Characterization and catalytic exercise of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA
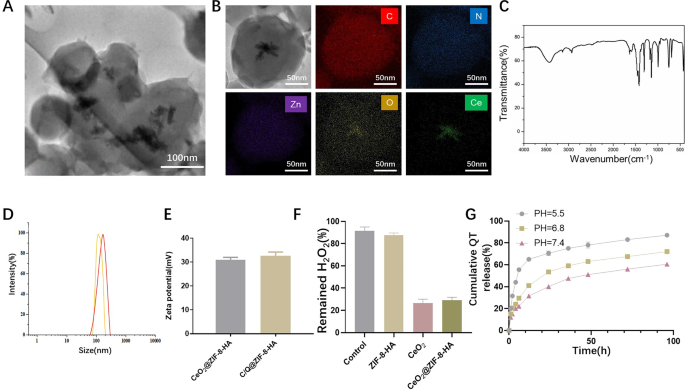
We’ve synthesized CeO2@ZIF-8 and C/Q@ZIF-8 nanoparticles utilizing a “one-pot” methodology. As a consequence of its good concentrating on and biocompatibility, HA has been extensively utilized in tumor therapy. Due to this fact, we modified HA on the floor of the nanoparticles to manufacture CeO2@ZIF-8-HA and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA (Fig. 1). As proven in Fig. 2A, we characterised the morphology (dimension and form) of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA by TEM. Elemental mapping pictures present that C, N, O and Zn components are uniformly distributed in C/Q@ZIF-8-HA nanoparticles, whereas Ce component is distributed contained in the nanoparticles (Fig. 2B). The FT-IR spectra in Fig. 2C present the hydrogen skeleton vibration of the amine group of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA at 3327 cm− 1 and the vibration peak of the carbonyl group at 1420 cm− 1, additional confirming the profitable synthesis of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. The common hydrodynamic particle diameter of was roughly 108 nm based on DLS measurements (Fig. 2D). After loading QT, the common hydrodynamic particle diameter of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA elevated to roughly 132 nm. The zeta potentials of CeO2@ZIF-8-HA and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA had been 31.0mV and 32.2mV, respectively, suggesting their glorious uniformity and stability (Fig. 2E). As a result of excessive porosity of ZIF-8, the CeO2 loading quantity of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA was calculated as 17.7% and the QT loading quantity as 11.2%. The above experimental outcomes have confirmed the profitable fabrication of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA nanoparticles.
As is understood to all, Fenton-like reactions are a common time period for reactions wherein some transition metals akin to Cu, Mn and Ce can speed up or substitute Fe(II) and catalyze the H2O2 response [23]. The extent of H2O2 in stable tumors is usually larger than in regular tissues, and contemplating the elevated degree of H2O2 in TME, a Fenton-like response might be utilized to realize extremely selective sensitization by RT. Fenton-like catalysts present nice promise for medical functions. Among the many catalysts reported up to now, Fenton-like catalysts present nice promise for medical functions. Zheng et al. synthesized an MnO-based nanoparticle as an inducer of iron toxicity, which may particularly launch Mn by way of depletion of glutathione after which activate Fenton-like reactions within the TME [24]. We examined the catalytic potential of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA nanoparticles in vitro utilizing 100 mmol/L H2O2 to simulate the H2O2 content material in TME. The catalytic exercise of the response resolution containing CeO2@ZIF-8-HA and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA in the direction of H2O2 was considerably larger in comparison with the opposite nanoparticles. As proven in Fig. 2F, the decomposition price of H2O2 for C/Q@ZIF-8-HA is considerably larger than that of the management group, however barely decrease than that of CeO2 group. This means that the CeO2 dispersed in ZIF-8 doesn’t have a big impression on its catalytic potential. Consequently, these outcomes point out that the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA nanozyme exhibited superior nanozyme exercise in decomposing H2O2 to O2. Subsequent, we measured the discharge of QT from C/Q@ZIF-8-HA nanoparticles underneath totally different pH circumstances. As proven in Fig. 2G, the discharge quantities reached 87.1% and 72.7% at pH 5.5 and pH 6.8, respectively, after 96 h, whereas the cumulative launch quantity at pH 7.2 was 60.5%, indicating that acidic circumstances had been extra favorable for the discharge of QT. This means C/Q@ZIF-8-HA nanoparticles have the perform of pH-responsive launch, permitting focused launch of the encapsulated QT.
