Packaging of nanoparticles into cell membranes and characterization of MNPs
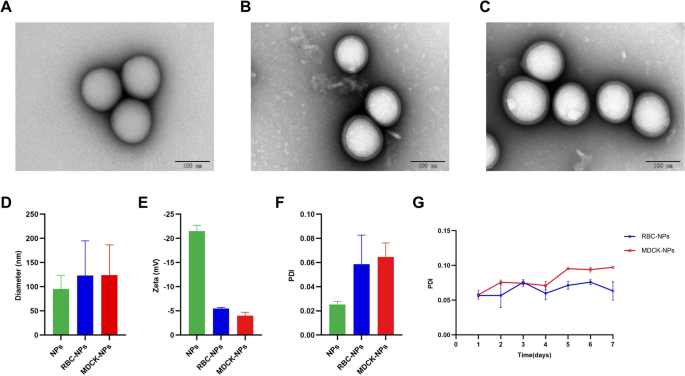
We ready the 50:50 Poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide) Carboxylate Finish Group (PLGA) nanoparticles, co-incubated them with purified cell membranes, and extruded the consequence from polycarbonate membranes to generate cell-membrane coated PLGA nanoparticles (Fig. 1). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to watch three kinds of nanoparticles: naked nanoparticles (naked NPs), coated with RBC cell membrane (RBC-NPs), and coated with MDCK cell membrane (MDCK-NPs) (Fig. 2A–C). All nanoparticles exhibited spherical buildings. When RBC-NPs and MDCK-NPs are in comparison with naked NPs, it may be clearly seen that the floor is roofed with a monolayer movie. A Stream NanoAnalyzer was used to measure the diameter (DH) of the three sorts of nanoparticles; naked NPs have been ~ 95 nm, and RBC-NPs and MDCK-NPs have been ~ 123 nm and ~ 124 nm, respectively, or ~ 30 nm bigger than naked NPs (Fig. 2D). Zeta potentials of the three nanoparticles measured utilizing dynamic gentle scattering (DLS), indicated that the zeta potentials of RBC-NPs and MDCK-NPs have been ~ 15 mV larger than naked NPs (Fig. 2E). To evaluate the dispersion of nanoparticles in liquids, the polydispersity index (PDI) of nanoparticles dispersed in PBS was measured; PDI was lower than 0.2, indicating that the three nanoparticles have good dispersion (Fig. 2F). No change in PDI per week later indicated that nanoparticles may be stably dispersed in PBS over the brief time period (Fig. 2G).
Characterization of nanoparticles. TEM photographs of A naked NPs, B RBC-NPs, and C MDCK-NPs. D Stream NanoAnalyzer measures of nanoparticle diameter (nm). E DLS measurements of zeta potential (Zeta, mV) of nanoparticles. F DLS measurements of PDI of nanoparticles. G DLS measurements of the adjustments within the PDI of the MNPs in PBS at 37 °C. Knowledge are introduced because the means ± SD
In vitro evaluations of MNPs
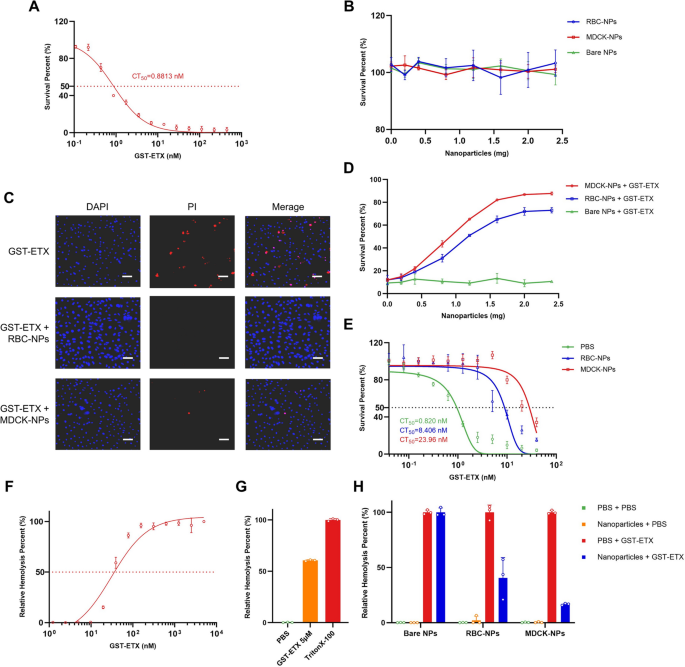
Neutralization capability in vitro is a crucial indicator of in vivo therapeutic efficacy. We due to this fact assessed the neutralization capability of the 2 sorts of MNPs (RBC-NPs and MDCK-NPs) to recombinant ETX with Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) tags (GST-ETX) in vitro by 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium inside salt (MTS) assay with cells. MDCK cells are essentially the most delicate cells to ETX and are generally utilized in ETX cytotoxicity. ETX with completely different tags (GST and 6 × His) didn’t considerably differ in toxicities (Further file 1: Fig. S1). Due to this fact, MDCK cells have been utilized in all evaluations of GST-ETX and MNPs in vitro. The focus of GST-ETX that killed 50% of MDCK cells (denoted by CT50) was 0.8813 nM (Fig. 3A). When the toxin reached a focus of 20 nM, most cell mortality was achieved. To research whether or not the three sorts of nanoparticles might harm MDCK cells, MDCK cells have been handled with a sequence of concentrations of nanoparticles. A measure of nanoparticles as excessive as 2.4 mg confirmed no cytotoxicity to MDCK cells (Fig. 3B).
