A crew of researchers from the ITACA Institute of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the Analysis Institute of Chemical Expertise, a joint middle of the Spanish Nationwide Analysis Council (CSIC) and the UPV, has found a brand new technique for the manufacture of metallic nanocatalysts that’s extra sustainable and economical.
With nice potential within the industrial sector, the strategy would contribute to the decarbonization of business. The work has been revealed within the journal ACS Nano.
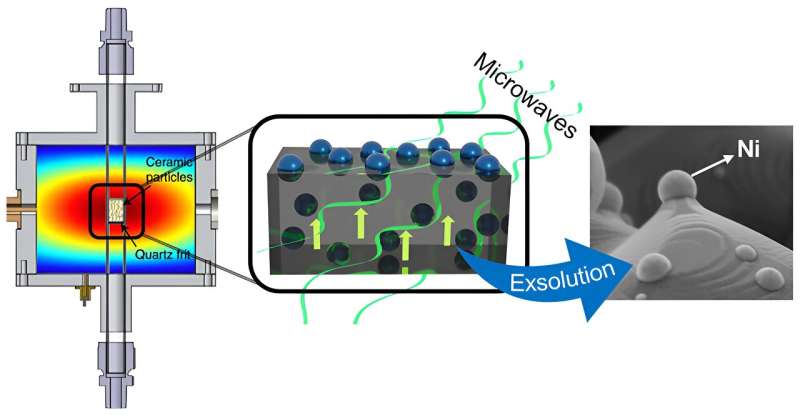
This new technique is predicated on the exsolution course of activated by microwave radiation. Exsolution is a technique of producing metallic nanoparticles on the floor of ceramic supplies. “At elevated temperatures and in a lowering ambiance (often hydrogen), metallic atoms migrate from the construction of the fabric to its floor, forming metallic nanoparticles anchored to the floor. This anchoring considerably will increase the energy and stability of those nanoparticles, which positively impacts the effectivity of those catalysts,” explains Beatriz García Baños, a researcher within the Microwave Space of the ITACA Institute on the UPV.
Within the examine, the UPV and CSIC researchers have proven that because of microwave radiation, this course of could be carried out at extra reasonable temperatures and with out the necessity to use lowering atmospheres.
“On this manner, lively nickel nanocatalysts could be produced in a extra energy-efficient exsolution course of. These catalysts have been confirmed to be lively and steady for the response of CO manufacturing from CO2, acquiring a product of business curiosity and contributing to the decarbonization of the sector,” says Alfonso Juan Carrillo Del Teso, researcher of the Vitality Conversion and Storage Group of the ITQ.
The exsolution course of demonstrated in nickel nanoparticles has been carried out at temperatures of about 400ºC and publicity instances of some seconds, whereas the traditional exsolution process in these supplies happens at temperatures of 900ºC, with instances of about 10 hours. As well as, this know-how permits exsolution to be carried out with out utilizing hydrogen.
“For all these causes, we enhance the sustainability of the method. Furthermore, by acquiring the catalysts at milder temperatures and shorter publicity instances, we scale back the prices of the method, which can also be influenced by not having to make use of hydrogen as a lowering fuel,” provides Beatriz García Baños.
Purposes
The method developed by the UPV and CSIC crew is primarily supposed for high-temperature catalytic procedures for storing and changing renewable vitality. It may be utilized to biogas reforming reactions for the manufacturing of synthesis fuel (precursor of liquid fuels), CO2 hydrogenation reactions relevant to Energy-to-X techniques, and functionalizing electrodes for gas cells and/or high-temperature electrolyzers.
Extra data:
Andrés López-García et al, Microwave-Pushed Exsolution of Ni Nanoparticles in A-Web site Poor Perovskites, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c08534
Supplied by
Universitat Politècnica de València
Quotation:
Scientists uncover new technique for producing metallic nanoparticles to make use of as catalysts (2023, December 29)
retrieved 30 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-scientists-method-generating-metal-nanoparticles.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.


