Software program touches virtually each aspect of trade, academia, and authorities. It’s obligatory for a lot of human endeavors, from leisure and leisure to security and protection to well being and important infrastructures. But, whereas sure proprietary software program producers have change into family names, free and open supply software program (FOSS) is usually much less recognized, but it’s a considerable element of the general software program panorama. The Linux Basis examine, Census II of Free and Open Supply Software program—Utility Libraries, confirmed that FOSS permeates the software program panorama. Furthermore, the latest Division of Protection (DoD) memo, Software program Growth and Open Supply Software program, underscores not solely the significance of FOSS software program utilized by the DoD but in addition how FOSS has reworked how software program is designed, developed, examined, distributed, deployed, operated, and maintained. Importantly, this similar memo additionally cautioned in regards to the elevated potential of vulnerabilities and provide chain dangers that may accompany the usage of all reused software program, together with FOSS.
The U.S. authorities and DoD depends on its federally funded analysis and growth facilities (FFRDCs), college affiliated analysis facilities (UARCs), and trade to coach about FOSS safety and implement sensible insurance policies, steerage, processes, and expertise to enact the intent of the Software program Growth and Open Supply Software program memo. For these causes, the SEI just lately performed the workshop “Open Supply Management Jam 2022: A dialog with FFRDCs & UARCs.” The aim of this workshop was to start out the dialog amongst these entities and start to coordinate work to raise the trustworthiness of FOSS and your entire FOSS ecosystem whereas persevering with to benefit from the velocity, innovation, transparency, and collaboration it fosters. This SEI weblog publish highlights the present FOSS panorama, describes the workshop and its floor guidelines, summarizes the concepts that emerged from this seminal occasion, and articulates a future imaginative and prescient for ongoing collaboration.
The Free and Open Supply Software program Panorama within the DoD
The DoD’s 2022 memo defines open supply software program (OSS) as “software program for which the human-readable supply code is obtainable to be used, examine, re-use, modification, enhancement, and redistribution by the customers of such software program.” For our functions we are going to use the phrases “free and OSS” (FOSS) as a synonym for OSS. In follow, FOSS is brazenly developed by collaborative networks of programmers. Creating proposed enhancements by anybody is each permitted and inspired. FOSS tasks vary in dimension from a single developer (the median) to many 1000’s (14 thousand for the Linux kernel). The Linux Basis examine Census II of Free and Open Supply Software program—Utility Libraries, produced in partnership with Harvard Laboratory for Innovation Science and the Open Supply Safety Basis (OpenSSF), highlighted the widespread use of FOSS and reported that FOSS is utilized in an estimated 98 % of codebases (together with proprietary codebases) throughout a broad spectrum of organizations in the private and non-private sectors. The DoD echoed this level in its memo on software program growth and open supply software program, noting, “There are hundreds of thousands of publicly-available OSS elements, libraries, and purposes able to accelerating software program modernization actions.” The DoD memo not solely underscored the widespread use of FOSS however harassed the significance of open supply software program to the DoD Modernization Technique:
The Division’s 2018 Cyber Technique … directed the Division to extend the usage of safe OSS and to make use of industrial off-the-shelf instruments when doable. The Division’s forthcoming Software program Modernization Technique facilities on the supply of resilient software program functionality on the velocity of relevance. OSS kinds the bedrock of the software-defined world and is essential in delivering software program quicker.
Clearly, the widespread use of FOSS and its significance to the DoD’s technique make making certain the security and safety of FOSS and the FOSS provide chain important. Because the Linux Basis examine famous, the necessity to take action got here into stark reduction when attackers found and exploited extreme vulnerabilities in broadly used FOSS merchandise, resembling OpenSSL, log4j, and the Linux kernel. But assessing FOSS is completely different from proprietary software program as a result of it requires augmented metrics and indicators of well being and stability. What’s extra, the DoD articulated two elementary issues about utilizing and releasing exterior software program (together with as FOSS):
- Utilizing externally maintained code in essential programs probably creates a path for adversaries to introduce malicious code into DoD programs.
- Imprudent sharing of code developed for DoD programs probably advantages adversaries by disclosing key improvements.
Attributable to these issues, the DoD famous that it should “clearly articulate how, the place, and when it participates, contributes, and interacts with the broader OSS neighborhood.” To this finish, it included steerage on software program growth and open supply software program. The next sections current key parts of the DoD’s steerage on FOSS use, FOSS growth, and contributing to FOSS tasks.