In vitro analysis of GST-ETX and MNPs. A In vitro toxicities of GST-ETX. CT50 values have been calculated primarily based on focus–survival curves. B MDCK cells have been uncovered to rising concentrations of nanoparticles for 1 h at 37 °C and survival of MDCK cells measured. C Cells have been noticed by confocal microscopy. (Scale bar: 100 μm). D MDCK cells have been uncovered to rising concentrations of nanoparticles and 20 nM of GST-ETX for 1 h at 37 °C. Survival of MDCK cells was measured. E A sequence of concentrations of GST-ETX have been handled with two sorts of nanoparticles or PBS for 1 h at 37 °C. Toxicities of the mixtures have been measured. F RBCs in 2.5% resolution have been incubated with rising concentrations of GST-ETX for 1 h at 37 °C. Relative hemolysis of RBCs was measured. G RBCs in 2.5% resolution have been incubated with GST-ETX (5 μM) or 1% TritonX-100 for 1 h at 37 °C. Hemolysis of RBCs brought on by Triton X-100 is outlined as 100%. Maximal extent of hemolysis induced by GST-ETX was measured. H RBCs in 2.5% resolution have been incubated with GST-ETX (30 nM) and nanoparticles for 1 h at 37 °C. An assay of relative hemolysis of RBCs was carried out. Knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD
Cell demise was examined utilizing a confocal high-content imaging system (Fig. 3C, Further file 1: Fig. S2). MDCK cells incubated with the 2 sorts of MNPs maintained a excessive survival charge underneath ETX problem. MDCK cells have been incubated with GST-ETX and a sequence of concentrations of MNPs. MNPs considerably diminished the toxicity of GST-ETX in a dose-dependent method, with 2 mg MNPs almost abolishing the toxicity of GST-ETX to MDCK cells (Fig. 3D). MDCK-NPs diminished the toxicity of GST-ETX greater than RBC-NPs, suggesting that MDCK-NPs can neutralize GST-ETX sooner. We subsequent handled a sequence of concentrations of GST-ETX with MNPs, to evaluate the neutralization capability of MNPs combined with toxin. Each MNPs neutralized ETX, decreasing the toxicity of the combination to MDCK cells (Fig. 3E). The 2 kinds of MNPs created mixtures that differed in CT50, with 2 mg of RBC-NPs neutralizing 3.793 pmol GST-ETX, and a pair of mg of MDCK-NPs neutralizing 11.75 pmol GST-ETX. Thus, whereas each sorts of MNPs can successfully neutralize ETX, the MDCK-NPs neutralized extra GST-ETX sooner when cells have been challenged by GST-ETX. Due to this fact, MDCK-NPs have a greater efficiency towards GST-ETX than RBC-NPs.
