As the amount, velocity and number of information grows, organizations are more and more counting on staunch information governance practices to make sure their core enterprise outcomes are adequately met. Unity Catalog is a fine-grained governance answer for information and AI powering the Databricks Lakehouse. It helps simplify the safety and governance of your enterprise information belongings by offering a centralized mechanism to manage and audit information entry.
Taking a journey down reminiscence lane, earlier than Unity Catalog unified the permission mannequin for information, tables and added assist for all languages, prospects have been implementing fine-grained information entry management on Databricks utilizing the legacy workspace-level Desk ACL (TACL), which have been basically restricted to sure cluster configurations and labored just for Python & SQL. Each Unity Catalog & TACL allow you to management entry to securable objects like catalogs, schemas (databases), tables, views, however there are some nuances in how every entry mannequin works.
An excellent understanding of the article entry mannequin is crucial for implementing information governance at scale utilizing Unity Catalog. Much more so, when you’ve got already carried out the Desk ACL mannequin and wish to improve to Unity Catalog to make the most of all the latest options, resembling multi-language assist, centralized entry management and information lineage.
The Axioms of Unity Catalog entry mannequin
- Unity Catalog privileges are outlined at metastore – Unity Catalog permissions at all times seek advice from account-level identities, whereas TACL permissions outlined inside the hive_metastore catalog at all times seek advice from the native identities within the workspace
- Privilege inheritance – Objects in Unity Catalog are hierarchical and privileges are inherited downward. The best degree object that privileges are inherited from is the catalog
- Object possession is essential – Privileges can solely be granted by a metastore admin, the proprietor of an object, or the proprietor of the catalog or schema that accommodates the article. Solely the proprietor of an object, or the proprietor of the catalog or schema that accommodates it may well drop the article
- USE privileges for boundaries – USE CATALOG/SCHEMA is required to work together with objects inside a catalog/schema. Nonetheless, USE privilege doesn’t enable one to browse the article metadata that’s housed inside the catalog/schema
- Permissions on derived objects are simplified – Unity Catalog solely requires the proprietor of a view to have SELECT privilege, together with USE SCHEMA on the views’ dad or mum schema and USE CATALOG on the dad or mum catalog. In distinction with TACL, a view’s proprietor must be an proprietor of all referenced tables and views
Some extra complicated axioms
- Safe by default – solely clusters with Unity-Catalog particular entry modes (shared or single-user) can entry Unity Catalog information. With TACL, all customers have entry to all information on non-shared clusters
- Limitation of single-user clusters – Single customers clusters don’t assist dynamic views. Customers will need to have SELECT on all referenced tables and views to learn from a view
- No assist for ANY FILE or ANONYMOUS FUNCTIONs: Unity Catalog doesn’t assist these permissions, as they might be used to bypass entry management restrictions by permitting an unprivileged person to run privileged code
Fascinating patterns
There are a lot of governance patterns that may be achieved utilizing the Unity Catalog entry mannequin.
Instance 1 – Constant permissions throughout workspaces
Axiom 1 permits product crew to outline permissions for his or her information product inside their very own workspace, and having these mirrored and enforced throughout all different workspaces, regardless of the place their customers are coming from
Instance 2 – Setting boundary for information sharing
Axiom 2 permits catalog/schema homeowners to arrange default entry guidelines for his or her information. For instance the next instructions allow the machine studying crew to create tables inside a schema and skim one another’s tables:
CREATE CATALOG ml;
CREATE SCHEMA ml.sandbox;
GRANT USE_CATALOG ON CATALOG ml TO ml_users;
GRANT USE_SCHEMA ON SCHEMA ml.sandbox TO ml_users;
GRANT CREATE TABLE ON SCHEMA ml.sandbox TO ml_users;
GRANT SELECT ON SCHEMA ml.sandbox TO ml_users;Extra apparently, axiom 4 now permits catalog/schema homeowners to restrict how far particular person schema and desk homeowners can share information they produce. A desk proprietor granting SELECT to a different person doesn’t enable that person learn entry to the desk until in addition they have been granted USE CATALOG privileges on its dad or mum catalog in addition to USE SCHEMA privileges on its dad or mum schema.
