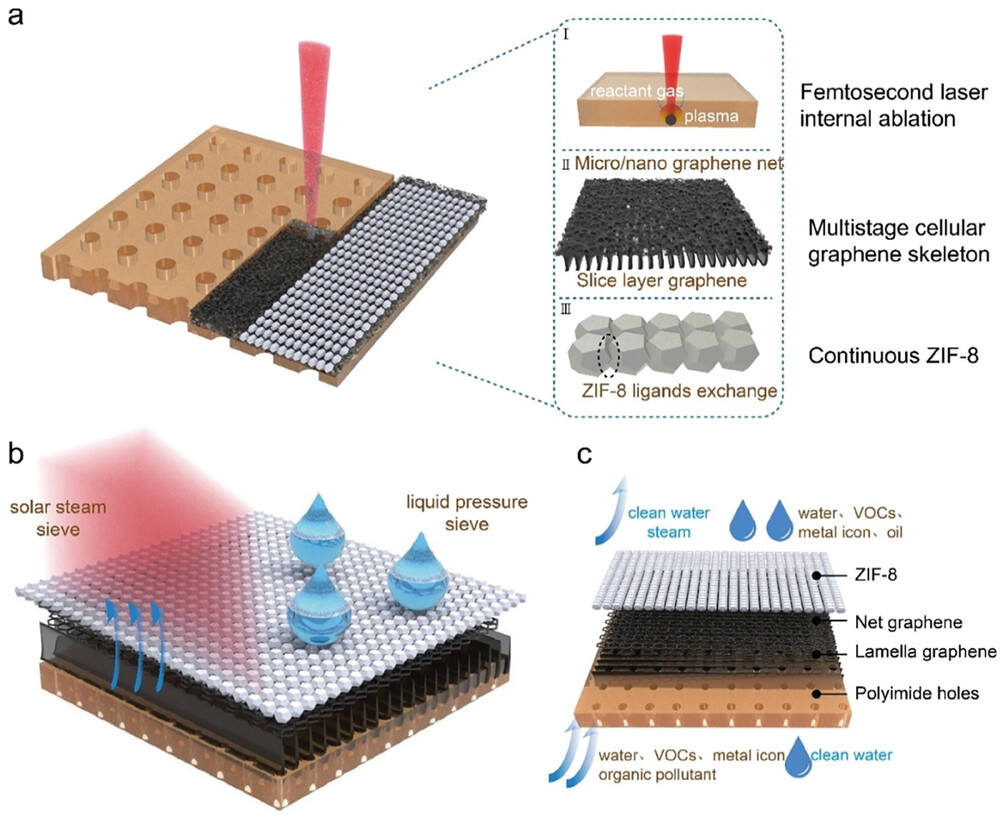
 Laser induced multilevel mobile graphene skeleton with steady MOFs nanolayer (CMN) for multiphase water molecular sieve. a) Schematic of the femtosecond laser induced multilevel graphene skeleton sieve and the concrete particulars. I) Femtosecond laser inside ablative and thermal shock. II) Laser induced multilevel graphene skeleton. III) In situ development and ligand alternate of MOFs, utilizing ZIF-8. b) Schematic of the molecular sieve in c) Multiphase water molecular sieving schematic diagram. (Reprinted with permission by Wiley-VCH Verlag)
Membrane-based water therapy makes use of porous movies to filter out contaminants and purify water by selective sieving. MOFs, a category of porous nanomaterials, present spectacular molecular sieving skill, however their utility has been restricted by restricted sieving vary, answer instability, and complicated processing necessities. Graphene gives excessive photo voltaic absorption and permeability however lacks the selective sieving capabilities of MOFs.
