| Dec 22, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) Neutron stars are the top merchandise of huge stars and collect collectively a big a part of the unique stellar mass in a super-dense star with a diameter of solely round ten kilometres. On 17 August 2017, researchers noticed the manifold signatures of an explosive merger of two orbiting neutron stars for the primary time: gravitational waves and large bursts of radiation together with a gamma-ray burst.
|
|
A world analysis crew has developed a way to concurrently mannequin these observable indicators of a kilonova. This allows them to exactly describe what precisely occurs throughout a merger, how nuclear matter behaves underneath excessive circumstances and why the gold on Earth should have been created in such occasions.
|
|
The crew printed their findings in Nature Communications (“NMMA: A nuclear-physics and multi-messenger astrophysics framework to investigate binary neutron star mergers”).
|
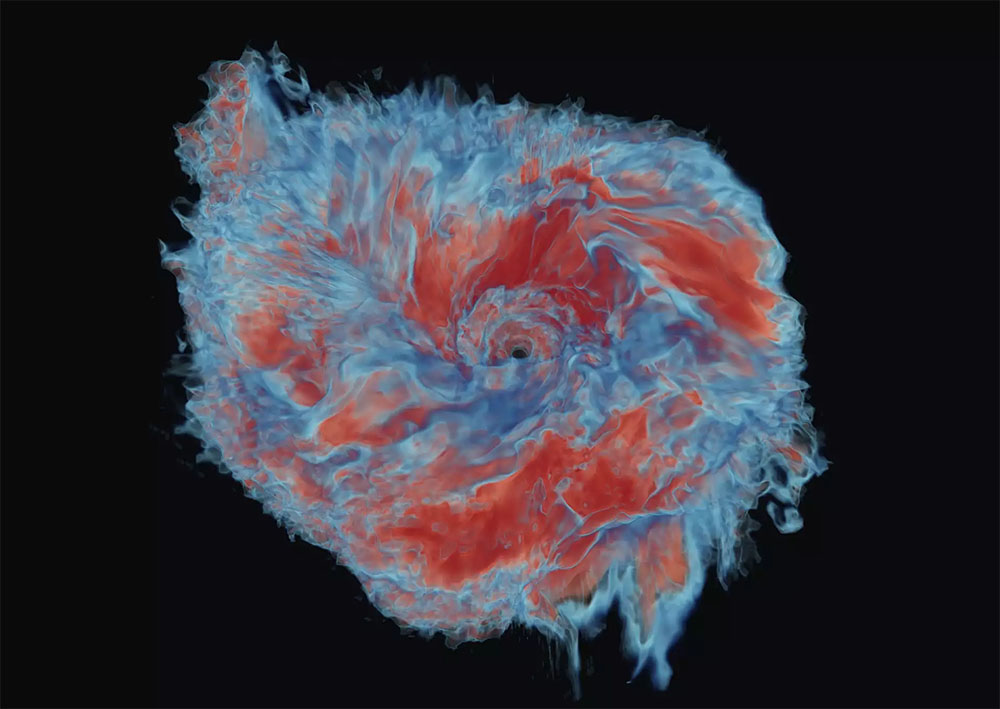 |
| Numerical simulation of the ensuing ejecta materials of two merging neutron stars. Purple colours check with ejected materials with a excessive fraction of neutrons which is able to seem sometimes redder than blue materials that accommodates a better fraction of protons. (Picture: I. Markin, College of Potsdam)
|
|
Utilizing a brand new software program device, a crew involving the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics and the College of Potsdam has succeeded in concurrently deciphering the varied sorts of astrophysical information from a kilonova. As well as, information from radio and X-ray observations of different neutron stars, nuclear physics calculations and even information from heavy-ion collision experiments on earthbound accelerators can be utilized. Till now, the varied information sources have been analysed individually and the information interpreted utilizing completely different bodily fashions in some instances.
|
|
“By analysing the information coherently and concurrently, we get extra exact outcomes,” says Peter T. H. Pang, scientist at Utrecht College. “Our new methodology will assist to investigate the properties of matter at excessive densities. It can additionally enable us to higher perceive the growth of the universe and to what extent heavy parts are shaped throughout neutron star mergers,” explains Tim Dietrich, professor on the College of Potsdam and head of a Max Planck Fellow group on the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics.
|
Excessive circumstances in a cosmic laboratory
|
|
A neutron star is a superdense astrophysical object shaped on the finish of a large star’s life in a supernova explosion. Like different compact objects, some neutron stars orbit one another in binary programs. They lose power via the fixed emission of gravitational waves – tiny ripples within the cloth of space-time – and ultimately collide. Such mergers enable researchers to check bodily ideas underneath probably the most excessive circumstances within the universe.
|
|
For instance, the circumstances of those high-energy collisions result in the formation of heavy parts comparable to gold. Certainly, merging neutron stars are distinctive objects for learning the properties of matter at densities far past these present in atomic nuclei.
|
|
The brand new methodology was utilized to the primary and up to now solely multi-messenger commentary of binary neutron star mergers. On this occasion, found on August 17, 2017, the celebrities’ previous couple of thousand orbits round one another had warped space-time sufficient to create gravitational waves, which had been detected by the terrestrial gravitational-wave observatories Superior LIGO and Superior Virgo.
|
|
As the 2 stars merged, newly shaped heavy parts had been ejected. A few of these parts decayed radioactively, inflicting the temperature to rise. Triggered by this thermal radiation, an electromagnetic sign within the optical, infrared, and ultraviolet was detected as much as two weeks after the collision. A gamma-ray burst, additionally brought on by the neutron star merger, ejected extra materials. The response of the neutron star’s matter with the encompassing medium produced X-rays and radio emissions that may very well be monitored on time scales starting from days to years.
|
Extra correct outcomes for future detections
|
|
The gravitational-wave detectors are at the moment of their fourth observing run. The following detection of a neutron star merger might come any day, and the researchers are eagerly ready to make use of the device they developed.
|