To confirm the distinction in sensitivity between RBCs and MDCK cells, we assessed the relative hemolysis harm in RBCs brought on by GST-ETX. Hemolysis elevated with the focus of GST-ETX (Fig. 3F). The focus of GST-ETX required to trigger hemolysis in RBCs is shut to twenty nM, and the utmost relative hemolysis was achieved at a toxin focus of roughly 150 nM. As well as, RBC hemolysis by GST-ETX was not full inside 1 h (Fig. 3G). In distinction, 20 nM GST-ETX brought about most cell mortality to MDCK cells inside 1 h. This means that RBCs and MDCK cells differ in sensitivity to ETX, and this distinction is mirrored within the variations between the 2 sorts of MNPs. We estimated the focus of 30 nM of GST-ETX that may trigger 50% relative hemolysis to confirm the neutralization capability of MNPs. We calculated {that a} full neutralization of 30 nM GST-ETX 1 ml would require about 5.1 mg of MDCK-NPs and about 15.8 mg of RBC-NPs. The outcomes of co-incubation with RBCs confirmed that MDCK-NPs might cut back the toxicity by 85%, and RBC-NPs might cut back the toxicity by 60% (Fig. 3H). Not one of the three sorts of nanoparticles brought about any harm to RBCs. This result’s in keeping with the distinction in protecting capability of the 2 MNPs within the MDCK cell safety experiment above. When MNPs and cells competitively bind to GST-ETX, MDCK-NPs can neutralize extra toxin sooner. This can be as a result of there are extra receptors on the membranes of MDCK cells, provided that MDCK cells are extra delicate than RBCs to GST-ETX.
In vivo security evaluation of MNPs
Security evaluation in vivo is a crucial precondition of in vivo therapeutic efficacy. We due to this fact assessed the security of the three sorts of nanoparticles to mice in vivo. Following injection of one of many three sorts of the nanoparticles to a few teams of mice intravenously, mice have been noticed for 7 consecutive days (Fig. 4A). Naked NPs and RBC-NPs have been protected to animals, whereas MDCK-NPs brought about demise in half of the mice (Fig. 4B). We examined a number of blood parameters, together with a complete serum chemistry panel and blood cell counts. Cells depend in mice injected with naked NPs and RBC-NPs have been in keeping with baseline ranges, indicating these two nanoparticles didn’t trigger any poisonous or immune response (Fig. 4C). In distinction, mice injected with MDCK-NPs, displayed vital anomalies in white blood cell (WBC), eosinophil (EOS), basophil (BAS) and platelet (PLT) counts, indicating that MDCK cell membranes might set off an immune response, which is presumably associated to MDCK-NP-induced demise in mice. As well as, we assessed blood markers of liver and kidney harm; alkaline phosphatase (ALP) [25] and glucose (GLU) within the blood are thought to replicate harm to the liver [26], whereas serum calcium (Ca), serum sodium (Na), and urea in blood are thought to replicate harm to the kidney [27,28,29,30,31]. Nonetheless, these indicators have been regular in all mice (Fig. 4D), indicating the short-term security of MNPs.