Characterization and catalytic exercise of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. (A) TEM picture of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. (B) TEM picture and component mapping C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. (C) FT-IR of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. (D) Particle dimension evaluation of CeO2@ZIF-8-HA and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. (E) Zeta potential evaluation of CeO2@ZIF-8-HA and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. (F) Catalase-mimicking exercise of ZIF-8, CeO2, CeO2@ZIF-8-HA and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. (G) In vitro launch curve of QT. **P < 0.01
In Vitro tumor cells internalization
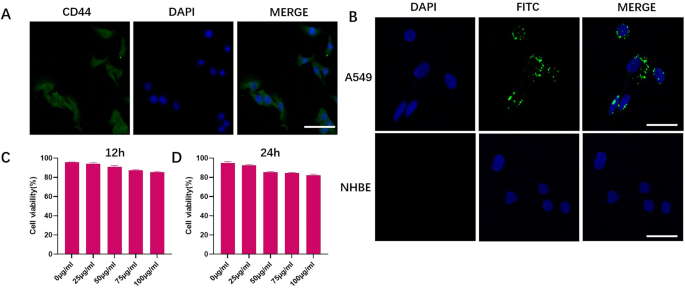
Because the passive concentrating on technique has restricted internalization of tumor cells as a result of EPR impact of the stable tumor [25], we constructed an lively concentrating on technique that depends on a receptor-ligand mechanism, utilizing HA with a molecular weight of roughly 200 kDa to switch the C/Q@ZIF-8. CD44 is a fancy transmembrane adhesion glycoprotein expressed in quite a lot of human cells, together with embryonic stem cells, differentiated cells and most cancers cells. As acknowledged marker of tumor stem cells, CD44 is a essential regulator of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), concerned in tumorigenesis, development, and metastasis. Zeng et al. constructed a nanoplatform consisting of copper-doped mesoporous Prussian blue (CMPB) encapsulated glucose oxidase (GOx) and a HA coating modified with a nitric oxide donor. The HA coating permits this nanoparticles to actively goal CD44 receptors in most cancers cells and in addition enhances vascular permeability [26]. Firstly, immunofluorescence assay was carried out by us to detect the expression of CD44 on the floor of A549 cells. As proven in Fig. 3A, the floor of A549 cells stained intensely, indicating sufficient CD44 expression. The tumor cell concentrating on potential of nanoparticles was investigated with FITC-labeled C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. Regular human bronchial epithelial cell (NHBE) was used to confirm whether or not the improved uptake of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA was restricted to tumor cells, however not regular lung epithelial cells. As illustrated in Fig. 3B, FITC-labeled C/Q@ZIF-8-HA-treated A549 cells confirmed a powerful inexperienced fluorescent sign within the cytoplasm. Nonetheless, NHBE cells handled with C/Q@ZIF-8-HA had no FITC fluorescence sign. These phenomena counsel that C/Q@ZIF-8-HA might considerably enhance the uptake of C/Q@ZIF-8 by A549 cells by means of the focused binding of HA and CD44. Moreover, the elevated uptake of C/Q@ZIF-8 was restricted to tumor cells, however to not regular lung epithelial cells. Subsequent, we evaluated the cytotoxicity profile of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA by CCK-8 assay, which is a vital parameter for nano-radiosensitizers in the direction of medical functions and to enhance the effectiveness of RT on tumor cells. Cell survival was examined after incubation of A549 with C/Q@ZIF-8-HA for 12 or 24 h. The cell survival price reached greater than 83% in any respect concentrations of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA from 0 to 100 µg/mL, indicating that C/Q@ZIF-8-HA has good cytocompatibility even at comparatively larger concentrations (Fig. 3C and D).