The brand new research tackles these limitations by integrating laser-induced graphene (LIG) and steady MOF layers into a sturdy hybrid membrane. LIG fabrication makes use of a femtosecond laser to induce graphene formation inside a industrial polymer movie, producing a multilevel “graphene skeleton” (MGKS) with micro/nanopores excellent for water therapy. Researchers then grew a steady nanolayer of MOF particles (ZIF-8) throughout the LIG skeleton by in situ hydrothermal synthesis. The ensuing multilayered membrane combines the strengths of each supplies – LIG gives a secure spine with wonderful photo voltaic absorption and water permeability, whereas the MOF layer allows exact molecular sieving.
The ensuing MGKS reveals ordered micro and nanopores on its floor, key for selective molecule sieving. The laser additionally types staggered lamellae on the underside, facilitating environment friendly multiphase water movement. To strengthen the graphene’s stability beneath filtration situations, the researchers grew a steady nanolayer of the MOF ZIF-8 all through the skeleton by way of in-situ nucleation and ligand alternate. The custom-made ZIF-8 synthesis yielded smaller nanopores that assist sieve smaller contaminants.
This graphene-MOF hybrid membrane employs a multilevel, multipore dimension sieving technique. The micron graphene community adsorbs oils and huge molecules. Its 10 nm nanopores present a big floor space for capturing contaminants. Embedded practical teams like hydroxyls and carboxyls cut back heavy steel ions within the feed water. Lastly, the ultrasmall 0.34 nm ZIF-8 pores filter out risky natural compounds whereas permitting water to move by.
Rigorous supplies characterization validated the hybrid membrane’s composition and properties. Checks confirmed the optimized LIG construction possessed excessive crystallinity and thermal stability wanted for real-world use. The MOF layer crammed defects within the graphene skeleton, enhancing membrane integrity. These outcomes indicated the membrane might preserve efficiency beneath the tough situations of business water therapy.
Testing validated the membrane’s photo voltaic steam era and contaminant elimination efficiency. It achieved distinctive daylight absorption and 90% benchmark evaporation effectivity beneath diversified irradiation, whereas successfully sieving 4 heavy steel ions beneath consuming water requirements. The ZIF-8 layer additionally utterly intercepted natural dyes and considerably eliminated risky natural solvents.
Underneath pressure-driven liquid filtration, the membrane’s hydrophobic and lipophilic properties enabled oil-water separation. It adsorbed the complete oil fraction when filtering an oil-water combination. Although much less environment friendly than solar-driven filtration, pressure-driven operation nonetheless decreased risky organics, heavy metals, and dyes to an considerable diploma.
Total, the optimized graphene skeleton’s stability and the ZIF-8’s selective sieving mixed to eradicate a large spectrum of water contaminants. This overcomes limitations of earlier graphene and MOF membranes alone. The facile fabrication technique additionally allows scalable manufacturing.
This analysis pioneers an thrilling new course in membrane expertise. The facile LIG-MOF fabrication technique and distinctive efficiency open doorways for graphene/MOF hybrids to satisfy their promise in real-world water purification. Whereas some limitations stay, particularly for liquid-phase functions, the solar-driven outcomes are extraordinarily promising.
With additional optimization, the method might broaden water therapy capabilities and allow sustainable utilization of non-traditional sources. Because the authors be aware, adjusting laser parameters and MOF choice gives flexibility to tailor the membrane’s construction for desired functions. The scalability of the method can be a significant benefit over standard nanomaterial fabrication strategies.
Laser induced multilevel mobile graphene skeleton with steady MOFs nanolayer (CMN) for multiphase water molecular sieve. a) Schematic of the femtosecond laser induced multilevel graphene skeleton sieve and the concrete particulars. I) Femtosecond laser inside ablative and thermal shock. II) Laser induced multilevel graphene skeleton. III) In situ development and ligand alternate of MOFs, utilizing ZIF-8. b) Schematic of the molecular sieve in c) Multiphase water molecular sieving schematic diagram. (Reprinted with permission by Wiley-VCH Verlag)
Membrane-based water therapy makes use of porous movies to filter out contaminants and purify water by selective sieving. MOFs, a category of porous nanomaterials, present spectacular molecular sieving skill, however their utility has been restricted by restricted sieving vary, answer instability, and complicated processing necessities. Graphene gives excessive photo voltaic absorption and permeability however lacks the selective sieving capabilities of MOFs.
