Within the final three years, because the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic in the US, the character of the office has modified considerably. As of February, 76 p.c of the workforce with a job that may be performed from house in the US was working a hybrid or fully distant schedule, in response to Pew Analysis. Of that quantity, roughly one-third is totally distant.
On this evolving work local weather, organizations have to be more and more vigilant in opposition to malicious and unintentional (non-malicious) insider incidents. Many organizations by no means expertise a headline-grabbing, large-scale insider incident. As a substitute, many insider incidents are unintentional or non-malicious, sometimes the results of a safety incident or coverage violation. In accordance with our analysis, distraction is a key think about unintentional insider risk incidents. Distracted employees usually tend to make errors that may endanger a company, corresponding to failing to make use of their firm’s digital non-public community (VPN) or clicking on phishing hyperlinks in electronic mail. For a lot of hybrid and distant employees, distractions involving workspaces in shut proximity to kids and different relations can result in unintentional threat. Complete enterprise threat administration that features an insider threat program is a key element to securing organizations on this new setting. On this put up, we current the 13 key parts of an insider risk program.
Necessities Associated to Insider Risk
In 2011, the U.S. federal authorities launched an government order requiring authorities companies that function or entry categorised laptop networks to construct a proper insider risk detection and safety program.
The federal authorities had been beforehand charged with constructing the Nationwide Insider Risk Process Power, which develops a government-wide insider risk program for deterring, detecting, and mitigating insider threats.
In 2016, the Nationwide Industrial Safety Program Working Guide (NISPOM), which outlines authorities requirements for protection contractors, through NISPOM Confirming Change 2, additionally adopted a requirement that members of the Protection Industrial Base (DIB) construct insider risk detection and safety packages. DIB members, like the federal government companies, should conduct yearly self-assessments of established insider risk packages or unbiased third-party assessments.
A variety of high-profile incidents have impacted for-profit corporations as properly, leading to important momentum to construct insider risk packages within the non-public sector.
Throughout the CERT Nationwide Insider Risk Heart, we now have developed a variety of sources to assist public- and private-sector organizations assess the danger posed by trusted insiders. These sources give attention to serving to organizations perceive the vital elements of an insider threat program and by what metrics a program is deemed efficient. We are able to additionally conduct third-party evaluations of insider risk packages for presidency or for-profit entities.
These sources embrace the CERT Frequent Sense Information to Mitigating Insider Risk, Seventh Version, which outlines 22 greatest practices that organizations can use to mitigate insider risk. Every greatest apply contains methods and techniques for fast wins and high-impact options, mitigations to reduce implementation challenges and roadblocks, and mappings to notable and related safety and privateness requirements. Finest apply #2, Develop a Formalized Insider Threat Administration Program, gives a roadmap for organizations to observe.
Different sources embrace
The Why and When of Insider Threat Administration
Incorporating insider risk into enterprise-wide threat administration permits this system or group to leverage current sources by
- avoiding duplication of effort with current safety controls centered on exterior risk mitigation
- making certain the insider threat program has participation from throughout the group, proving risk intelligence (data) from threat administration, data know-how, bodily safety, personnel administration, human sources, threat administration, common counsel, and features of enterprise.
When contemplating insider threats, it is very important first develop a threat administration mindset. A threat administration mindset understands that one of the best time to develop an insider threat program and a course of for mitigating incidents, each malicious and non-malicious, is earlier than an incident happens. When contemplating the right way to defend organizational property, it is very important return to foundational cybersecurity rules and establish the vital property or providers or enterprise processes that, if attacked, wouldn’t enable your group to realize its mission as outlined by Brett Tucker within the put up 10 Steps for Managing Threat: OCTAVE FORTE.
In figuring out vital property (folks, services, know-how, data), it is very important ask
- What services or products do we offer?
- What data are we entrusted to guard?
- What can we do to offer these providers or merchandise?
- What property can we use when performing these duties?
- What are the safety necessities of those property?
- What’s the worth of those property?
Key Parts of an Insider Risk Program
Whereas data know-how (IT) is vital to an insider threat program, it’s only one element. Too typically organizations fall into the lure of contemplating their program full as soon as they buy an insider threat administration device. Managing insider risk must be an ongoing, enterprise-wide effort that includes the IT division and others, corresponding to human sources, common counsel, threat administration, and bodily safety.