In vivo security evaluations of the three sorts of the nanoparticles. A Schematic illustration of the experiments. 4 teams of 8-week-old feminine BALB/c mice have been injected with 100 μL PBS or PBS with naked NPs, with RBC-NPs or with MDCK-NPs (2% w/v) intravenously. B Survival curves of the mice within the subsequent 7 days (n = 6). 5 teams of 8-week-old feminine BALB/c mice, have been injected intravenously with 100 μL PBS or PBS with nanoparticles (2% w/v) or N2a cell membrane (100 μL, roughly 5 × 10.7 cells). C Blood cell counts of the mice (n = 3). D Chemical composition evaluation of serum (n = 3). E The focus of IgE in plasma within the mice (n = 3). Knowledge are introduced because the imply ± SD. p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***), p ≥ 0.05 (ns)
Immune response triggered by MDCK-NPs, which embrace elevated EOS, BAS and decreased PLT, are presumed to be associated to hypersensitivity [32,33,34]. To confirm whether or not the anomalies of MDCK-NPs have been associated to hypersensitivity, we measured IgE in mouse serum. The outcomes of serum IgE detection confirmed that IgE within the serum of mice injected with MDCK cells membrane was considerably elevated (Fig. 4E), whereas no apparent IgE response was detected within the serum of the opposite mice. These outcomes counsel that MDCK cell membranes induced sturdy hypersensitivity in mice, which is probably going the principle reason behind demise in mice injected with MDCK-NPs. MDCK cells originate from regular kidney cells of a cocker spaniel canine [35], which is distantly associated to murine species, and we infer that the injection of membranes from a distantly associated species are prone to induce sturdy immune response and hypersensitivity. To check our speculation, we injected membranes from N2a cells, which originate from a murine species. Membrane from N2a cells induced slight immune response however didn’t set off hypersensitivity, in step with our speculation.
Given the unstable security profile of MDCK-NPs, we deserted the usage of MDCK-NPs in additional animal experiments, regardless of their glorious capability to compete and bind ETX.
In vivo therapeutic efficacy evaluations of MNPs
After assessing neutralization capability in vitro and the security in vivo, we subsequent assessed therapeutic efficacy of RBC-NPs in vivo. We first intravenously injected GST-ETX into mice of every group, after which 10 min later, we intravenously injected RBC-NPs or PBS into mice of the therapy and constructive management group, respectively (Fig. 5A). The dose of 20 ng GST-ETX led to 100% demise of mice within the constructive management group inside 24 h (Further file 1: Fig. S3), whereas mice given RBC-NPs had 100% survival for 7 days (Fig. 5B). Histopathological evaluation confirmed that the kidneys, brains, livers and lungs of mice within the constructive management group had completely different levels of harm, primarily manifested as congestion or edema; nonetheless, these signs have been considerably relieved by RBC-NPs (Fig. 5C).
In vivo therapeutic efficacy evaluations of the RBC-NPs. A Schematic illustration of the experiments. Three teams of mice have been injected with 20 ng GST-ETX intravenously; 10 min later, mice within the therapy group have been injected with 2 mg RBC-NPs intravenously and mice within the constructive management group have been injected with PBS intravenously. On the identical time, mice within the unfavourable management group have been injected each instances with PBS intravenously. B The survival curves of mice within the 7 days post-injection (n = 6). C Blood cell counts within the mice (n = 3). D Chemical composition evaluation of serum (n = 3). E Main organs have been stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Consultant sections are proven for varied organs of the mice in several teams (scale bar: 200 μm). Knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD. p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***), p ≥ 0.05 (ns)
In one other three teams of mice, 6 h after completion of the 2 injections, blood for evaluation was performed (Fig. 5A). Blood biochemical evaluation revealed that, in comparison with the unfavourable management group, WBC depend within the blood of ETX-infected mice within the constructive management group was considerably elevated 300%, and the change of WBC was brought about primarily by 900% elevation of neutrophils (NEU) (Fig. 5D). WBC depend within the blood of mice handled with RBC-NPs was nearer to that of the unfavourable management group of mice. This means that RBC-NPs successfully attenuated the inflammatory response triggered in vivo by the ETX problem [36]. As well as, we assessed blood markers of liver and kidney harm. The livers and kidneys of mice have been broken to various levels through the ETX problem, and RBC-NPs can play a job in defending these organs, which was in keeping with the outcomes of histopathology evaluation (Fig. 5E, Further file 1: Fig. S4). Thus, RBC-NPs have been sufficiently in a position to competitively bind ETX in vivo to guard host organs from harm and might successfully deal with GST-ETX an infection in vivo.
