
Peter is an IT supervisor for a know-how producer that acquired hit with a Russian ransomware pressure referred to as “Zeppelin” in Might 2020. He’d been on the job lower than six months, and due to the best way his predecessor architected issues, the corporate’s knowledge backups additionally had been encrypted by Zeppelin. After two weeks of stalling their extortionists, Peter’s bosses had been able to capitulate and pay the ransom demand. Then got here the unlikely name from an FBI agent. “Don’t pay,” the agent mentioned. “We’ve discovered somebody who can crack the encryption.”
Peter, who spoke candidly concerning the assault on situation of anonymity, mentioned the FBI advised him to contact a cybersecurity consulting agency in New Jersey referred to as Unit 221B, and particularly its founder — Lance James. Zeppelin sprang onto the crimeware scene in December 2019, nevertheless it wasn’t lengthy earlier than James found a number of vulnerabilities within the malware’s encryption routines that allowed him to brute-force the decryption keys in a matter of hours, utilizing practically 100 cloud pc servers.
In an interview with KrebsOnSecurity, James mentioned Unit 221B was cautious of promoting its capability to crack Zeppelin ransomware keys as a result of it didn’t wish to tip its hand to Zeppelin’s creators, who had been more likely to modify their file encryption strategy in the event that they detected it was one way or the other being bypassed.
This isn’t an idle concern. There are a number of examples of ransomware teams doing simply that after safety researchers crowed about discovering vulnerabilities of their ransomware code.
“The minute you announce you’ve acquired a decryptor for some ransomware, they alter up the code,” James mentioned.
However he mentioned the Zeppelin group seems to have stopped spreading their ransomware code progressively over the previous 12 months, presumably as a result of Unit 221B’s referrals from the FBI allow them to quietly assist practically two dozen sufferer organizations get well with out paying their extortionists.
In a weblog submit printed at this time to coincide with a Black Hat speak on their discoveries, James and co-author Joel Lathrop mentioned they had been motivated to crack Zeppelin after the ransomware gang began attacking nonprofit and charity organizations.
“What motivated us essentially the most through the leadup to our motion was the concentrating on of homeless shelters, nonprofits and charity organizations,” the 2 wrote. “These mindless acts of concentrating on those that are unable to reply are the motivation for this analysis, evaluation, instruments, and weblog submit. A basic Unit 221B rule of thumb round our workplaces is: Don’t [REDACTED] with the homeless or sick! It is going to merely set off our ADHD and we’ll get into that hyper-focus mode that’s good should you’re a superb man, however not so nice in case you are an ***gap.”
The researchers mentioned their break got here once they understood that whereas Zeppelin used three various kinds of encryption keys to encrypt recordsdata, they may undo the entire scheme by factoring or computing simply considered one of them: An ephemeral RSA-512 public key that’s randomly generated on every machine it infects.
“If we are able to get well the RSA-512 Public Key from the registry, we are able to crack it and get the 256-bit AES Key that encrypts the recordsdata!” they wrote. “The problem was that they delete the [public key] as soon as the recordsdata are absolutely encrypted. Reminiscence evaluation gave us a few 5-minute window after recordsdata had been encrypted to retrieve this public key.”
Unit 221B in the end constructed a “Stay CD” model of Linux that victims might run on contaminated programs to extract that RSA-512 key. From there, they’d load the keys right into a cluster of 800 CPUs donated by internet hosting large Digital Ocean that may then begin cracking them. The corporate additionally used that very same donated infrastructure to assist victims decrypt their knowledge utilizing the recovered keys.
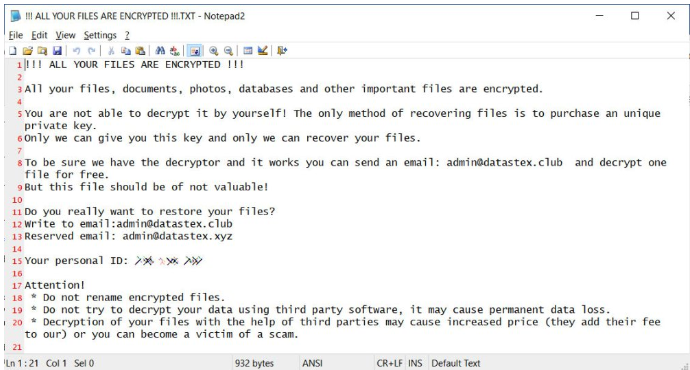
A typical Zeppelin ransomware observe.
Jon is one other grateful Zeppelin ransomware sufferer who was aided by Unit 221B’s decryption efforts. Like Peter, Jon requested that his final identify and that of his employer be omitted from the story, however he’s in control of IT for a mid-sized managed service supplier that acquired hit with Zeppelin in July 2020.
The attackers that savaged Jon’s firm managed to phish credentials and a multi-factor authentication token for some instruments the corporate used to assist clients, and in brief order they’d seized management over the servers and backups for a healthcare supplier buyer.
Jon mentioned his firm was reluctant to pay a ransom partly as a result of it wasn’t clear from the hackers’ calls for whether or not the ransom quantity they demanded would supply a key to unlock all programs, and that it might accomplish that safely.
“They need you to unlock your knowledge with their software program, however you may’t belief that,” Jon mentioned. “You wish to use your personal software program or another person who’s trusted to do it.”
In August 2022, the FBI and the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) issued a joint warning on Zeppelin, saying the FBI had “noticed cases the place Zeppelin actors executed their malware a number of occasions inside a sufferer’s community, ensuing within the creation of various IDs or file extensions, for every occasion of an assault; this ends in the sufferer needing a number of distinctive decryption keys.”
The advisory says Zeppelin has attacked “a spread of companies and important infrastructure organizations, together with protection contractors, academic establishments, producers, know-how firms, and particularly organizations within the healthcare and medical industries. Zeppelin actors have been recognized to request ransom funds in Bitcoin, with preliminary quantities starting from a number of thousand {dollars} to over one million {dollars}.”
The FBI and CISA say the Zeppelin actors achieve entry to sufferer networks by exploiting weak Distant Desktop Protocol (RDP) credentials, exploiting SonicWall firewall vulnerabilities, and phishing campaigns. Previous to deploying Zeppelin ransomware, actors spend one to 2 weeks mapping or enumerating the sufferer community to determine knowledge enclaves, together with cloud storage and community backups, the alert notes.
Jon mentioned he felt so fortunate after connecting with James and listening to about their decryption work, that he toyed with the concept of shopping for a lottery ticket that day.
“This simply doesn’t normally occur,” Jon mentioned. “It’s one hundred pc like successful the lottery.”
By the point Jon’s firm acquired round to decrypting their knowledge, they had been compelled by regulators to show that no affected person knowledge had been exfiltrated from their programs. All advised, it took his employer two months to completely get well from the assault.
“I undoubtedly really feel like I used to be ill-prepared for this assault,” Jon mentioned. “One of many issues I’ve realized from that is the significance of forming your core group and having these individuals who know what their roles and duties are forward of time. Additionally, attempting to vet new distributors you’ve by no means met earlier than and construct belief relationships with them may be very troublesome to do when you have got clients down onerous now and so they’re ready on you to assist them get again up.”
A extra technical writeup on Unit 221B’s discoveries (cheekily titled “0XDEAD ZEPPELIN”) is offered right here.