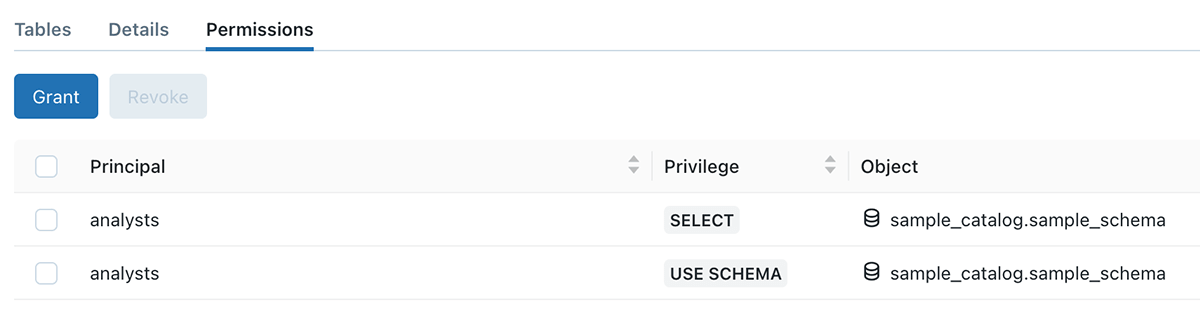
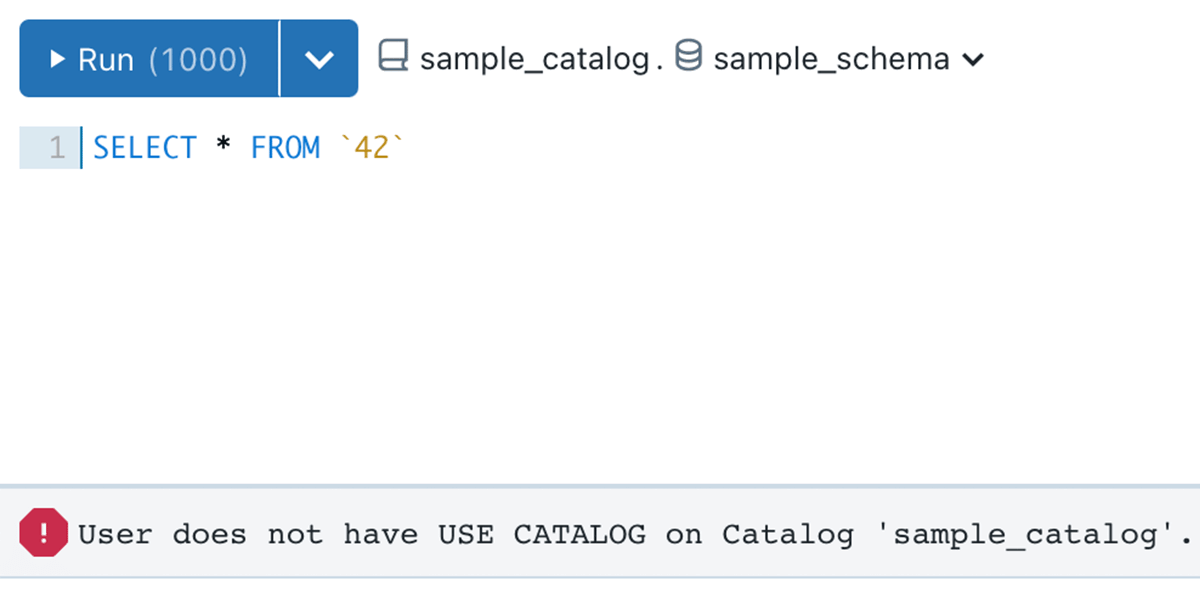
Within the under instance, sample_catalog is owned by person A, person B created a sample_schema schema, and desk 42. Though USE SCHEMA and SELECT permission is granted to the analysts crew, they nonetheless can not question the desk, attributable to permission boundary set by person A
Instance 3 – Simpler sharing of enterprise logic