The interplay between RBC-NPs and ETX and its metabolism in vivo
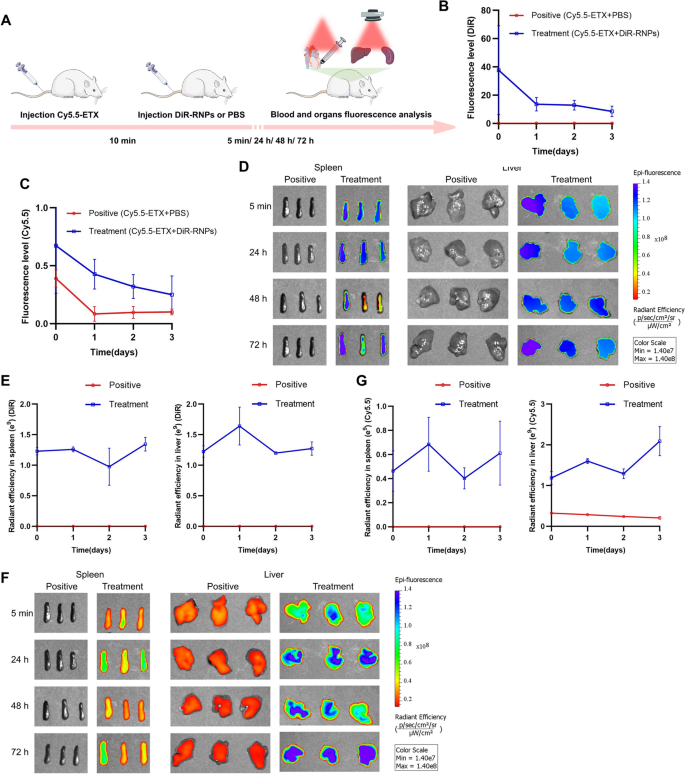
We additional investigated the interplay between in metabolisms of RBC-NPs and GST-ETX in vivo to confirm how the RBC-NPs defend the host. We injected mice intravenously with fluorescently-labeled RBC-NPs and GST-ETX, and the distribution of radiant effectivity in blood and tissues mirrored their interactions and metabolisms. To show the metabolism of ETX toxin and RBC-NPs in mouse tissues, the NIR dye DiOC18(7) (DiR) was used to label RBC-NPs (DiR-RNPs), the NIR dye cyanine 5.5 (Cy5.5) was used to label GST-ETX (Cy5.5-ETX). We intravenously injected Cy5.5-ETX into mice of every group and 10 min later, intravenously injected DiR-RNPs or PBS into mice of the therapy group and the constructive management group, respectively. At a number of time factors post-injection (after 5 min, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h), blood of random mice in every group was taken for quantitative evaluation of fluorescence intensities and its main organs have been taken on the identical time for fluorescence photographs in vitro (Fig. 6A). The quantitative evaluation of fluorescence intensities in blood confirmed that DiR-RNPs within the blood of mice within the therapy group decreased over time (Fig. 6B). It must be famous that Cy5.5-ETX within the blood of mice within the therapy group was not utterly cleared after three days, however persistently decreased together with DiR-RNPs (Fig. 6C). Ranges of Cy5.5-ETX within the blood of mice within the therapy group was decrease than that of the constructive management group all time factors and was diminished to a really low stage 24 h after injection. Thus, inside 5 min of injection, RBC-NPs neutralized the bulk ETX, stopping ETX from spreading in vivo. As well as, the RBC-NPs that neutralized ETX remained secure within the blood and didn’t launch toxins into the blood once more.
