Mars is an unlimited, frozen desert. Nowhere is that extra evident than at its poles, that are the coldest areas on the planet. Nevertheless, it seems just like the climate forecast for its harsh winters and barely extra forgiving springs might be totally different from we thought.
Like Earth, Mars has a risky cycle that sees snow and ice ranges fluctuate as temperatures plummet within the winter and begin to rise once more within the spring. Not like Earth, Martian snowfall consists of CO2 snow and is influenced by totally different phenomena. Now, a group of researchers led by Haifeng Xiao of Berlin Technical College in Germany is reexamining the change in snowfall over the course of a yr on the Martian north pole. Their findings recommend that forces akin to sublimation may imply there’s extra snow within the winter—and fewer within the spring—than beforehand thought.
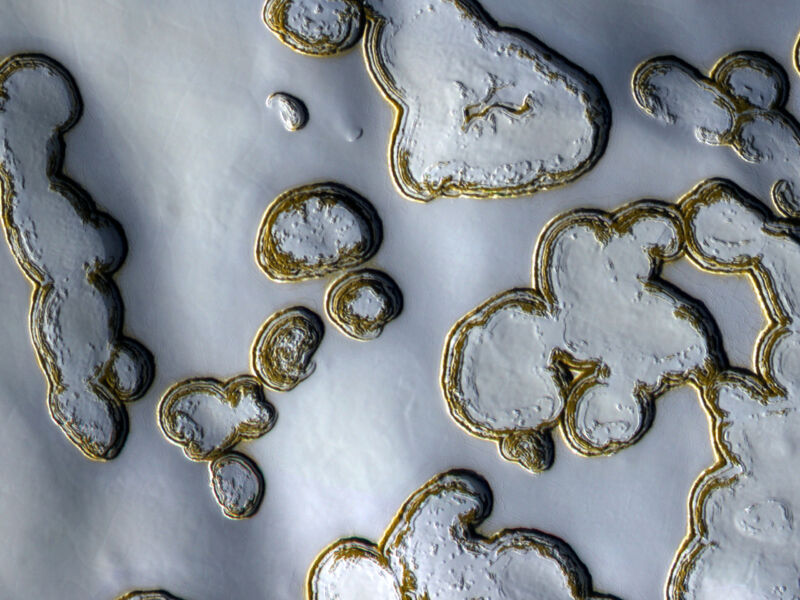
“We suggest to make use of the shadow variations [of ice blocks] to deduce the seasonal depths at excessive polar latitudes,” Xiao and his group stated in a draft manuscript just lately revealed within the Earth and Area Science Open Archive.
Not like Earth
How snow accumulates on Mars could seem alien in comparison with the best way it occurs on Earth. The composition of Martian snow explains why it could actually snow in areas on Mars the place situations would make it almost inconceivable for snow to type right here on our planet. Earth snowfall requires the presence of atmospheric water, which is why frigid however in any other case dry areas don’t see a lot of the white stuff. Whereas water ice and snow exist on Mars, dry areas should still expertise a buildup of CO2 snow and ice. Frozen carbon dioxide sublimates as an alternative of melting when it will get too heat. Subsequently, each sublimation and evaporation affect how a lot snow and ice buildup there’s on Mars throughout a given season.
There are different phenomena affecting Martian snow and ice accumulation that do happen on Earth however are nonetheless totally different on Mars. Katabatic winds, which come up from the sinking of chilly air that then spirals furiously throughout the ice, are discovered on the poles on Earth, however they’ve twice to 3 occasions the energy on Mars. That is due largely to the purple planet’s extraordinarily skinny ambiance. On Mars, katabatic winds additionally have an effect on bigger areas than they do on Earth, blowing large troughs of ice and snow that may be as much as 10 km (about 6.2 miles) large and 1 km (about .62 miles) deep.
Nonetheless, a number of the ways in which ice and snow accumulate on Mars largely mirror results on Earth. Photo voltaic warmth turns into saved in regolith under the snow and ice in the course of the summer season, and snow round a big rock will vanish as late as the autumn as a result of a lot warmth continues to be retained by the rock. Although moating (the empty area the place the snow as soon as was seems like a moat across the rock) usually occurs the identical means because it does on our planet, the distinction on Mars is that ice and snow often elegant from the nice and cozy space versus melting and evaporating on Earth. Crowning ice caps, which type over rocks within the winter after warmth has escaped from the underlying rock, may also be discovered on Earth.
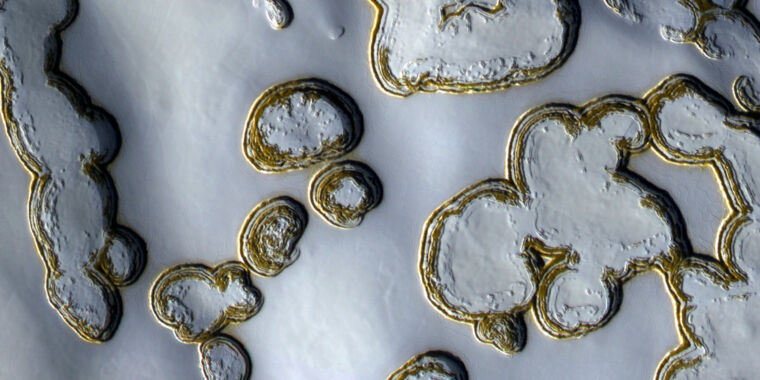
Xiao and his group wished to estimate the general accumulation of snow and ice on the Martian north pole and examine their estimate to earlier observations from NASA’s MOLA (Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter) spacecraft. They examined for the depth of seasonal deposits of snow by measuring the shadows forged by ice blocks within the North Pole Layered Deposits, as seen in hi-res NASA HiRISE (Excessive Decision Imaging Experiment) photographs. As temperatures modified over the course of a Martian yr, or sol, these deposits would evolve, and so would their shadows. Snowfall and depth predictably decreased from winter to spring.
Peak accumulation
What was much less predictable was the quantity of snow and ice current at sure occasions. “The massive snow depth measured makes us marvel if snowfalls are extra frequent and violent than beforehand thought,” Xiao and his group stated in the identical examine, later stating that snow within the later years studied was deeper than anticipated.
There have been some obstacles. Ice crowns did typically get in the best way, as they made ice blocks and snow-covered rocks thicker, which meant they forged longer shadows. The absence of snow in moats round rocks diminished shadows and likewise needed to be corrected for. Total, uncertainties have been lower than a meter (about three toes)—which is substantial given the quantity of snow that fell.
So how a lot snow can we anticipate on Mars every year? At its highest, the thickness of Martian snowfall is near a meter in winter, lowering to .21 m (about .7 foot) in spring and persevering with to drop all through summer season till colder climate units in. Snowfall contributes considerably extra to whole accumulation than frosts that immediately condense on the floor.
Whereas the snowfall on Mars would have simply made for a lot of snow days (at the very least earlier than the Web made distant college widespread), Xiao thinks that additional examine of the variations of snow and ice depth on Mars might sometime reveal extra concerning the planet’s usually mysterious insides. The snow nonetheless has secrets and techniques to inform.