The DoD as a Client of FOSS
The DoD espouses Undertake, Purchase, Create steerage, in that order, for software program acquisitions. Software program adoption entails utilizing off-the-shelf (OTS) software program, together with FOSS and government-off-the-shelf (GOTS) software program, and proprietary options. DoD applications, nonetheless, are sometimes unable to amass total options OTS, which necessitates customized options and consumption that can nearly actually incorporate FOSS.
The panorama of applied sciences is huge, and applications are largely free to decide on for themselves precisely which mixture of languages and elements they are going to use to construct their options. A sampling of the FOSS element panorama reveals the magnitude of prospects:
- Maven Central (Java): 482K modules
- PyPI (Python): 385K modules
- Nuget (.NET): 313K modules
- Rubygems.org (Ruby): 172K modules
Bigger options usually incorporate software program written in a couple of language and/or expertise stack, so the variety of doable configurations is large. DoD program managers are anticipated to handle the complete lifecycle of FOSS inside their applications, which is a tough activity given the magnitude of the options.
The DoD as a Producer of FOSS
The memo encourages non-Nationwide Safety Programs applications to undertake an open-by-default posture when creating customized software program. This requires applications to architect their options in a method that separates essential and non-critical elements. Packages are then inspired to launch non-critical elements as open supply. Packages are required to stability the wants of program safety with the advantages of releasing non-critical elements as open supply, resembling lowering ongoing growth and upkeep prices for themselves and different DoD applications that undertake these elements.
The DoD as a Contributor to FOSS
DoD applications are inspired to actively contribute to FOSS, as a result of lowering the variety of customizations a program manages straight improves the maintainability of the software program and reduces prices. Laws permit each authorities personnel and contractors to straight contribute to FOSS whether it is within the pursuits of the federal government to take action. As with producing FOSS, contributing to present FOSS requires this system to stability the necessity for program safety with the advantages of contributing. Specifically, as famous within the DoD memo, “making a separate, DoD-specific model of any OSS challenge, for any cause, will increase assist threat and must be prevented each time doable.”
Un-Convention: Sparking a Dialog
The “Open Supply Management Jam workshop passed off June 9, 2022 and was led by Aeva Black (Open Supply Hacker, Microsoft), Jacob Inexperienced (Mosslabs and OSPO++) and David A. Wheeler (Linux Basis). The assembly was facilitated by my Software program Engineering Institute (SEI) colleagues Linda Parker Gates and Aaron Reffett. I additionally served as a facilitator. We organized the occasion as an “un-conference” to foster a wide-ranging, free, and open dialogue. The un-conference idea permits members to steer the assembly, counting on their experience to find out dialogue subjects and durations. Subjects have been permitted to evolve through the day, and we put no strict time restrict on discussions. Likewise, the legislation of private mobility allowed members to maneuver freely between conversations. We operated beneath Chatham Home Guidelines:
- Individuals are free to make use of the knowledge acquired.
- Neither the id nor the affiliation of the audio system could also be attributed (except particularly licensed).
The workshop leads framed the workshop theme and briefly mentioned the structure of the DoD FOSS memo. After a interval of debate, attendees generated twelve dialogue subjects. We then used a multi-voting method to establish the preliminary subjects for dialogue for the rest of the day. We positioned the seven remaining subjects in a backlog to be addressed if time permitted. The primary 5 subjects have been chosen for dialogue, creating an total construction for the rest of the workshop that paralleled a lot of the “shopper” context established by the DoD’s OSS memo.
The ordered record of subjects was as follows:
- trusted processes over particular person identities
- zero-trust structure contained in the FOSS course of
- threat administration within the consumption of open supply
- provide chain artifact decision
- institutional constructions for neighborhood/conversations (OSPO networks)
- worldwide collaboration
- blockers for launch of FOSS and the way can we resolve them?