Interplay and metabolism between RBC-NPs and GST-ETX in vivo. A Schematic illustration of the experiments. Two teams of mice have been injected with 5 ng GST-ETX intravenously, and 10 min later, mice within the therapy group have been injected with 2 mg DiR-RNPs intravenously and mice within the constructive management group have been injected with PBS intravenously. Blood and organs have been analyzed at 5 min, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h in vitro. B The fluorescence stage of the DiR in blood (n = 3). C The fluorescence stage of Cy5.5 in blood (n = 3). D In vitro fluorescence photographs of DiR in liver and spleen, E radiant effectivity of the DiR in liver and spleen (n = 3). F In vitro fluorescence photographs of Cy5.5 in liver and spleen. G Radiant effectivity of Cy5.5 in liver and spleen (n = 3). The constructive management group was injected with Cy5.5-ETX and PBS, the therapy group was injected with Cy5.5-ETX and DiR-NPs. Knowledge are introduced because the imply ± SD
Quantitative knowledge of fluorescence photographs in vitro of DiR in tissues indicated that DiR-RNPs have been captured by the liver and spleen (Fig. 6D–E, Further file 1: Figs. S5, S6). The Cy5.5 sign of mice within the constructive management group instructed Cy5.5-ETX step by step decreased within the liver, and no fluorescence sign was noticed within the spleen (Fig. 6F–G, Further file 1: Figs. S7, S8). Within the therapy group, Cy5.5-ETX was a lot greater within the liver and in addition had a excessive sign within the spleen. As with the fluorescence sign in blood of the therapy group, the distribution sign of GST-ETX in organs is in keeping with that of RBC-NPs. This was particularly evident within the spleen, during which GST-ETX was not detected within the spleen within the constructive management group, however as a result of RBC-NPs had been captured by the spleen, it was detected within the spleen of the therapy group. The distinction is that the 2 fluorescence alerts are inclined to lower over time within the blood, whereas fluorescent alerts within the spleen and liver present an inclination to stabilize or improve. The outcomes present that as immune and cleansing organs of animals, the spleen and liver captured RBC-NPs that had neutralized GST-ETX from the blood. That is how RBC-NPs deal with GST-ETX an infection in vivo.
In vivo therapeutic efficacy evaluations of nebulized pulmonary inhalation
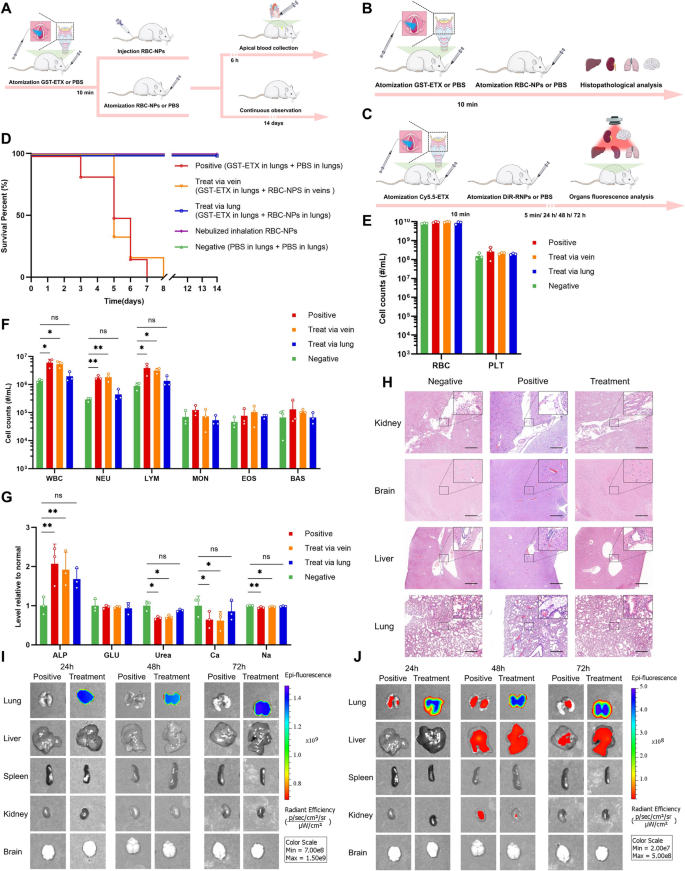
Poisonous aerosols can be utilized as weapons in terrorist assaults. For ETX, which was categorised as a possible organic weapon, whether or not RBC-NPs can play a protecting position in ETX challenges from pulmonary inhalation is of key import. We due to this fact assessed the therapeutic efficacy of the RBC-NPs throughout nebulized pulmonary inhalation of mice in vivo. Liquid aerosol gadgets have been used to manage GST-ETX and RBC-NPs from the mouse trachea by quantitative nebulization, thereby simulating ETX aerosol challenges and lung drug supply. The benefit of utilizing liquid aerosol gadgets is that the drug may be evenly distributed into the lungs of mice (Further file 1: Fig. S9) and ensures that every mouse receives the drug on the identical distribution location and reduces the chance of pulmonary edema brought on by lung administration. This not solely permits us to simulate an ETX aerosol weapons problem, but additionally minimizes potential hostile results throughout lung supply of RBC-NPs. We first administered 50 ng GST-ETX into the tracheas of mice in every group, and 10 