This enterprise-wide strategy is required as a result of the power to watch consumer exercise on a community doesn’t all the time assure that monitoring is permitted or that it isn’t an invasion of privateness. The identical requirements and tips that require federal companies and contractors to determine insider threat packages to watch consumer exercise on networks additionally requires privateness and civil liberty safety, which is an space the place a company’s common counsel performs a key position. A holistic strategy to insider threat administration includes enterprise-wide participation into necessities, monitoring, governance, and oversight of this system—somebody watching the watchers. Oversight is a core precept in our greatest practices.
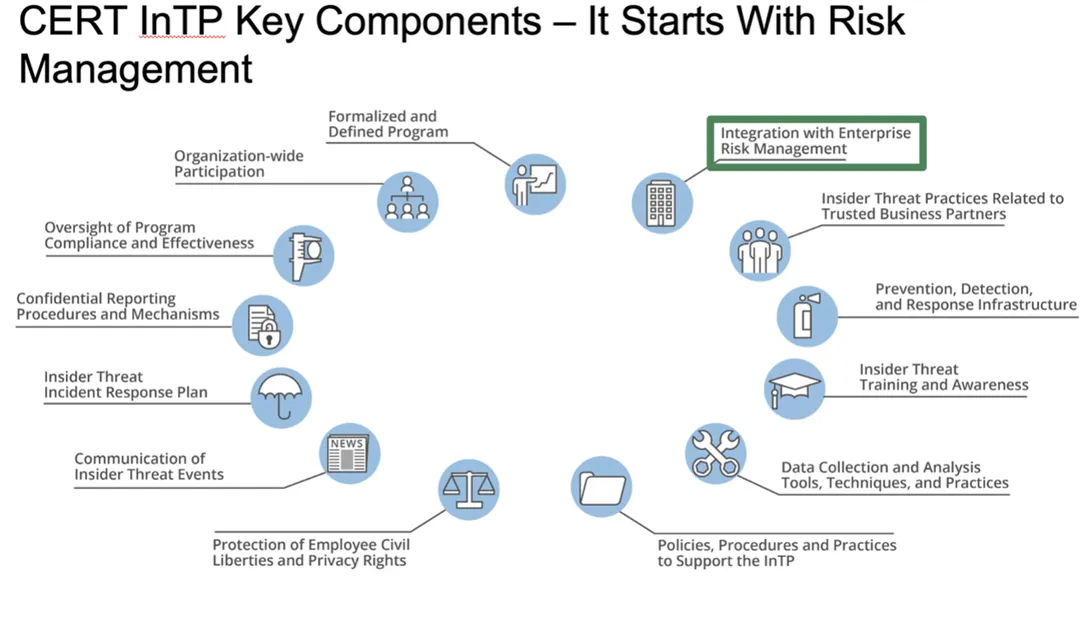
In September 2022, we printed the seventh version of our Frequent Sense Information to Mitigating Insider Threats, which is predicated on analysis and evaluation of greater than 3,000 incidents. Along with greatest practices for mitigating insider threats and sources for varied stakeholders inside a company (i.e., administration, human sources, authorized counsel, bodily safety, IT, data safety, knowledge homeowners, and software program), the information outlines the vital parts of an insider threat program, proven within the determine under:
- Formalized and Outlined Insider Threat Administration Program (IRMP)—This system ought to embrace parts corresponding to directives, authorities, a mission assertion, management intent, governance, and a funds.
- Group-Vast Participation—This system ought to have lively participation from all organizational elements that share or use program knowledge. Senior management ought to present seen help for this system, particularly when the info the IRMP wants is in siloes (i.e., knowledge lives completely in areas or departments corresponding to human sources [HR], bodily safety, data know-how [IT], or data safety).
- Oversight of Program Compliance and Effectiveness—A governance construction, corresponding to an IRMP working group or change management board, ought to assist the IRMP program supervisor formulate requirements and working procedures for the IRMP and suggest adjustments to current practices and procedures. Additionally, an government council or steering committee ought to approve adjustments beneficial by the working group/change management board. Oversight contains annual self-assessments and exterior entity assessments that consider the compliance and effectiveness of the IRMP.
