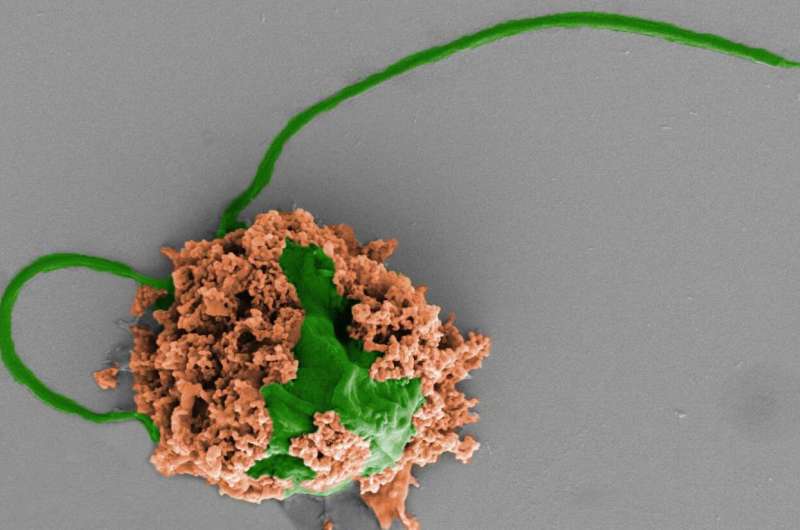
Nanoengineers on the College of California San Diego have developed microscopic robots, referred to as microrobots, that may swim round within the lungs, ship medicine and be used to clear up life-threatening instances of bacterial pneumonia.
In mice, the microrobots safely eradicated pneumonia-causing micro organism within the lungs and resulted in 100% survival. In contrast, untreated mice all died inside three days after an infection.
The outcomes are revealed Sept. 22 in Nature Supplies.
The microrobots are made from algae cells whose surfaces are speckled with antibiotic-filled nanoparticles. The algae present motion, which permits the microrobots to swim round and ship antibiotics on to extra micro organism within the lungs. The nanoparticles containing the antibiotics are made from tiny biodegradable polymer spheres which can be coated with the cell membranes of neutrophils, that are a sort of white blood cell. What’s particular about these cell membranes is that they take up and neutralize inflammatory molecules produced by micro organism and the physique’s immune system. This provides the microrobots the flexibility to scale back dangerous irritation, which in flip makes them more practical at preventing lung an infection.
The work is a joint effort between the labs of nanoengineering professors Joseph Wang and Liangfang Zhang, each on the UC San Diego Jacobs Faculty of Engineering. Wang is a world chief within the subject of micro- and nanorobotics analysis, whereas Zhang is a world chief in growing cell-mimicking nanoparticles for treating infections and illnesses. Collectively, they’ve pioneered the event of tiny drug-delivering robots that may be safely utilized in stay animals to deal with bacterial infections within the abdomen and blood. Treating bacterial lung infections is the newest of their line of labor.
“Our purpose is to do focused drug supply into more difficult components of the physique, just like the lungs. And we need to do it in a method that’s protected, straightforward, biocompatible and lengthy lasting,” stated Zhang. “That’s what we have demonstrated on this work.”
The crew used the microrobots to deal with mice with an acute and doubtlessly deadly type of pneumonia brought on by the micro organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This type of pneumonia generally impacts sufferers who obtain mechanical air flow within the intensive care unit. The researchers administered the microrobots to the lungs of the mice by a tube inserted within the windpipe. The infections totally cleared up after one week. All mice handled with the microrobots survived previous 30 days, whereas untreated mice died inside three days.
Therapy with the microrobots was additionally more practical than an IV injection of antibiotics into the bloodstream. The latter required a dose of antibiotics that was 3000 instances greater than that used within the microrobots to attain the identical impact. For comparability, a dose of microrobots supplied 500 nanograms of antibiotics per mouse, whereas an IV injection supplied 1.644 milligrams of antibiotics per mouse.
The crew’s method is so efficient as a result of it places the medicine proper the place it must go relatively than diffusing it by the remainder of the physique.
“These outcomes present how focused drug supply mixed with energetic motion from the microalgae improves therapeutic efficacy,” stated Wang.
“With an IV injection, typically solely a really small fraction of antibiotics will get into the lungs. That is why many present antibiotic remedies for pneumonia do not work in addition to wanted, resulting in very excessive mortality charges within the sickest sufferers,” stated Victor Nizet, professor at UC San Diego Faculty of Medication and Skaggs Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, who’s a co-author on the examine and a physician-scientist collaborator of Wang and Zhang. “Based mostly on these mouse information, we see that the microrobots may doubtlessly enhance antibiotic penetration to kill bacterial pathogens and save extra sufferers’ lives.”
And if the considered placing algae cells in your lungs makes you squeamish, the researchers say that this method is protected. After therapy, the physique’s immune cells effectively digest the algae, together with any remaining nanoparticles. “Nothing poisonous is left behind,” stated Wang.
The work remains to be on the proof-of-concept stage. The crew plans to do extra fundamental analysis to grasp precisely how the microrobots work together with the immune system. Subsequent steps additionally embody research to validate the microrobot therapy and scaling it up earlier than testing it in bigger animals and ultimately, in people.
“We’re pushing the boundary additional within the subject of focused drug supply,” stated Zhang.
The analysis paper is titled “Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic supply to deal with acute bacterial pneumonia.”
Liangfang Zhang, Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic supply to deal with acute bacterial pneumonia, Nature Supplies (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41563-022-01360-9. www.nature.com/articles/s41563-022-01360-9
Quotation:
Swimming nanorobots deal with lethal pneumonia in mice (2022, September 22)
retrieved 22 September 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-09-nanorobots-deadly-pneumonia-mice.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.