min later, administered 2 mg RBC-NPs by trachea or intravenously to mice within the two therapy teams; PBS was administered by trachea to mice within the constructive management group. Mice within the unfavourable management group had PBS administered by tracheas every time (Fig. 7A). Mice have been noticed for 14 days post-infection. Introduction of fifty ng GST-ETX into mouse lungs resulted in 100% mortality of the mice within the constructive management group inside 8 days (Further file 1: Fig. S10). Remedy mice that had RBC-NPs launched by aerosol into the lungs had 100% survival (Fig. 7D). Nonetheless, RBC-NPs given intravenously didn’t play a protecting position to mice, mice on this group all died inside 8 days.
The in vivo therapeutic efficacy of RBC-NPs and metabolism of RBC-NPs and GST-ETX in lung. A Schematic illustration of the experiment. 4 teams of mice have been administered 50 ng GST-ETX by way of trachea; 10 min later, two therapy teams of mice have been administered 2 mg RBC-NPs by way of trachea or intravenous, and a constructive management group of mice was administered PBS by way of trachea. A unfavourable management group of mice have been administered PBS by way of trachea twice. B Schematic illustration of the experiment. Three teams of mice have been administered 50 ng GST-ETX by way of trachea, 10 min later, therapy teams of mice have been administered 2 mg RBC-NPs by way of trachea, and a constructive management group of mice have been administered PBS from tracheas. On the identical time, a unfavourable management group of mice have been administered PBS by way of trachea twice. C Schematic illustration of metabolism experiment. Two teams of mice have been administered 12.5 ng Cy5.5-ETX by way of trachea; 10 min later, the therapy group of mice have been administered 2 mg DiR-RNPs by way of trachea, and the constructive management group of mice have been administered PBS from trachea. D Survival curves of mice over 14 days post-infection (n = 6). E, F Blood cell counts in mice (n = 3). G The chemical composition evaluation of serum (n = 3). H Consultant sections constructed from varied organs of experimental mice, stained with H&E (scale bar: 200 μm). I In vitro fluorescence photographs of DiR in liver and spleen. J In vitro fluorescence photographs of Cy5.5 in liver and spleen. Knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD. p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***), p ≥ 0.05 (ns)
In one other teams of mice, blood samples have been taken for evaluation 6 h post-infection (Fig. 7A). In comparison with the unfavourable management group of mice, WBC counts in ETX-infected mice have been elevated 300%. The WBC counts of mice handled with RBC-NPs in lungs have been nearer to the unfavourable management group of mice, however the WBC counts of mice handled with RBC-NPs intravenously have been nearer to these of mice within the constructive management group. The rise in WBCs was primarily brought on by 600% will increase in NEU (Fig. 7E–F). This consequence confirmed that solely RBC-NPs in lungs successfully attenuate the inflammatory response triggered in vivo by the ETX problem in lungs. As earlier than, we additionally examined blood markers of liver and kidney harm. The livers of mice weren’t broken through the ETX problem in lungs, however kidneys, essentially the most delicate organ to ETX, have been barely broken with ETX problem to lungs. In contrast with injection of MNPs by way of veins, RBC-NPs in lungs seem to play a crucial position in defending kidneys of mice (Fig. 7G).
