In Java, tables are used to rearrange knowledge into columns and rows. A column is house that runs horizontally on a desk, whereas a row is an area that runs horizontally in your desk. The intersection between a column and a row known as a cell and is used to carry singular piece of knowledge.
In Java, builders can use the JTable technique to create a desk of their functions. JTable is a Swing part that inherits from the JComponent class.
Learn: High On-line Programs to Be taught Java Programming
The right way to Create a Desk in Java
To create a desk, you have to make an occasion of the JTable class. It’s worthwhile to present two arguments (row and column) in its constructor for the desk to be constructed, as proven on this instance code snippet:
JTable desk = new JTable (row, column);
The row and column values can encompass two integer values, like beneath:
JTable desk = new JTable (5,3);
The above assertion creates a desk with 5 rows and 3 columns.
As an alternative of offering the JTable constructor with integers, programmers also can provide a two dimensional array for the information in every row, and a one dimensional array for the column names. Right here is how you need to use arrays to create a desk in Java:
JTable(Object[][] rowData, Object[] columnNames)
Right here is a few instance code exhibiting how you can create a desk in Java and fill it with knowledge:
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.desk.*;
import java.awt.*;
class Desk{
public static void most important(String args[]){
JFrame body = new JFrame();
String[] columnNames = {"Identify", "Age", "Scholar"};
Object[][] knowledge = {
{"Ken", new Integer(5), new Boolean(false)},
{"Tom", new Integer(3), new Boolean(true)},
{"Susam", new Integer(2), new Boolean(false)},
{"Mark",new Integer(20), new Boolean(true)},
{"Joe", new Integer(10), new Boolean(false)}
};
JTable desk = new JTable(knowledge, columnNames);
body.add(desk);
body.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
body.setSize(400,400);
body.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
body.setVisible(true);
}
}
When you run this code in your built-in improvement atmosphere (IDE) or code editor, it would produce the next output:

Once you click on on any one of many above cells, you’ll discover that the information in it’s editable. This isn’t a very fascinating function if you’re simply presenting knowledge to your person. Additionally, all the information is handled as a string when in its presentation to a person.
One other level of concern is that, in case you had been querying a database object for explicit values, you would need to copy all values to an array or vector.
To keep away from these issues, you’ll be able to as a substitute create your Java desk utilizing a mannequin.
Learn: Java Instruments to Enhance Productiveness
The right way to Create a Desk Utilizing a Mannequin in Java
First, it is very important perceive how desk knowledge is dealt with. All tables (together with a desk created utilizing JTable()) use a desk mannequin to handle their knowledge. When builders don’t present a desk mannequin to the constructor of JTable, an occasion of DefaultTableModel will likely be robotically created for it. Due to this fact, if you have to use a customized mannequin, you have to present it to the JTable constructor, as proven on this instance code:
JTable desk = new JTable(new MyTableModel());
To outline a desk mannequin, programmers must create a category that extends the AbstractTableModel class:
class MyTableModel extends AbstractTableModel{
}
In your desk mannequin, you’ll be able to embrace the information on your rows and column names, simply as proven within the earlier JTable instance. To make sure that your desk mannequin class is a concrete class, you have to implement the next three strategies of AbstractTableModel:
public int getRowCount(); public int getColumnCount(); public Object getValueAt(int row, int column);
You’ll be able to implement extra strategies, however you have to make sure that the above strategies are amongst these you implement. You could find the outline of different strategies from the official Oracle API docs.
The code instance beneath exhibits how you need to use a desk mannequin in Java:
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.desk.*;
import java.awt.*;
class TableUsingModel{
public static void most important(String args[]){
JFrame body = new JFrame();
JTable desk = new JTable(new MyTableModel());
body.add(desk);
body.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
body.setSize(400,400);
body.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
body.setVisible(true);
}
}
class MyTableModel extends AbstractTableModel {
String[] columnNames = {"Identify", "Age", "Location"};
Object[][] knowledge = {
{"Ken", new Integer(25), "Nairobi"},
{"Tom", new Integer(31), "Geneva"},
{"Sheila", new Integer(29), "Paris"},
{"Mark",new Integer(20), "Cairo"},
{"Jessie", new Integer(18), "Miami"}
};
public int getRowCount() {
return knowledge.size;
}
public int getColumnCount() {
return columnNames.size;
}
public Object getValueAt(int row, int col) {
return knowledge[row][col];
}
}
This ends in the next output (Show):
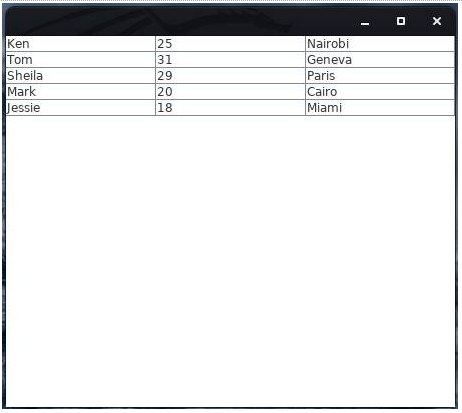
This time, in case you strive double-clicking on any cell, you’ll discover that it isn’t editable.
Learn: The right way to Use Databases in Java
The right way to Handle Column Width & Peak in Java
If you wish to set the peak of rows, you need to use the setRowHeight() technique.
JTable desk = new JTable(knowledge, columnNames); desk.setRowHeight(80);
The above instance units the peak of every row 80 pixels.
To set the width of columns, you need to use the setPreferredWidth() technique. First, you have to create a column mannequin of sort TableColumnModel. Then you will get the actual column you need after which set its most popular width. Right here is a few instance code exhibiting how you can set the column width of a desk in Java:
TableColumnModel columnModel = desk.getColumnModel(); columnModel.getColumn(2).setPreferredWidth(200);
Ultimate Ideas on Java Tables
On this programming tutorial, programmers realized how you can use JTable, or a desk mannequin, to create a desk in Java. The code examples proven above add the tables on to the JFrame container. Nonetheless, you’ll be able to as a substitute add your desk to a scroll pane in order that your person can simply navigate by the information when it doesn’t match its container.
Learn extra Java programming tutorials and software program improvement suggestions.


