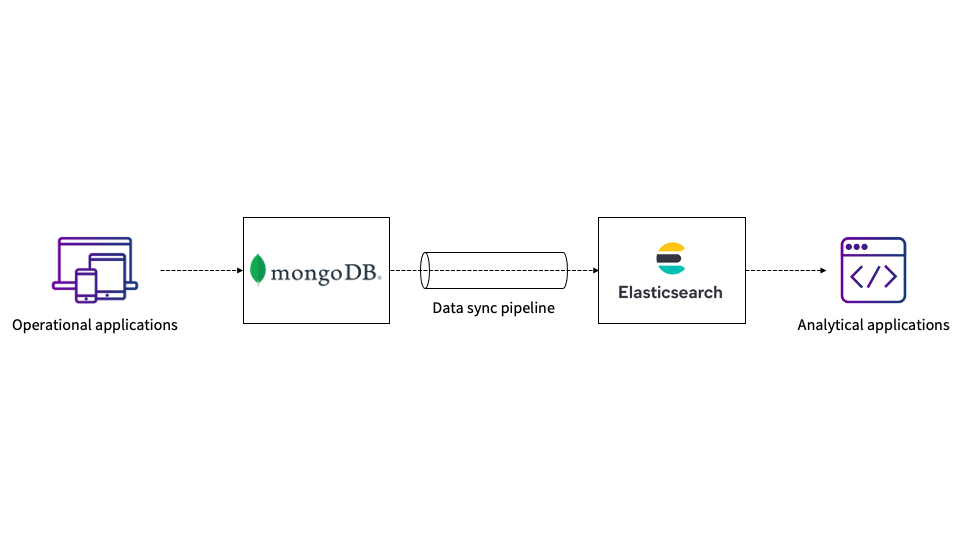
Offloading analytics from MongoDB establishes clear isolation between write-intensive and read-intensive operations. Elasticsearch is one instrument to which reads might be offloaded, and, as a result of each MongoDB and Elasticsearch are NoSQL in nature and provide comparable doc construction and information sorts, Elasticsearch could be a well-liked alternative for this function. In most eventualities, MongoDB can be utilized as the first information storage for write-only operations and as assist for fast information ingestion. On this scenario, you solely have to sync the required fields in Elasticsearch with customized mappings and settings to get all the benefits of indexing.
This weblog put up will look at the assorted instruments that can be utilized to sync information between MongoDB and Elasticsearch. It can additionally focus on the assorted benefits and downsides of building information pipelines between MongoDB and Elasticsearch to dump learn operations from MongoDB.
Instruments to Sync Information Between Elasticsearch and MongoDB
When establishing an information pipeline between MongoDB and Elasticsearch, it’s necessary to decide on the fitting instrument.
Initially, it is advisable to decide if the instrument is suitable with the MongoDB and Elasticsearch variations you might be utilizing. Moreover, your use case would possibly have an effect on the way in which you arrange the pipeline. When you’ve got static information in MongoDB, it’s possible you’ll want a one-time sync. Nonetheless, a real-time sync will probably be required if steady operations are being carried out in MongoDB and all of them must be synced. Lastly, you’ll want to think about whether or not or not information manipulation or normalization is required earlier than information is written to Elasticsearch.
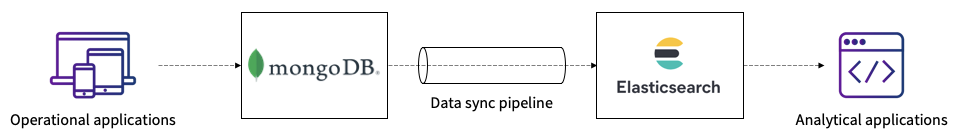
Determine 1: Utilizing a pipeline to sync MongoDB to Elasticsearch
If it is advisable to replicate each MongoDB operation in Elasticsearch, you’ll have to depend on MongoDB oplogs (that are capped collections), and also you’ll have to run MongoDB in cluster mode with replication on. Alternatively, you possibly can configure your utility in such a means that every one operations are written to each MongoDB and Elasticsearch cases with assured atomicity and consistency.