As with our experiment testing therapeutic efficacy injecting intravenously, we once more dissected the principle organs and stained tissue with H&E (Fig. 7B) for aerosol-challenged mice. Histopathological evaluation confirmed that the brains of mice had no apparent pathological adjustments (Fig. 7H, Further file 1: Fig. S11). The lungs of mice within the constructive management group had critical harm, primarily manifested as congestion and edema, whereas the liver and kidneys of those mice had delicate harm, primarily manifested as edema. Nonetheless, these signs have been considerably relieved by RBC-NPs in lungs.
To confirm why pulmonary an infection with ETX causes much less harm to organs apart from the lungs, and the way RBC-NPs in lungs can defend mice, Cy5.5-ETX and DiR-RNPs have been used to measure their interactions and metabolism in lungs (Fig. 7C). Quantitative knowledge of fluorescence photographs in vitro of the DiR indicated that DiR-RNPs can not escape the lungs (Fig. 7I). Quantitative knowledge of fluorescence photographs in vitro of the Cy5.5 of the mice within the constructive management group indicated that the majority Cy5.5-ETX stays within the lungs after 24 h, however after 48 h, some Cy5.5-ETX was detected within the livers and a smaller quantity of Cy5.5-ETX was detected within the kidneys (Fig. 7J). This consequence confirmed why GST-ETX causes little harm to different organs when administered by way of the lung. Nonetheless, for mice within the therapy group all Cy5.5-ETX was within the lungs and the distribution of the sign of GST-ETX was in keeping with that of RBC-NPs. Thus, GST-ETX was utterly neutralized within the lungs by RBC-NPs, stopping it from inflicting harm to the lungs and in addition stopping it from spreading past the lungs. That is how RBC-NPs protects the host towards an ETX problem to the lungs. This experiment demonstrated the efficacy of utilizing RBC-NPs in lungs to deal with of GST-ETX an infection in lungs in vivo.
Sustained safety of MNPs in vivo
Earlier tissue in vitro imaging experiments had proven that RBC-NPs have a considerably longer circulation time than anticipated in vivo. This implies that the soundness of RBC-NPs can offers long-term safety in vivo. To check this, we delivered RBC-NPs to mice 1–3 days prematurely of a toxin problem by way of intravenous and aerosol, after which delivered GST-ETX to mice utilizing the identical supply system. Mice have been then noticed for survival (Fig. 8A, C). RBC-NPs given intravenously 3 days prematurely nonetheless offered safety for mice towards ETX, and RBC-NPs in lungs 2 days prematurely offered partial safety for mice (Fig. 8B, D). In different teams of mice, 6 h after finishing toxin supply, blood was taken for evaluation (Fig. 8A, C). Blood biochemical evaluation reveals that, in line with the 2 requirements of WBC and NEU counts, acceptable early injection of RBC-NPs can present safety to the host, though the protecting impact decreases with time (Fig. 8E, F). This experiment demonstrated the efficacy of utilizing RBC-NPs prematurely to deal with of GST-ETX an infection in vivo.
In vivo analysis of projection offered by preinjected RBC-NPs. A Schematic illustration of the experiments. Three therapy teams of mice have been injected with 2 mg RBC-NPs intravenously 24, 48, and 72 h previous to injection with 20 ng GST-ETX intravenously. The unfavourable and constructive management teams of mice have been injected with PBS intravenously within the 72 h previous to toxin problem, and mice have been injected with 20 ng GST-ETX or PBS intravenously on the final day. B Survival curves of the mice for 7 days post-intravenous toxin problem (n = 6). C Schematic illustration of the experiments. Three therapy teams of mice have been injected with 2 mg RBC-NPs by way of aerosol into the lungs at 24, 48, and 72 h previous to aerosol problem with 50 ng GST-ETX. The unfavourable and constructive management teams of mice had PBS by way of aerosol within the 72 h previous to aerosol lung publicity with 20 ng GST-ETX or PBS on the final day. D Survival curves of the mice for 7 days after aerosol toxin problem (n = 6). E Blood cell counts of cells of mice injected intravenously (n = 3). F Blood cell counts of mice injected by way of aerosol into lungs (n = 3). Knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD. p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***), p ≥ 0.05 (ns)