- Confidential Reporting Procedures and Mechanisms—Not solely do these mechanisms and procedures allow the reporting of suspicious exercise, however when intently coordinated with the IRMP, in addition they be sure that professional whistleblowers should not inhibited or inappropriately monitored.
- Insider Risk Incident Response Plan—This plan should be greater than only a referral course of to outdoors investigators. It ought to element how alerts and anomalies are recognized, managed, and escalated, together with timelines for each motion and formal disposition procedures.
- Communication of Insider Risk Occasions—Occasion data needs to be appropriately shared with the proper organizational elements, whereas sustaining workforce member confidentiality and privateness. This kind of communication contains insider threat traits, patterns, and potential future occasions in order that insurance policies, procedures, coaching, and so on., could be modified as applicable.
- Safety of Workforce Member Civil Liberties and Privateness Rights—Authorized counsel ought to evaluate the IRMP’s choices and actions in any respect phases of program improvement, implementation, and operation.
- Integration with Enterprise Threat Administration—The IRMP should be sure that all features of the group’s threat administration embrace insider risk concerns (not simply outdoors attackers), and the group ought to take into account establishing a standalone element for insider threat administration.
- Practices Associated to Managing Trusted Exterior Entities (TEEs)—These practices embrace agreements, contracts, and processes reviewed for insider risk prevention, detection, and response capabilities.
- Prevention, Detection, and Response Infrastructure—This infrastructure contains elements, corresponding to community defenses, host defenses, bodily defenses, instruments, and processes.
- Insider Risk Coaching and Consciousness—This coaching encompasses three features of the group: (1) insider risk consciousness coaching for the group’s whole workforce (e.g., staff, contractors, consultants), (2) coaching for IRMP personnel, and (3) role-based coaching for mission specialists who’re more likely to observe sure features of insider risk occasions (e.g., HR, Info Safety, Counterintelligence, Administration, Finance).
- Information Assortment and Evaluation Instruments, Strategies, and Practices—These instruments, strategies, and practices embrace consumer exercise monitoring (UAM), knowledge assortment, and evaluation parts of this system. Detailed documentation is required for all features of information assortment, processing, storage, and sharing to make sure compliance with workforce member privateness and civil liberties.
- IRMP Insurance policies, Procedures, and Practices—The IRMP should have formal paperwork that element all features of this system, together with its mission, scope of threats, directives, directions, and customary working procedures.
- Optimistic Incentives—Organizations ought to encourage optimistic workforce habits slightly than coerce it by leveraging positive-incentive-based organizational practices centered on growing job engagement, perceived organizational help, and connectedness at work.
Insider Threat and AI
Machine studying (ML) and synthetic intelligence (AI) have been on the forefront of insider risk anomaly detection for a variety of years. Conventional safety controls have concerned instruments that may monitor consumer exercise, however solely after receiving steerage from an analyst on particular behavioral anomalies to be looking out for. This association limits the scope of monitoring to what’s accessible inside conventional controls and at an analyst’s discretion. Such an strategy could flag exercise if a consumer downloads 100 paperwork in a day, however what if an insider does one doc a day over 100 days?
AI and ML can delve deeper to find out probably worrisome patterns of exercise by a person by taking into consideration statistical and human anomalies.
A brand new class of insider risk instruments, which depend on consumer entity and habits analytics (UEBA), widens the aperture past technical anomalies involving an worker’s laptop use to include totally different knowledge units. If an worker is leaving a company, for instance, the instruments would pull knowledge from the HR administration system. These instruments additionally account for exercise in a company’s bodily safety techniques, together with badging information or digicam techniques.
UEBA instruments are utilizing AI at the beginning by incorporating totally different knowledge from throughout a company and informing analysts of anomalies with out analysts telling the instruments what needs to be reported.
Most staff don’t be part of a company desiring to do hurt, and, as we referenced earlier, most insider incidents that do happen are unintentional. No matter intent, all insider incidents contain a misuse of licensed entry to a company’s vital property, and a lot of the incidents are unintentional. We within the CERT Division of the SEI are working to know the underlying causes behind stressors and regarding behaviors to detect insider threats early and supply staff help earlier than they commit a dangerous act.