- main versus trailing indicators of software program high quality
- requirements/frameworks
- launch with out attribution
- actionable experiment era
- area composition categorization of priorities
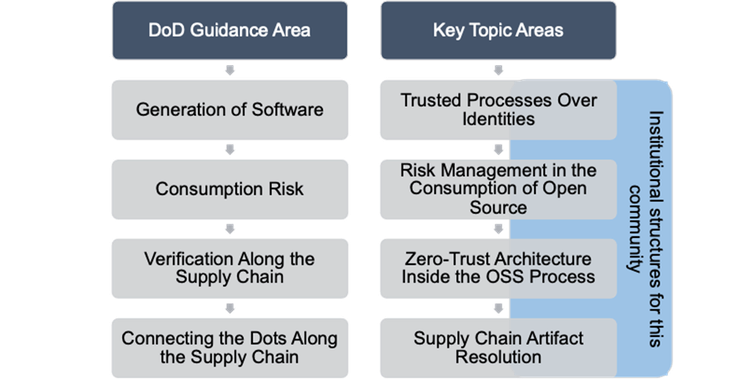
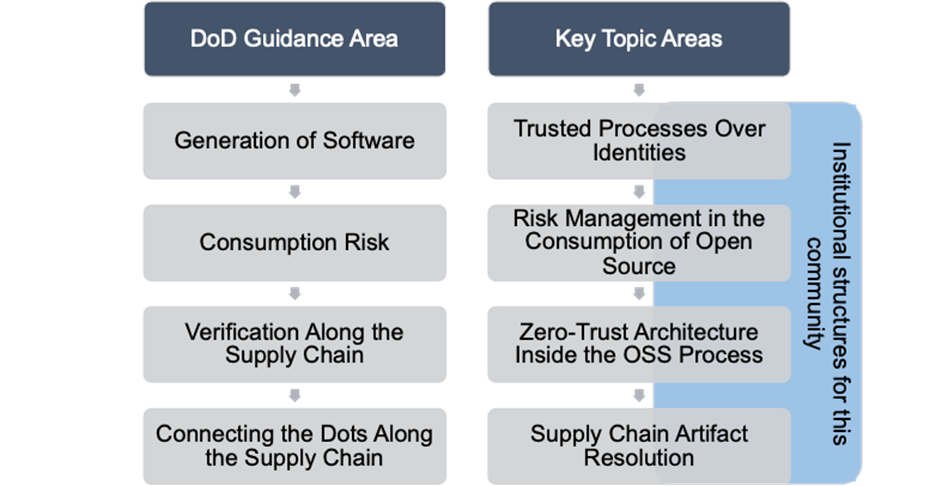
Determine 1: Relationship of Key Subjects Recognized to DoD Steerage Areas
A abstract of the highest 5 subjects chosen for dialogue seems beneath.
Trusted Processes Over Particular person Identities
Whereas a lot experience rests on the neighborhood of stakeholders, counting on these people or particular person entities to forge a path for executing the DoD’s steerage on FOSS and software program growth presents a variety of issues. Particular person consultants come and go, and open supply software program is usually developed both by self-interested volunteers or workers of firms looking for to advance their specific targets inside open supply challenge communities. Whereas particular person experience ebbs and flows over time, many open supply establishments create a steady and sustainable state of affairs by facilitating the switch of institutional information to future generations of contributors and maintainers, and set up rigorous growth practices to make sure the standard of releases. Consequently, the group agreed that instruments and strategies that assess processes and applied sciences of open supply tasks are acceptable to measure trustworthiness, relatively than strategies that target people, firms, or nations in a blanket method. They cited Debian, OpenStack, Kubernetes, and Linux Kernel as examples of the gold customary for such processes.
Any course of utilized to the problem of FOSS software program growth within the DoD ought to be capable to tackle the next questions:
- How do shoppers know if a challenge has a vulnerability embargo course of as a part of their course of?
- What’s the finest follow for assessing the well being and stability of a FOSS challenge?
- How do you get entry to information and data relating to these trusted processes?
- How will you “see” the rigor of FOSS processes (e.g., SLSA)?
- How will you confirm human processes (e.g., human evaluation)?
What’s extra, the group argued that any course of developed to handle the problem of FOSS within the DoD ought to embody the next specifics:
- Growth course of adjustments must be reviewed like code (e.g., infrastructure as code [IaaC]).
- Static and dynamic evaluation instruments are wanted to search for malicious FOSS packages (e.g., package-analysis at OpenSSF).
- Verified reproducible builds are wanted to counter malicious builds and attributions (e.g., to counter assaults just like the one on SolarWinds’ Orion). One participant famous that the device diffoscope is helpful for figuring out sudden variations.
- A number of instruments must be utilized in steady integration/steady supply (CI/CD) pipelines to search for vulnerabilities to be addressed.
- The method ought to depend on mechanisms, resembling The Replace Framework (TUF) and instruments resembling in-toto to supply safe updates and proof of processes carried out.
- Privileges granted to packages should be diminished.
- Packages mustn’t run at set up time (this capacity is usually used for exfiltration).
- Digital signatures must be used to forestall tampering in transit.
- The method ought to incorporate unbiased evaluation (e.g., safety audits).
Zero Belief
The zero belief safety mannequin has change into an essential a part of the nation’s safety posture. In Could 2021, President Joseph Biden signed Government Order 14028, “Enhancing the Nation’s Cybersecurity,” which explicitly requests businesses to undertake zero belief cybersecurity ideas and alter their community architectures accordingly. The zero belief safety mannequin strives to cut back threat inherent in perimeter-based safety architectures by eradicating implied belief and explicitly authenticating and authorizing topics, property, and workflows. To assist Government Order 14028, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) developed a Zero Belief Maturity Mannequin to assist businesses implement zero belief architectures.
