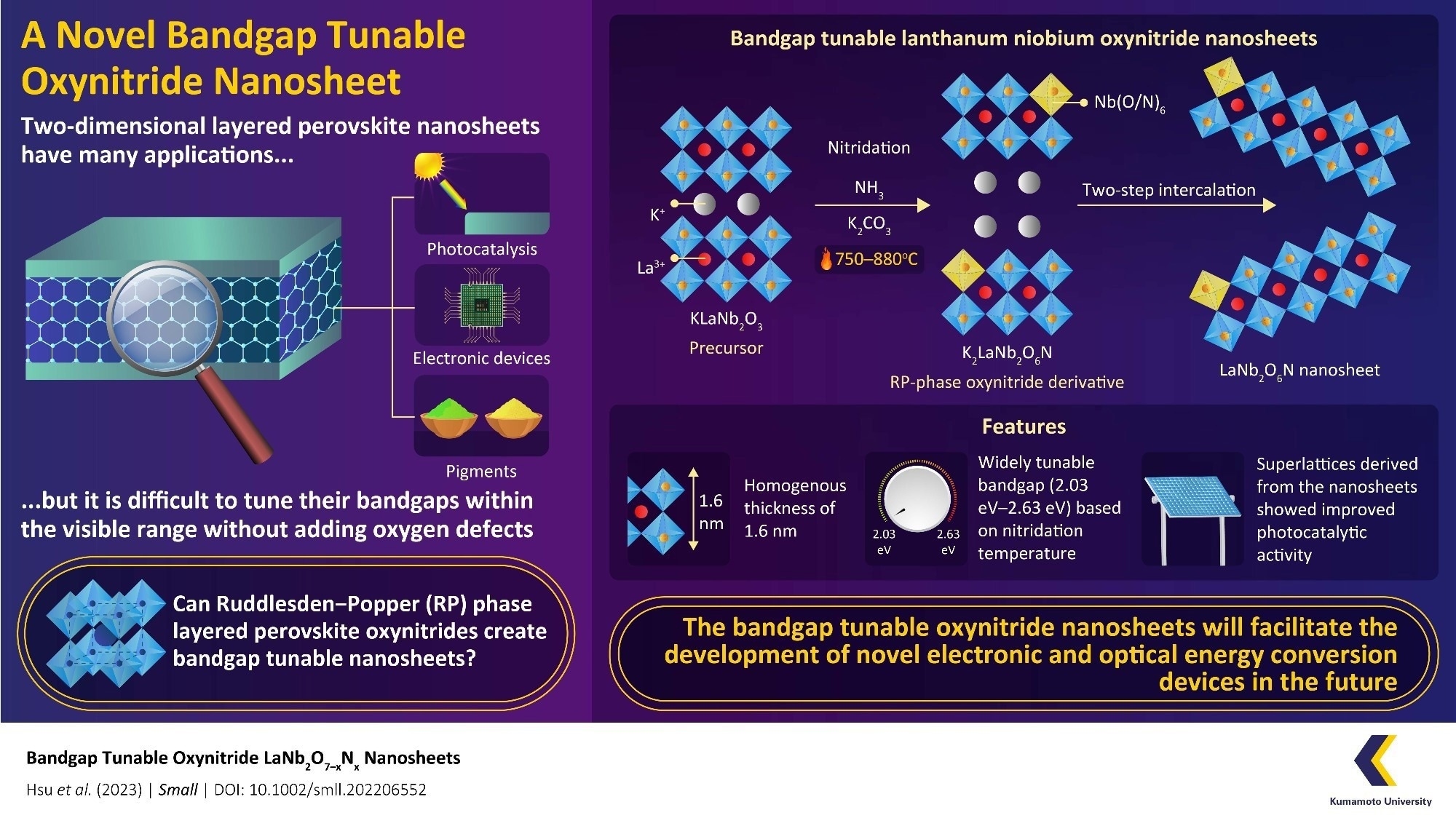
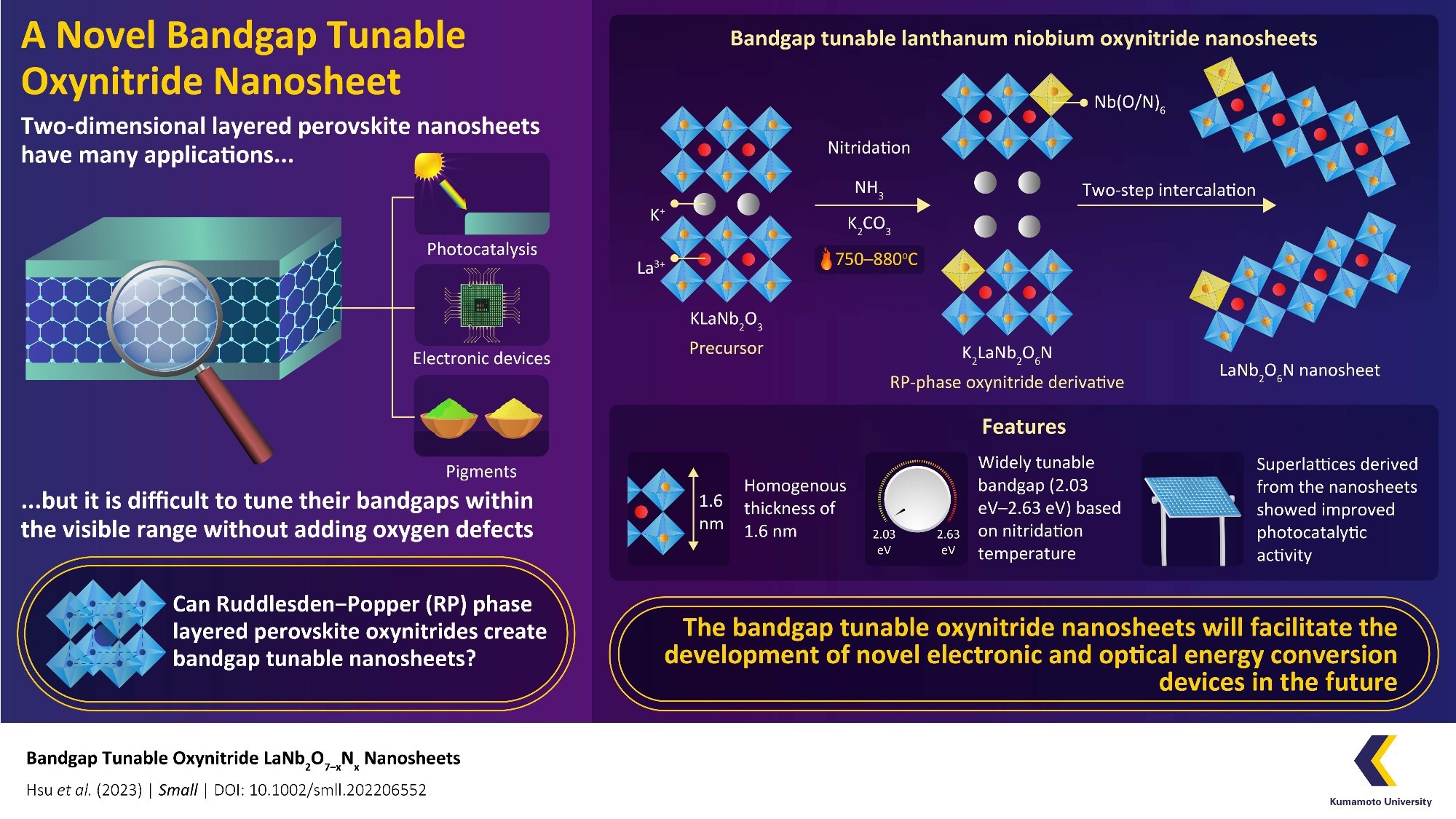
2D monolayer nanosheets composed of layered perovskite include a number of enticing properties. Nonetheless, it has been difficult to construct them with tunable bandgaps within the seen area with no addition of oxygen defects.