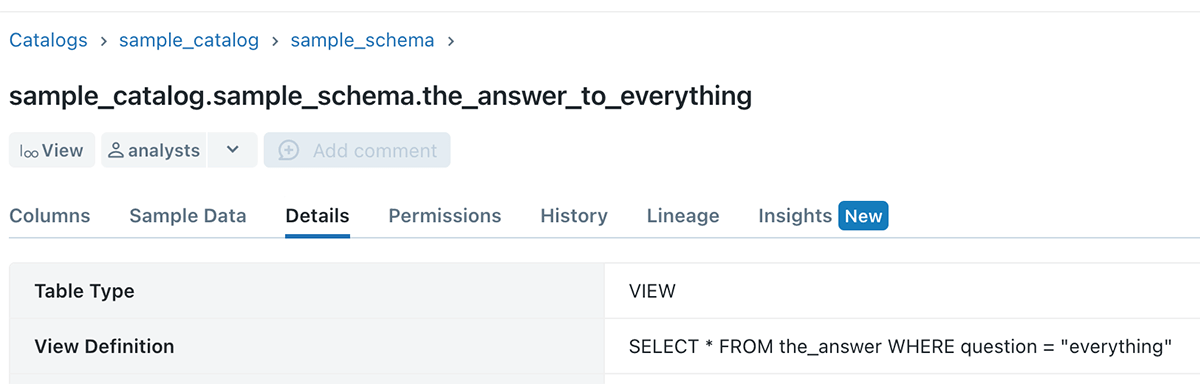
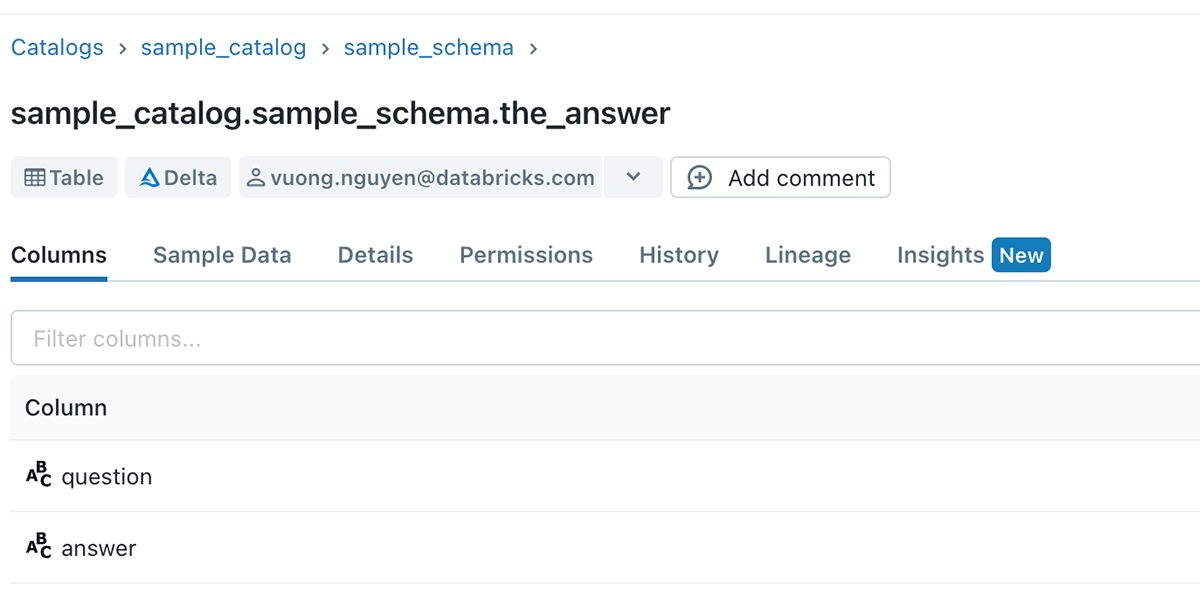
Information customers have a must share their workings and transformation logic, and a reusable means of doing it’s by creating and sharing views to different customers.
Axiom 5 unlocks the power for information customers to do that seamlessly, with out requiring guide forwards and backwards with the desk homeowners.