Along with Government Order 14028, the NIST Particular Publication 800-207, Zero Belief Structure, served as a basis for the dialogue of this key subject. One proposal rising from the dialogue is to include zero belief structure (ZTA) into FOSS growth. It was proposed that zero belief structure must also be included as an addendum to the subsequent replace of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and that FOSS and 0 belief must be included as a basis for the NIST Good Cities and Communities Framework. One of many members famous that FOSS has already been raised within the context of sensible cities, citing the panel “OSS Framework in Good Cities” on the September 2020 Good Cities Join Convention and Expo.
Different concepts put forth included advocating for
- funding analysis for zero belief
- making use of least privileges to particular packages
- making a recall system that might generate computerized remembers to prospects and/or house owners
- researching whether or not zero belief ideas may be utilized to the CI/CD pipeline
Danger Administration within the Consumption of FOSS
Individuals supplied a variety of concrete approaches for serving to DoD FOSS shoppers navigate dangers inherent in its use. As an illustration, one thought was to supply instruments that would assist determination makers analyze present metrics and data on FOSS that point out threat; for instance, OpenSSF Scorecard (which might be invested in and improved), the OpenSSF Finest Practices Badge Program, deps.dev (a service that examines websites resembling github.com to search out up-to-date details about FOSS packages and creates a graph that makes seen any issues), and, generically, repo information (e.g., the variety of maintainers, the final commit date, and details about the final commits).
Different concepts included
- funding in instruments to detect and forestall malicious packages and automation for such instruments
- coverage and instruments to establish purple flag tasks
- a CVE for any bundle and/or department whose assist has ended (e.g., log4j 1.x)
Individuals additionally famous that, for the patron aspect, due diligence issues. They prompt the event of insurance policies and/or measures that would tackle issues resembling how effectively a shopper is at updating FOSS software program. The next can be useful for this goal:
- use of dependency displays
- use of bundle managers
- use of automated check suite
- readiness to replace in hours or days
- institution of a imply time from bundle replace to manufacturing launch (or comparable metric)
- use and monitoring of DORA metrics that align with the patron’s threat tolerance, resembling deployment frequency (DF); lead time for adjustments (LT); imply time to restoration (MTTR); and alter failure charge (CFR)
Provide Chain Artifact Decision
One participant described analyzing the availability chain as “an enormous spider tree.” Actually, this area is dense, complicated, and stuffed with intersecting paths. The dialogue rapidly moved to the software program invoice of supplies (SBOM), which the Nationwide Telecommunications and Data Administration (NTIA) describes as “a nested stock for software program, an inventory of substances that make up software program elements.” Within the NTIA doc Framing Software program Element Transparency: Establishing a Frequent Software program Invoice of Supplies (SBOM), the NTIA additional defines the SBOM as
… a proper, machine-readable stock of software program elements and dependencies, details about these elements, and their hierarchical relationships. These inventories must be complete–or ought to explicitly state the place they might not be. SBOMs could embody open supply or proprietary software program and may be broadly accessible or access-restricted.
Some workshop members, nonetheless, acknowledged that SBOMs they obtain are presently targeted on a “depth of 1” and on managing license threat. They famous that SBOMs want extra depth and perception (e.g., dependencies, libraries inside packages or containers, to call a couple of). Furthermore, the DoD is extra involved about full depth for vulnerability evaluation relatively than license threat. As well as, merely having an SBOM is inadequate. Specifically, customers should examine the record of elements to present lists of recognized vulnerabilities after which ignore vulnerabilities that can’t be exploited in that context. So, whereas SBOMs signify one strategy to get readability in regards to the provide chain, by themselves they continue to be inadequate in assembly the DoD’s necessities for FOSS software program growth.
Individuals additionally recognized one other challenge associated to the availability chain: How will you uniquely establish tasks, packages, and software program (a degree additionally made by the Census II examine famous above)? Any methodology for doing so would have to be immutable, canonical, and ideally distinctive. A requirements physique, such because the IETF, may evaluation and endorse such identification methodology(s). One proposal looking for to assist tackle inputs is the GitBOM challenge, which constructs a Merkle Tree utilizing the Git Object ID of all software program artifacts in a provide chain after which depends on the tree’s identifier (primarily its git hash) to establish the inputs that created a software program bundle.