With these issues in thoughts, let’s have a look at some instruments that can be utilized to duplicate MongoDB information to Elasticsearch.
Monstache
Monstache is among the most complete libraries out there to sync MongoDB information to Elasticsearch. Written in Go, it helps as much as and together with the most recent variations of MongoDB and Elasticsearch. Monstache can also be out there as a sync daemon and a container.
Mongo-Connector
Mongo-Connector, which is written in Python, is a extensively used instrument for syncing information between MongoDB and Elasticsearch. It solely helps Elasticsearch via model 5.x and MongoDB via model 3.6.
Mongoosastic
Mongoosastic, written in NodeJS, is a plugin for Mongoose, a well-liked MongoDB information modeling instrument primarily based on ORM. Mongoosastic concurrently writes information in MongoDB and Elasticsearch. No further processes are wanted for it to sync information.

Determine 2: Writing concurrently to MongoDB and Elasticsearch
Logstash JDBC Enter Plugin
Logstash is Elastic’s official instrument for integrating a number of enter sources and facilitating information syncing with Elasticsearch. To make use of MongoDB as an enter, you possibly can make use of the JDBC enter plugin, which makes use of the MongoDB JDBC driver as a prerequisite.
Customized Scripts
If the instruments described above don’t meet your necessities, you possibly can write customized scripts in any of the popular languages. Keep in mind that sound data of each the applied sciences and their administration is important to jot down customized scripts.
Benefits of Offloading Analytics to Elasticsearch
By syncing information from MongoDB to Elasticsearch, you take away load out of your major MongoDB database and leverage a number of different benefits provided by Elasticsearch. Let’s check out a few of these.
Reads Don’t Intrude with Writes
In most eventualities, studying information requires extra assets than writing. For quicker question execution, it’s possible you’ll have to construct indexes in MongoDB, which not solely consumes plenty of reminiscence but additionally slows down write pace.
Extra Analytical Performance
Elasticsearch is a search server constructed on prime of Lucene that shops information in a novel construction referred to as an inverted index. Inverted indexes are significantly useful for full-text searches and doc retrievals at scale. They’ll additionally carry out aggregations and analytics and, in some instances, present further companies not provided by MongoDB. Widespread use instances for Elasticsearch analytics embody real-time monitoring, APM, anomaly detection, and safety analytics.
A number of Choices to Retailer and Search Information
One other benefit of placing information into Elasticsearch is the potential for indexing a single discipline in a number of methods through the use of some mapping configurations. This characteristic assists in storing a number of variations of a discipline that can be utilized for several types of analytic queries.
Higher Assist for Time Collection Information
In purposes that generate an enormous quantity of information, equivalent to IoT purposes, attaining excessive efficiency for each reads and writes could be a difficult activity. Utilizing MongoDB and Elasticsearch together could be a helpful strategy in these eventualities since it’s then very simple to retailer the time sequence information in a number of indices (equivalent to each day or month-to-month indices) and search these indices’ information by way of aliases.
Versatile Information Storage and an Incremental Backup Technique
Elasticsearch helps incremental information backups utilizing the _snapshot API. These backups might be carried out on the file system or on cloud storage instantly from the cluster. This characteristic deletes the outdated information from the Elasticsearch cluster as soon as the backup is taken. At any time when entry to outdated information is important, it could actually simply be restored from the backups utilizing the _restore API. This lets you decide how a lot information must be saved within the reside cluster and in addition facilitates higher useful resource assignments for the learn operations in Elasticsearch.
Integration with Kibana
As soon as you place information into Elasticsearch, it may be linked to Kibana, which makes it simple to discover the information, plus construct visualizations and dashboards.
Disadvantages of Offloading Analytics to Elasticsearch
Whereas there are a number of benefits to indexing MongoDB information into Elasticsearch, there are a variety of potential disadvantages you ought to be conscious of as effectively, which we focus on under.