(A) Immunofluorescence microscopy picture of A549 cells stained by CD44. (B) Immunofluorescence pictures of cultured A549 cells after 4 h of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA therapy. (C) and (D) The biocompatibility of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA on A549 cells at totally different focus (0, 12.5, 25, 50, 75 and 100 µg ml− 1) after incubation for 12 and 24 h. Scale bar: 20 μm
C/Q@ZIF-8-HA nanozymes attenuate hypoxia and improve radiosensitivity in vitro
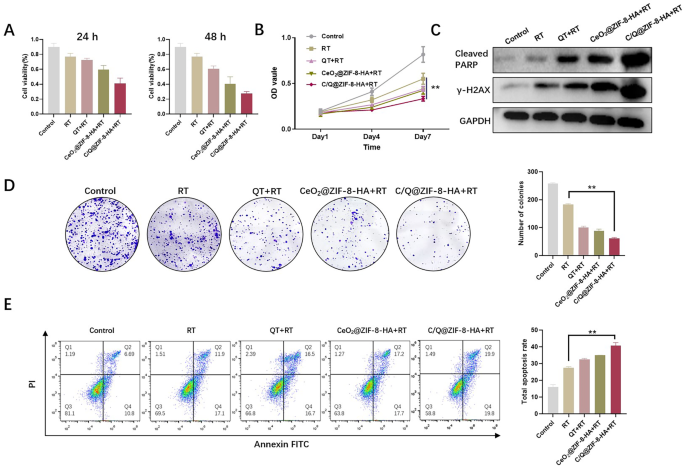
Within the in vitro experiments we’ve arrange a complete of 5 subgroups: Group (a): wild kind A549 cells; Group (b): a + X-ray(6 Gy); Group (c): b + QT; Group (d): b + CeO2@ZIF-8-HA; Group (e): b + C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. For investigating the sensitizing impact of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA on NSCLC radiotherapy, we utilized in vitro mobile assays. QT, a flavonoid aldose reductase inhibitor of pure plant origin, has quite a lot of antitumor actions, presumably on account of its potential to inhibit the MAPK and Akt signaling system exercise in quite a lot of tumor cells [27]. To confirm the synergistic sensitizing impact of QT and CeO2 on RT in vitro, we co-cultured C/Q@ZIF-8-HA with A549 cells for twenty-four and 48 h. At these two time factors, the cell survival price of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group was considerably decrease than that of RT alone. Accordingly, the cell survival price within the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group was additionally considerably decrease than the cell survival price in CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT and QT + RT teams (Fig. 4A). These outcomes tentatively point out that mixed RT with C/Q@ZIF-8-HA might exert the mixed sensitizing impact of QT and CeO2 to maximise tumor cell killing and inhibit cell proliferation. We subsequent sought to research the consequences of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA on the proliferation of A549 cells. C/Q@ZIF-8-HA considerably inhibited the speed of cell proliferation in contrast with the management group. Accordingly, The CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT and QT + RT teams confirmed larger inhibition of cell proliferation than the RT group, however weaker than the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA group (Fig. 4B).
(A) Consultant outcomes of the A549 MTT assay in numerous teams together with the management, RT, QT + RT, CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT, and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT teams. The outcomes from 24 and 48 h time factors exhibiting statistically important distinction. (B) CCK-8 assay was used to research the proliferation potential of 5 teams. (C) Western blotting evaluation of cleaved PARP and γH2AX in management, RT, QT + RT, CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT, and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT teams, respectively. (D) A colony of A549 cells handled with QT, CeO2@ZIF-8-HA, or C/Q@ZIF-8-HA mixed X-ray (6 Gy). (E) Annexin V-FITC/PI staining was carried out to find out the apoptosis of A549 cells in management, RT, QT + RT, CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT, and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT teams. **P < 0.01
Focused DNA restore pathways have proven nice potential in enhancing the consequences of radiation remedy on tumor cells. Poly ADP-ribosepolymerase (PARP) is a multifunctional nuclear protein that performs an important position in DNA injury restore. Ionizing radiation may cause intracellular DNA double-strand breaks to exert its therapeutic impact, and DNA restore after injury can have an effect on the efficacy of radiotherapy. γ-H2AX is the simplest early biomarker for detecting DNA double-strand breaks and is related to tumorigenesis, development and apoptosis [7]. We employed Western Blot assay to judge the impression of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA on the expression of Cleaved PARP and γ-H2AX. As proven in Fig. 4C, Cleaved PARP and γ-H2AX had been considerably elevated in C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group, indicating that C/Q@ZIF-8-HA considerably enhanced DNA double-strand breaks in tumor cells induced by ionizing radiation.
Subsequently, we evaluated the power of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA to boost the radiosensitivity of A549 cells by means of clonogenic assay. Within the management group, the variety of A549 cell colonies was roughly 275, whereas within the RT group, it was roughly 164. In distinction, the variety of colonies of the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group was 64, which was considerably decrease than that of the QT + RT (92) and CeO2@ZIF-8 + RT teams (87) (Fig. 4D). Determine 4E exhibits that the apoptosis charges of various teams of cells had been in contrast by circulate cytometry experiments. Much like the CCK-8 assay outcomes, the apoptosis price of A549 cells reached 31.2% and 33.4% after QT + RT or CeO2@ZIF-8 + RT therapy, respectively, which was considerably totally different in comparison with the RT group. Nonetheless, a big enhance within the whole apoptosis price (39.7%) was noticed within the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group, which was nearly 1.5-fold larger than that within the RT group and a pair of.5-fold larger than that within the management group.
