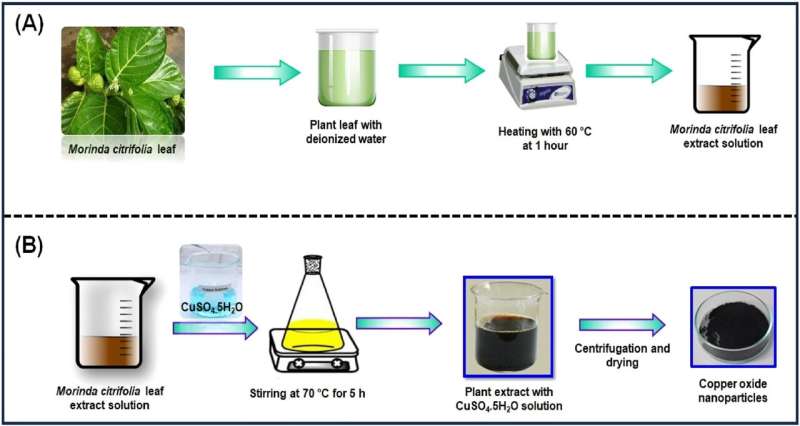
Researchers have described a inexperienced methodology for acquiring copper oxide nanoparticles from the noni plant (Morinda citrifolia), widespread in Asia. These copper oxide nanoparticles exhibit bactericidal properties. Furthermore, antibacterial exercise relies on the bodily properties of the particles—dimension, construction, and focus of copper oxide.
Biochemists are learning numerous methods to acquire such particles. Chemical and bodily strategies are recognized, however they require poisonous supplies. Due to this fact, the trendy method is to make use of organic strategies, that’s, acquiring nanoparticles from crops, micro organism, or fungi.
A RUDN Unviersity biotechnologist and colleagues from India, Korea, and Saudi Arabia have discovered a inexperienced methodology for producing copper oxide nanoparticles, and their findings are printed within the journal Scientific Experiences.
“Copper oxide nanoparticles are of curiosity in lots of areas of science. Biosynthetic nanoparticles are produced by way of organic processes from micro organism, fungi, or plant extracts. The significance of such nanoparticles lies of their potential for sustainable, efficient, and biocompatible options in well being care and environmental safety, in addition to in supplies science and vitality,” mentioned Alexandre Vetcher, Ph.D., Deputy Director of the Nanotechnology Middle at RUDN College.
Noni grows within the South Pacific area. It’s a tall plant with edible fruits. Biologists took an extract of noni leaves and combined it with an aqueous answer of copper sulfate. A catalyst, sodium hydroxide, was additionally used. The function of noni extract on this course of is the stabilization of nanoparticles. The ensuing nanoparticles had been examined for exercise towards gram-positive and gram-negative micro organism, in addition to towards fungi. The antimicrobial impact was in contrast with the broad-spectrum antibiotic chloramphenicol.
The end result was secure spherical copper oxide nanoparticles ranging in dimension from 20 to 50 nanometers. They had been lively towards Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and three forms of fungi (Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger, and Penicillium frequentans). Particles obtained from options through which the focus of noni extract was 25 microliters confirmed higher outcomes, similar to chloramphenicol.
“The ensuing copper oxide nanoparticles can be utilized in biomedicine, the manufacturing of gas cells, batteries, and meals storage. Nevertheless, extra analysis is required to reduce toxicity whereas sustaining their organic effectiveness. It will contribute to the biomedical use of particles,” famous Dr. Vetcher.
Extra info:
Manogar Priya et al, Inexperienced synthesis, characterization, antibacterial, and antifungal exercise of copper oxide nanoparticles derived from Morinda citrifolia leaf extract, Scientific Experiences (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-46002-5
Supplied by
RUDN College
Quotation:
Scientists develop inexperienced methodology for producing bactericidal copper oxide nanoparticles from noni plant (2024, January 10)
retrieved 11 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-scientists-green-method-bactericidal-copper.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