The brand new research tackles these limitations by integrating laser-induced graphene (LIG) and steady MOF layers into a sturdy hybrid membrane. LIG fabrication makes use of a femtosecond laser to induce graphene formation inside a industrial polymer movie, producing a multilevel “graphene skeleton” (MGKS) with micro/nanopores excellent for water therapy. Researchers then grew a steady nanolayer of MOF particles (ZIF-8) throughout the LIG skeleton by in situ hydrothermal synthesis. The ensuing multilayered membrane combines the strengths of each supplies – LIG gives a secure spine with wonderful photo voltaic absorption and water permeability, whereas the MOF layer allows exact molecular sieving.
The ensuing MGKS reveals ordered micro and nanopores on its floor, key for selective molecule sieving. The laser additionally types staggered lamellae on the underside, facilitating environment friendly multiphase water movement. To strengthen the graphene’s stability beneath filtration situations, the researchers grew a steady nanolayer of the MOF ZIF-8 all through the skeleton by way of in-situ nucleation and ligand alternate. The custom-made ZIF-8 synthesis yielded smaller nanopores that assist sieve smaller contaminants.
This graphene-MOF hybrid membrane employs a multilevel, multipore dimension sieving technique. The micron graphene community adsorbs oils and huge molecules. Its 10 nm nanopores present a big floor space for capturing contaminants. Embedded practical teams like hydroxyls and carboxyls cut back heavy steel ions within the feed water. Lastly, the ultrasmall 0.34 nm ZIF-8 pores filter out risky natural compounds whereas permitting water to move by.
Rigorous supplies characterization validated the hybrid membrane’s composition and properties. Checks confirmed the optimized LIG construction possessed excessive crystallinity and thermal stability wanted for real-world use. The MOF layer crammed defects within the graphene skeleton, enhancing membrane integrity. These outcomes indicated the membrane might preserve efficiency beneath the tough situations of business water therapy.
Testing validated the membrane’s photo voltaic steam era and contaminant elimination efficiency. It achieved distinctive daylight absorption and 90% benchmark evaporation effectivity beneath diversified irradiation, whereas successfully sieving 4 heavy steel ions beneath consuming water requirements. The ZIF-8 layer additionally utterly intercepted natural dyes and considerably eliminated risky natural solvents.
Underneath pressure-driven liquid filtration, the membrane’s hydrophobic and lipophilic properties enabled oil-water separation. It adsorbed the complete oil fraction when filtering an oil-water combination. Although much less environment friendly than solar-driven filtration, pressure-driven operation nonetheless decreased risky organics, heavy metals, and dyes to an considerable diploma.
Total, the optimized graphene skeleton’s stability and the ZIF-8’s selective sieving mixed to eradicate a large spectrum of water contaminants. This overcomes limitations of earlier graphene and MOF membranes alone. The facile fabrication technique additionally allows scalable manufacturing.
This analysis pioneers an thrilling new course in membrane expertise. The facile LIG-MOF fabrication technique and distinctive efficiency open doorways for graphene/MOF hybrids to satisfy their promise in real-world water purification. Whereas some limitations stay, particularly for liquid-phase functions, the solar-driven outcomes are extraordinarily promising.
With additional optimization, the method might broaden water therapy capabilities and allow sustainable utilization of non-traditional sources. Because the authors be aware, adjusting laser parameters and MOF choice gives flexibility to tailor the membrane’s construction for desired functions. The scalability of the method can be a significant benefit over standard nanomaterial fabrication strategies.

By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is creator of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Know-how,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Abilities and Instruments Making Know-how Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
Develop into a Highlight visitor creator! Be a part of our massive and rising group of visitor contributors. Have you ever simply revealed a scientific paper or produce other thrilling developments to share with the nanotechnology group? Right here is the way to publish on nanowerk.com.