These outcomes counsel that CeO2 and QT have potential as radiosensitizers. ZIF-8 encapsulated with CeO2 and QT can higher exert the synergistic impact of each radiotherapy sensitizers. On the one hand, CeO2 can enhance tumor hypoxia, enhance hydroxyl radical manufacturing and enhance DNA uptake for ionizing radiation capability, and then again, QT can maximally induce tumor cell apoptosis by growing X-ray uptake, thus attaining the aim of radiation sensitization.
C/Q@ZIF-8-HA attenuated TME hypoxia and enhanced therapeutic efficacy in vivo
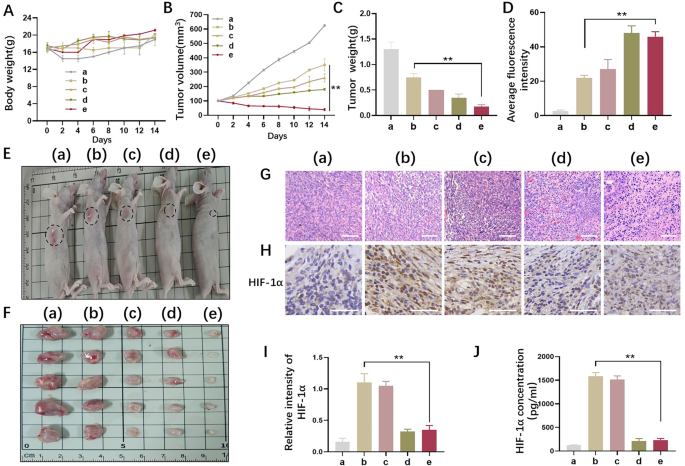
Impressed by the effectiveness of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA mixed with RT from our in vitro outcomes, the therapeutic potential of twin sensitization of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA in vivo was additional investigated by intravenous administration. The tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice had been randomly divided into 5 teams: (a) management group, (b) RT alone group, (c) QT + RT group, (d) CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT group, and (e) C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group. As proven in Fig. 5A, there was no statistically important distinction in physique weight of mice among the many 5 teams after 14 days of therapy. Not solely that, sensitized nanoparticles didn’t have an effect on the survival of mice in every group. Notably, as proven in, the imply tumor quantity and tumor weight within the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA group had been the bottom amongst all 5 teams (Fig. 5B C), suggesting that the synergistic impact of the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA twin sensitizing nanoparticles enhanced the efficacy of RT and supplied a bonus in tumor eradication.
A549 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice had been injected intravenously with C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. The tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice had been randomly divided into 5 teams: (a) management group, (b) RT alone group, (c) QT + RT group, (d) CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT group, and (e) C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group. (A) Physique weight of A549 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice in every group over 14 days after therapy. (B) Tumor weights of various teams in A549 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice. (C) Tumor volumes of various teams in A549 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice. (D) ROS ranges in tumor tissue after therapy in numerous teams. (E-F) Tumors had been collected from 5 totally different teams 14 days after totally different remedies. The photographs of the tumors are displayed. (G) Consultant hematoxylin-eosin staining in NSCLC tissue in 5 teams. Scale bar: 100 μm. (H-I) Consultant HIF-1α immunohistochemical staining and relative expression depth had been noticed within the 5 teams of tumor tissues. Scale bar: 20 μm. (J) The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of HIF-1α in 5 teams in tumor tissue. **P < 0.01
Radiation generates a big quantity of ROS in RT, which may straight or not directly trigger DNA injury and cell apoptosis, thereby disrupting the expansion and metastasis of most cancers cells. Moreover, ROS can induce a cascade of sign pathways and inflammatory reactions, which additional improve the therapeutic impact. Due to this fact, ROS performs a essential position in RT. Utilizing circulate cytometry, ROS ranges had been measured in numerous tumor tissues. The outcomes confirmed that the relative fluorescence intensities within the management group, RT group, and QT + RT group had been 2.1 ± 1, 20.3 ± 1.7, and 23.1 ± 3.6, respectively. The ROS content material within the CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT group and C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group was considerably larger than that of the RT group (P < 0.01) (Fig. 5D).