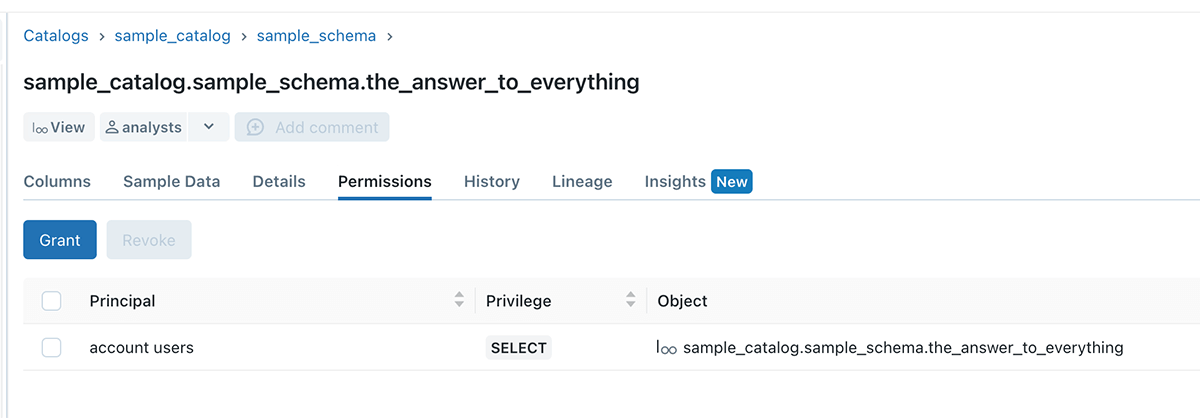
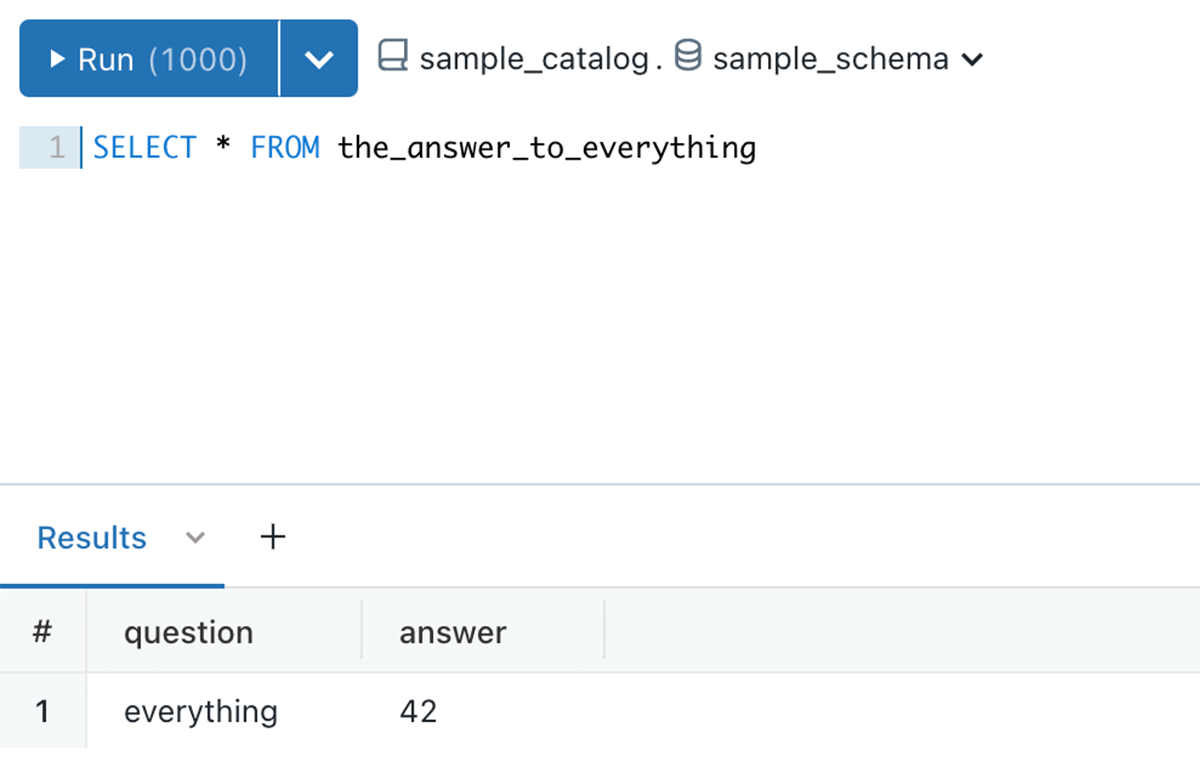
Instance 4 – No extra information leakage
Due to axiom 6, information homeowners might be sure that there can be no unauthorized entry to their information attributable to cluster misconfiguration. Any cluster that’s not configured with the right entry mode will be unable to entry information in Unity Catalog.
Customers can verify that their clusters can entry Unity Catalog information due to this useful tooltip on the Create Clusters web page
Now that information homeowners can perceive the information privilege mannequin and entry management, they’ll leverage Unity Catalog to simplify entry coverage administration at scale.
There are upcoming options that may additional empower information directors and homeowners to creator much more complicated entry coverage:
- Row filtering and column masking: Use commonplace SQL capabilities to outline row filters and column masks, permitting fine-grained entry controls on rows and columns.
- Attribute Based mostly Entry Controls: Outline entry insurance policies based mostly on tags (attributes) of your information belongings.