In latest occasions, Japanese researchers might effectively design chemically secure nanosheets from perovskite oxynitrides that possessed controllable bandgaps. Such nanosheets include big potential for future functions in electrocatalysts, photocatalysis, and different sustainable applied sciences.
Nanosheets, comprising the acknowledged materials graphene, are supplies which have nanoscale homogenous thicknesses, excessive crystallinity, and flat surfaces. Nanosheets have broad functions in photoluminescence, photocatalysis, and electronics.
Perovskites with semiconductor properties have gained focus within the scientific neighborhood as a possible materials for creating two-dimensional (2D) monolayer nanosheets. Nonetheless, these nanosheets would want a bandgap pertaining to the power of seen mild to be advantageous, as this may determine when the semiconductor conducts electrical energy.
For scientists, the tunability of the bandgap has stayed a significant issue as a result of creating 2D nanosheets from perovskite with a tunable bandgap is difficult.
To handle this concern, a analysis staff from Kumamoto College, together with Professor Shintaro Ida from the Institute of Industrial Nanomaterials, agreed to focus on a gaggle of perovskite supplies known as Ruddlesden–Popper (RP) section layered perovskite oxynitrides.
The scientists might effectively create 2D perovskite oxynitride nanosheets with a tunable bandgap with their new technique. This examine was revealed in Small.
Metallic oxynitride semiconductor nanosheets containing oxygen, nitrogen, and a metallic haven’t been researched a lot. Skinny movies made of those supplies show capabilities superior to these of oxides. Thus, their synthesis can have a huge effect on this subject. We synthesized nanosheets from RP-phase perovskite oxynitrides whose properties, reminiscent of its bandgap, are freely tunable.
Prof. Shintaro Ida, Research Corresponding Creator, Institute of Industrial Nanomaterials, Kumamoto College
Firstly, the scientists utilized pristine Dion–Jacobson section lanthanum niobium oxide (KLaNb2O7) as a precursor materials. Then, they went on to incorporate nitrogen via an strategy generally known as nitridation. The scientists added nitrogen to the fabric at numerous temperatures ranging between 750 and 800 ℃.
This resulted within the formation of the RP-phase oxynitride by-product. After that, they may make use of a two-step intercalation strategy to exfoliate out lanthanum niobium oxynitride nanosheets with the components LaNb2O7-xNx (“x” being the amount of nitrogen included within the perovskite).
When these nanosheets have been examined, the scientists discovered that the fabric had a 1.6 nm homogenous thickness and confirmed numerous colours, ranging between white and yellow, based mostly on the nitridation temperature. The nanosheets additionally possessed the enticing semiconductor property of getting a tunable bandgap within the seen area, starting from 2.03 to 2.63 eV, relying on the nitridation temperature.
Then, the staff ready a “superlattice” construction comprising alternating layers of the synthesized nanosheets and oxide (Ca2Nb3O10) nanosheets. When the properties of this superlattice have been examined, they found that it had wonderful photocatalytic exercise and superior proton conductivity.
The outcomes of this examine will open new prospects for producing a number of superlattices by using delicate−chemical nano−architectonics based mostly on 2D nanosheets. This may get us one step nearer to a sustainable society, as these nanosheets would allow environment friendly splitting of water as a photocatalyst and likewise in creating extra advanced and higher performing electronics.
Prof. Shintaro Ida, Research Corresponding Creator, Institute of Industrial Nanomaterials, Kumamoto College
Journal Reference:
Hsu, C., et al. (2023). Bandgap Tunable Oxynitride LaNb2O7–xNx Nanosheets. Small. doi.org/10.1002/smll.202206552.