In contrast with the management group, the tumor progress inhibition values had been 27.5% and 36.8% within the QT + RT and CeO2@ZIF-8-HA + RT teams, respectively. And extra considerably, the tumor progress inhibition worth of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA + RT group reached 77.3%, in comparison with the RT group. Accordingly, the final tumor specimens additionally confirmed such modifications, as proven in Fig. 5E and F. The sensitizing impact of radiotherapy was most noticeable within the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA group. Subsequent, hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining was used to evaluate the radiosensitizing impact of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA (Fig. 5G). Tumor necrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration had been considerably elevated within the RT group, QT group and CeO2@ZIF-8-HA group in comparison with the management group. Extra important elevated necrosis, mobile alterations, and nuclear condensation had been noticed within the C/Q@ZIF-8-HA group. These outcomes counsel that this twin sensitization technique can enhance the effectiveness of radiation remedy for tumors.
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a key transcriptional regulator that mediates the mobile hypoxic response. Below normoxic circumstances HIF-1α is liable to enzymatic degradation; however underneath hypoxic circumstances, HIF-1α protein stays extremely lively in tumors. Bettering TME hypoxia is the important thing to attaining tumor radiosensitization. To detect the oxygenating potential of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA in vivo, we examined the expression of HIF-1α by immunohistochemistry assay and ELISA assay. As proven in Fig. 5H and I, HIF-1α expression was low in group a (wild-type A549) and considerably elevated in A549 cells after X-ray irradiation, suggesting that hypoxia is a typical function of tumor cell resistance to RT and a essential consider radiosensitization. Furthermore, the expression of HIF-1α in X-ray irradiated A549 cells was considerably lowered after therapy with C/Q@ZIF-8-HA. We additional obtained outcomes just like immunohistochemistry assay by detecting the expression of HIF-1α in tumors by means of ELISA assay (Fig. 5J).
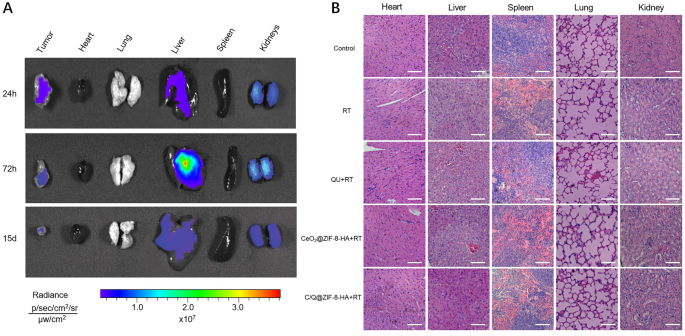
Evaluating the protection of nanoparticles in biomedical functions is crucial. To research the biodistribution of nanoparticles, C/Q@ZIF-8-HA was injected into tumor-bearing mice. Animals had been sacrificed at designated time factors after injection, and the fluorescence depth of Cy5 in remoted tissues was measured. As proven in Fig. 6A, the fluorescence depth was weak within the coronary heart, lungs, and spleen, whereas comparatively excessive within the tumor, liver, and kidneys. Subsequent, we utilized H&E staining to evaluate the potential organ toxicity and deposition of nanoparticles in essential organs. Mice had been sacrificed 14 days after nanoparticles injection, and coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney tissues had been taken for histological remark and evaluation. As proven in Fig. 6B, histopathological evaluation of the most important organs confirmed that C/Q@ZIF-8-HA injection didn’t lead to important pathological modifications in comparison with different therapy teams, indicating its favorable biocompatibility.
Within the histopathological analysis, not one of the 4 therapy teams precipitated pathological modifications in comparison with the management group. In comparison with extra studied tumors, akin to cervical, prostate and nasopharyngeal cancers, NSCLC is inherently troublesome to research as a result of it’s typically situated deep within the physique cavity, reasonably than on the floor, and native injection is troublesome to realize. Therefore, our research evaluated the concentrating on and security of intravenous administration of C/Q@ZIF-8-HA, and the outcomes counsel its potential for intravenous administration in NSCLC. Lastly, C/Q@ZIF-8-HA not solely improves native tumor management, but additionally reduces the dose of RT with out compromising the tumor suppression impact. Decreasing the radiation dose might result in decrease toxicity and higher immune system safety, thus growing the potential for antitumor immunity.