Different associated issues embody the next
- a verification mechanism is required for provide chain artifacts
- verification proof should journey with the artifacts
- a number of language platforms (the tactic should work throughout languages, packaging kinds, and platforms)
Regardless of how we proceed on this space, members acknowledged the necessity to search neighborhood involvement and extra DoD stakeholder enter.
Institutional Constructions
To generate headway on the important thing subjects cited above (and extra shared subjects), this dialogue targeted on concrete methods to arrange and collaborate in a structured and sustainable method to fulfill the DoD’s tips for FOSS software program growth. Individuals agreed on the necessity to leverage present institutional constructions and create new ones the place obligatory. Individuals additionally typically agreed on the necessity to create a mechanism and discussion board for sustaining dialog and implementation inside this neighborhood and take a look at the prevailing institutional constructions of FFRDCs and UARCs paired with the open supply organizational construction of Open Supply Program Workplaces (OSPOs), which exist in lots of non-public firms in trade. To take action, the next concepts have been prompt:
- Leverage FFRDCs, UARCs, and the community between them.
- Create a working group and carry out neighborhood constructing with related mailing lists and meetups for stakeholders by
- avoiding a excessive barrier to participation
- making it accessible as a unbroken skilled growth alternative for members
- conducting outreach
- participating high-profile audio system
- Carry new folks in by making a recruiting and outreach community with authorities, academia, and trade (as these are shared challenges).
- Decide one-to-three work outputs, for example:
- a DoD FOSS FAQ replace developed with this neighborhood working group
- a common coverage paperwork replace and evaluation by the group
- a coaching course (e.g., Linux Basis’s Creating Safe Software program)
- a domain-specific collaboration, information change, and assembly (for instance, NIST and Good Cities)
- Add MiL-OSS (an present mailing record/neighborhood) as a subgroup.
- Place studying and coaching choices as skilled growth alternatives which might be related and enticing to software program builders. Require coaching in safe software program growth for these growing customized software program for the federal government (e.g., Open OSS fundamentals).
- Interact high-profile authorities audio system, particularly from sponsor businesses (e.g., the NIST Good Cities Convention).
- Coordinate with the U.S. OSS Coverage Meeting, as software program safety is a core public coverage concern driving FOSS globally.
- Coordinate with different FOSS safety efforts (OpenSSF, OSTIF, and many others.).
- Foster worldwide cooperation.
- Leverage cross-agency incentives.
- Fund accredited safe growth practices (together with FOSS) as a part of laptop science levels and associated applications (e.g., software program engineering). Don’t restrict FOSS to a safety silo.
Synthesizing FOSS Management Jam Discussions
Following a productive day of freewheeling dialogue of the important thing subjects, members then started to make associations between the important thing subjects and the main target areas outlined within the DoD’s memo on open supply software program and software program growth. The members from the open supply software program ecosystems supplied suggestions encouraging the DoD shoppers to attach with a few of the rising and evolving expertise in reproducible builds, SBOM requirements, and verifiable provide chain artifact bushes.
The members from the DoD software program factories would examine integrating capabilities into their approval processes and CI/CD pipelines which might be amenable to assessing FOSS challenge well being and standing (e.g., finest follow badges, scorecard, and many others.). They’d additionally examine different applied sciences for deeper evaluation of SBOMs, reproducible builds, and the usage of proof of full and verifiable artifact bushes, all of which might inform cyber threat administration actions to higher perceive their consumption of FOSS. In doing so, the software program factories would supply suggestions on the usage of such capabilities “from the manufacturing unit flooring” on to the open supply communities growing these instruments. This may enhance the usage of such instruments by all communities (together with the DoD) and would align to the DoD memorandum’s steerage on contributing to FOSS (part 4 of the DoD memo).
The DoD memorandum on open supply software program represents a wonderful stability between the potential and alternative of open supply software program and the comprehensible issues about safety and provide chain dependencies. Individuals agreed that the Undertake, Purchase, Create steerage and the open by default posture are acceptable, and acknowledged that safety and provide chain points are finest addressed by threat administration. Furthermore, members acknowledged that the SBOM is a key facet (although not ample) for safety and provide chain administration. The members additionally agreed that instruments and strategies that assess the trustworthiness of the event processes of open supply tasks are acceptable, versus strategies that target monitoring open supply contributions from people, firms, or nations in a blanket method. The members recognized a number of particular concepts that would assist such an strategy. We welcome the chance to associate with different federal businesses who may align to efforts in accordance with DoD management, notably these efforts associated to the memo that characterizes related points from each the patron and the producer views.
It’s anticipated that this group will convene once more to report on experiences gleaned from using a lot of what was mentioned throughout this workshop and to increase these concepts to extra DoD stakeholders and different DoD applications that profit from FOSS.