Constructing and Sustaining a Information Sync Pipeline
Whether or not you employ a instrument or write a customized script to construct your information sync pipeline, sustaining consistency between the 2 information shops is at all times a difficult job. The pipeline can go down or just develop into arduous to handle as a consequence of a number of causes, equivalent to both of the information shops shutting down or any information format modifications within the MongoDB collections. If the information sync depends on MongoDB oplogs, optimum oplog parameters must be configured to ensure that information is synced earlier than it disappears from the oplogs. As well as, when it is advisable to use many Elasticsearch options, complexity can enhance if the instrument you’re utilizing just isn’t customizable sufficient to assist the mandatory configurations, equivalent to customized routing, parent-child or nested relationships, indexing referenced fashions, and changing dates to codecs recognizable by Elasticsearch.
Information Sort Conflicts
Each MongoDB and Elasticsearch are document-based and NoSQL information shops. Each of those information shops enable dynamic discipline ingestion. Nonetheless, MongoDB is totally schemaless in nature, and Elasticsearch, regardless of being schemaless, doesn’t enable totally different information kinds of a single discipline throughout the paperwork inside an index. This could be a main problem if the schema of MongoDB collections just isn’t fastened. It’s at all times advisable to outline the schema prematurely for Elasticsearch. It will keep away from conflicts that may happen whereas indexing the information.
Information Safety
MongoDB is a core database and comes with fine-grained safety controls, equivalent to built-in authentication and person creations primarily based on built-in or configurable roles. Elasticsearch doesn’t present such controls by default. Though it’s achievable within the X-Pack model of Elastic Stack, it’s arduous to implement the safety features in free variations.
The Issue of Working an Elasticsearch Cluster
Elasticsearch is difficult to handle at scale, particularly in the event you’re already operating a MongoDB cluster and establishing the information sync pipeline. Cluster administration, horizontal scaling, and capability planning include some limitations. Challenges come up when the applying is write-intensive and the Elasticsearch cluster doesn’t have sufficient assets to deal with that load. As soon as shards are created, they will’t be elevated on the fly. As an alternative, it is advisable to create a brand new index with a brand new variety of shards and carry out reindexing, which is tedious.
Reminiscence-Intensive Course of
Elasticsearch is written in Java and writes information within the type of immutable Lucene segments. This underlying information construction causes these segments to proceed merging within the background, which requires a major quantity of assets. Heavy aggregations additionally trigger excessive reminiscence utilization and will trigger out of reminiscence (OOM) errors. When these errors seem, cluster scaling is often required, which could be a troublesome activity you probably have a restricted variety of shards per index or budgetary issues.
No Assist for Joins
Elasticsearch doesn’t assist full-fledged relationships and joins. It does assist nested and parent-child relationships, however they’re often sluggish to carry out or require further assets to function. In case your MongoDB information relies on references, it could be troublesome to sync the information in Elasticsearch and write queries on prime of them.
Deep Pagination Is Discouraged
One of many largest benefits of utilizing a core database is you can create a cursor and iterate via the information whereas performing the type operations. Nonetheless, Elasticsearch’s regular search queries don’t help you fetch greater than 10,000 paperwork from the overall search outcome. Elasticsearch does have a devoted scroll API to realize this activity, though it, too, comes with limitations.
Makes use of Elasticsearch DSL
Elasticsearch has its personal question DSL, however you want a very good hands-on understanding of its pitfalls to jot down optimized queries. Whereas you too can write queries utilizing Lucene Syntax, its grammar is hard to study, and it lacks enter sanitization. Elasticsearch DSL just isn’t suitable with SQL visualization instruments and, subsequently, affords restricted capabilities for performing analytics and constructing stories.
Abstract
In case your utility is primarily performing textual content searches, Elasticsearch could be a good choice for offloading reads from MongoDB. Nonetheless, this structure requires an funding in constructing and sustaining an information pipeline between the 2 instruments.
The Elasticsearch cluster additionally requires appreciable effort to handle and scale. In case your use case includes extra complicated analytics—equivalent to filters, aggregations, and joins—then Elasticsearch is probably not your finest answer. In these conditions, Rockset, a real-time indexing database, could also be a greater match. It gives each a local connector to MongoDB and full SQL analytics, and it’s provided as a totally managed cloud service.
Study extra about offloading from MongoDB utilizing Rockset in these associated blogs: