Remodeling human stem cells into embryo-like constructions was beforehand unthinkable.
But seemingly in a single day, a number of groups printed preliminary outcomes that attain in direction of this aim. Every workforce has a singular recipe for producing lab-grown embryoids, blobs of cells that mimic points of the earliest phases of human life.
Though typically dubbed “artificial embryos,” they’re something however. The 3D mobile clumps are extremely intricate, with some starting to diverge into lineages of cells wanted to help progress of the embryo right into a fetus. But the fashions are removed from their sperm-meets-egg real-life counterparts.
Every embryo-like construction—scientists haven’t but settled on calling them “embryoids” or “stembryos”—partially replicates genetic, molecular, and mobile points of a human embryo as much as roughly two weeks after implantation. However the constructions all disintegrate after a number of weeks. They will’t be transferred into an precise womb, and positively can’t develop right into a viable fetus.
The controversial subject isn’t aiming to engineer human embryos from scratch. Reasonably, it hopes to shine a lightweight on the black field of the primary weeks after human conception, and probably provide a lifeline to {couples} with infertility or to fight miscarriage.
“That is the stage…the place most pregnancies fail for unknown causes,” stated Dr. Berna Sozen at Yale College, who led one effort printed in Nature. “Our mannequin platform captures a particular snapshot of human growth about which we all know maybe the least.”
The Reproductive Black Field
The primary weeks after conception are the last word enigma in human growth.
We all know the fundamentals: a single fertilized egg expands to roughly 200 cells, forming a hole blob that attaches to the uterine wall, a course of referred to as implantation.
The following few days lay the muse for growth. The embryo quickly grows into three numerous layers, every with its personal distinct cell lineage. One varieties the “core” of the physique, the epiblast, which incorporates cells that make up the embryo. The second is the hypoblast, which helps orient the principle axes of the embryo—put merely, sketching the general design of the human physique—and additional varieties the supportive yolk sac. Lastly, there’s the trophoblast, which supplies rise to the placenta to supply vitamins for the rising fetus.
These are solely broad brushstrokes. As a result of moral, technological, and regulatory restrictions, we all know little of the intricacies behind these processes, together with when and the way they go improper. It’s why scientists have been striving for a extra ethically acceptable alternative: embryo-like fashions produced from human stem cells. Two groups got here shut in 2021, reconstructing essential occasions just like the primary 4 days after fertilization. The last word aim is to imitate all three lineages—the holy grail for reproductive analysis—and probably push the developmental time-frame additional alongside.
The query is, how?
Cracking the Black Field
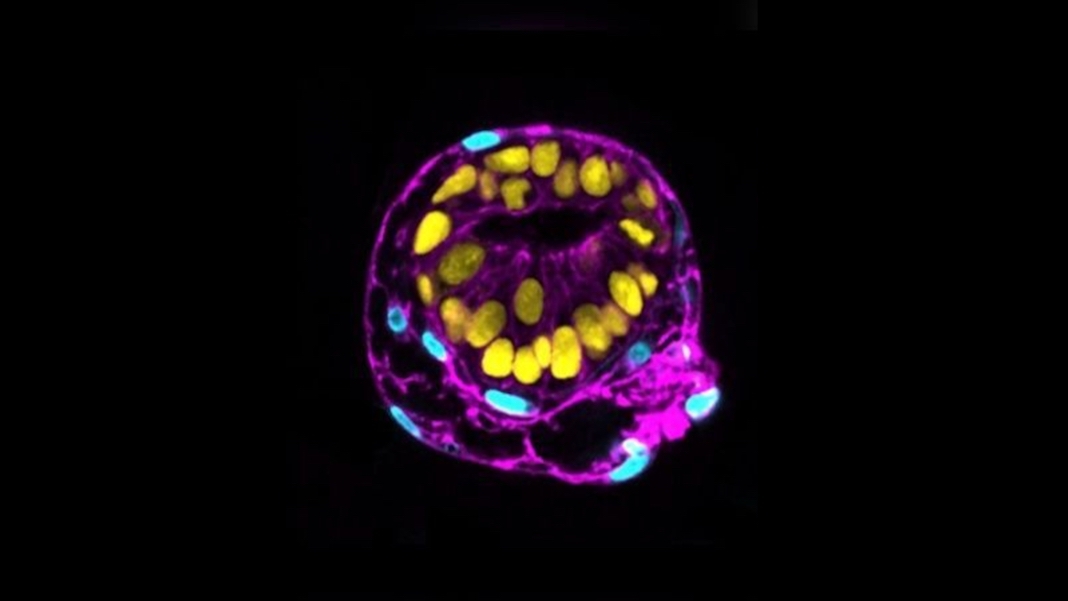
Sozen’s workforce began with human pluripotent stem cells. These multi-taskers fortunately renew themselves and might turn into virtually each single cell kind within the physique.
When bathed in a chemical soup, the cells spontaneously organized into 3D constructions inside 48 hours. The recipe was the key contact: usually, the cells turn into disorganized aggregates that hardly resemble an early human embryo. Right here, nevertheless, the cells expressed protein markers and fashioned constructions that resembled early-stage epiblasts and hypoblasts after implantation, all of the whereas adopting an embryo’s typical spherical form.
To additional check the cells’ operate, the workforce injected the lab-grown hypoblast cells—ones that normally assist orient the physique’s blueprint—into early mouse embryos. Lower than a 3rd took maintain. Nevertheless, people who did built-in into their new hosts, and remained after the chimeric embryos have been transplanted right into a surrogate (no mouse infants have been born).
Digging deeper, Sozen’s workforce examined gene expression in single cells from the embryo fashions. The outcomes additional verified that their recipe cooked up two cell lineages, with their “extra-embryoids” exhibiting genetic patterns strikingly just like their human embryo counterparts, however missing indicators of forming the placenta. The blobs additionally weren’t capable of seize the epigenetic panorama—the management over gene expression with out altering its sequence—that’s extremely outstanding throughout implantation.
Nonetheless, the workforce is pleased with their outcomes. The platform, they clarify, makes use of just one cell kind and is scalable and versatile. It’ll assist “dissect the mechanisms underpinning early destiny selections occurring at inaccessible phases of our species’ growth,” and probably the origins of developmental problems, stated research writer Monique Pedroza.
The work “is a exceptional research that has been carried out with nice care,” stated Dr. Roger Sturmey on the College of Manchester, who was not concerned within the work. Sturmey can also be the chair for the G-SCBEM (Governance of Stem Cell-Based mostly Embryo Fashions) Pointers Working Group, which goals to ascertain moral and regulatory pointers for the more and more heated subject. “This work describes an especially vital mannequin to help our pursuit of understanding the mobile and molecular occasions that happen across the time that the early embryo implants into the uterus in early being pregnant,” he stated.
A Multiverse of Strategies
In the meantime, in a sister paper printed in Nature, embryoid veteran Dr. Magdelena Zernicka-Goetz on the College of Cambridge—a earlier advisor to Sozen—took a special technique. Reasonably than altering the exterior bathtub recipe, they instantly tapped into the genetic program guiding embryoid growth.
Zernicka-Goetz isn’t any stranger to engineering embryo-like constructions from stem cells. Again in 2022, her lab made headlines for constructing the beginnings of an embryoid utilizing mouse embryonic stem cells (as did one other main knowledgeable, Dr. Jacob Hanna on the Weizmann Institute in Israel). The ensuing construction contained all three potential cell lineages and roughly resembled their pure counterparts at 8.5 days outdated.
The brand new research adopts an analogous technique. The secret is transcription components, a gaggle of proteins that assist management how genes activate or off. The aim, defined the workforce, is to over-express sure components and push cells into “genetic packages” that assist kind totally different cell lineages throughout growth.
The technique labored—however solely partially. By genetically including the transcription components, the mannequin skipped roughly per week of “regular” growth to kind a ball-like construction just like a post-implantation embryo. The embryoids self-organized right into a primitive physique axis—the head-to-toe patterning essential to this developmental stage. Additional deep dives into the molecular mechanisms recognized a number of biomolecules that assist orchestrate this patterning.
Though the technique didn’t kind the trophoblast—the elusive golden goose lineage that finally varieties the placenta—the outcomes “spotlight the worth” of utilizing embryoids to review how embryonic and supporting tissues work together at an early stage, the authors stated.
Gradual and Regular?
Along with the 2 printed papers, different giants within the subject have put forth their very own gambit in direction of an correct human embryo imitation on a preprint server.
Hanna, who led an effort to construct an early mouse embryo, describes a technique to realize the identical for human cells—forming embryoids that mimic a 14-day-old pure human embryo, together with the elusive trophoblast. In the meantime, Dr. Mo Ebrahimkhani on the College of Pittsburgh describes a reprogramming technique utilizing human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and rewired with an artificial gene circuit to develop each the embryo and its surrounding tissues. In keeping with Stat, the research are at the moment beneath peer evaluate.
No doubt, the race to construct embryoids that resemble the true factor is turning into more and more heated. The query is: the place’s the crimson line?
In Sturmey’s (the chair of G-SCBEM’s Pointers Working Group) opinion, we’d like solutions quickly. The group, led by scientists and authorized and bioethics specialists, is main the cost to ascertain an moral path ahead for embryoid analysis. Though primarily established for UK analysis, the following pointers pave the trail for a global settlement.
G-SCBEM goals to publish their first unified proposal in November and welcomes steering from others within the subject. It might be a tough promote; competitors within the subject is fierce. However establishing guidelines for such a posh and ethically ambiguous subject, particularly if public opinion may be included, will assist in the long term—and hopefully keep away from one other CRISPR child scandal.
The present race “additional illustrates the need for a coherent set of pointers supporting work of this nature,” stated Sturmey.
Picture Credit score: Monique Pedroza, Ipek Gassaloglu, Berna Sozen/Yale College