| Nov 12, 2022 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) Underneath the microscope, wholesome and unhealthy cells could be very tough to differentiate. Scientists use stains or fluorescent tags focusing on particular proteins to establish cell varieties, characterize their state, and research the impression of medicine and different therapies. Whereas its impression on medication has been transformational, the method has its limitations. For one, tagging cells is dear, time-consuming, and strongly depending on the researcher’s ability. On prime of that, the staining course of could be detrimental to the cells beneath investigation.
|
|
That’s why researchers have been growing alternative routes to rapidly and reliably display screen particular person cells. In a latest article printed within the journal Nature Photonics (“Stain-free identification of cell nuclei utilizing tomographic section microscopy in stream cytometry”), researchers from EPFL’s College of Engineering and colleagues from the Institute of Utilized Sciences & Clever Methods, CNR, in Pozzuoli, Italy, current a stain-free method able to precisely distinguishing particular areas inside residing cells.
|
|
Uniquely combining holographic imaging and microfluidics with neural network-based sign processing, the work paves the way in which for liquid biopsies for circulating tumor cell detection and high-throughput assays for drug testing.
|
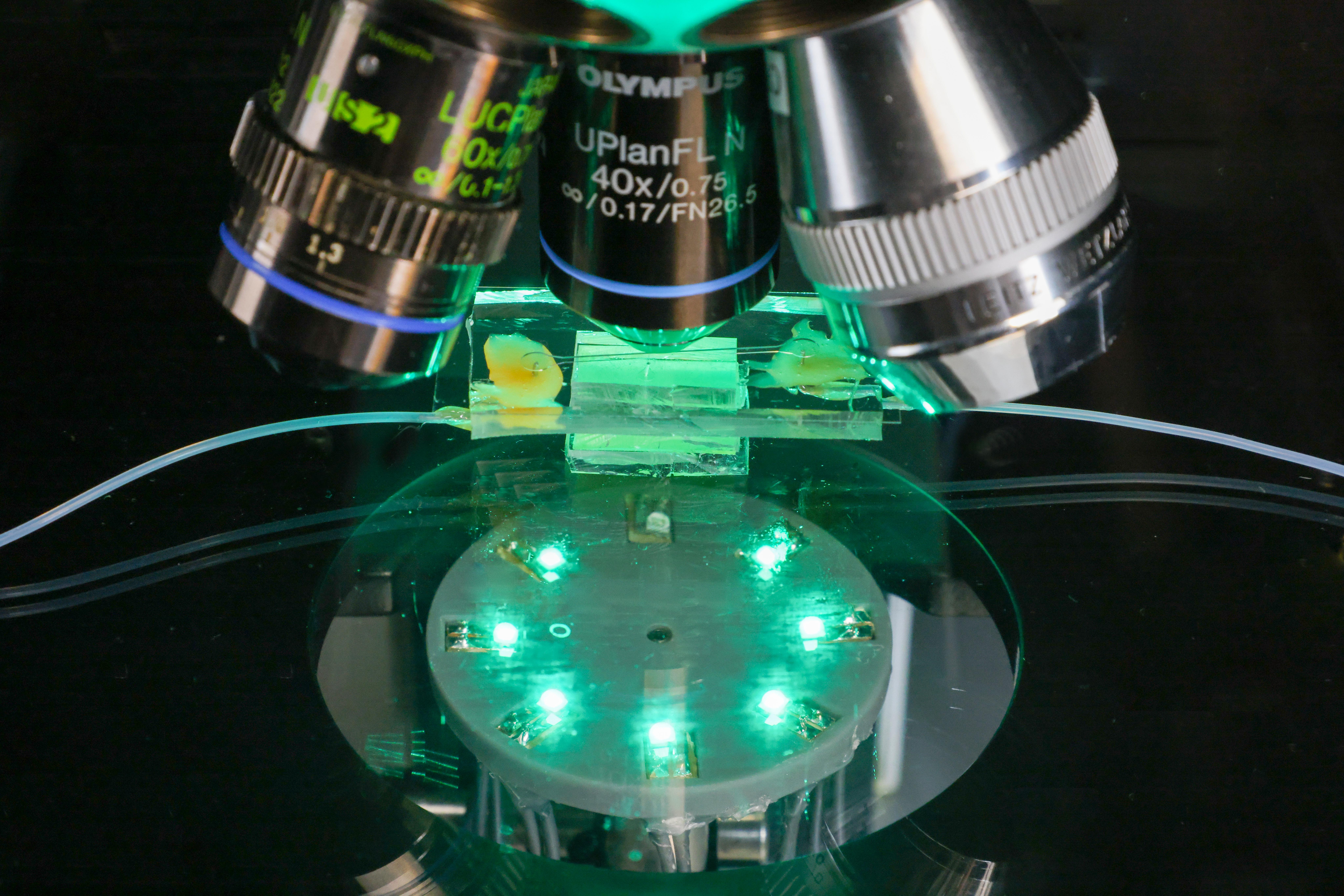 |
| The brand new methodology for 3 dimensional imaging of cells with out fluorescence staining. (Picture: Alain Herzog)
|
From the section delay to the refractive index
|
|
The research builds on studying tomography, a way beforehand developed by Demetri Psaltis and his crew on the EPFL Optics Laboratory. Moderately than utilizing a microscope to create a visible picture of the specimen beneath research, studying tomography depends on quantitative section imaging, a holographic imaging method that reveals the section delay incurred because the microscope’s gentle beam passes via the matter that makes up the cell.
|
|
Repeating this course of at a number of totally different angles and working the section information via a neural community allowed the researchers to generate 3D maps of the refractive index of every particular person voxel – every three-dimensional quantity resolved by the strategy. “The refractive index is influenced by the density of molecules and the fabric,” explains Psaltis. Growing the variety of iterations additional improved the accuracy of the refractive index distribution estimate.
|
Classifying mobile elements
|
|
Of their publication, Psaltis and his crew current how they overcame a long-standing limitation of quantitative section imaging approaches: the shortcoming to establish intracellular elements. “Utilizing a self-clustering method that teams voxels with an identical refractive index coupled with machine studying instruments allowed us to assemble the clusters into shapes that we may classify. Various kinds of nuclei, for instance, have totally different indices of refraction,” says Psaltis. Closing this hole paves the way in which for quantitative section imaging to ship insights beforehand solely obtainable utilizing fluorescence microscopy.
|
|
A second problem was growing a way to display screen cells that didn’t require immobilizing them. The answer to this problem got here from co-author Pietro Ferraro and his laboratory at CNR, who had huge expertise engaged on in-flow tomography utilizing lab-on-chip units. “The thought was to place the cells in a fluidic channel 50 to 100 microns throughout and let the stream velocity gradient within the channel rotate the cells,” says Psaltis. “By observing the cells as they tumble alongside the channel utilizing a stationary beam and detector, we are able to detect the section delay, estimate the orientation of the cell, and apply our studying tomography method to generate the 3D refractive index maps.”
|
|
“The achievable transverse decision is of half a micron to at least one micron,” says Psaltis. “We will’t detect particular person proteins, however we are able to see protein aggregates, which are typically tens of microns throughout. It additionally allow us to assess the dimensions of the nucleus and the define of the cell, which turns into much less clean when cells turn into cancerous.” The researchers validated their methodology by evaluating their findings with observations made utilizing confocal fluorescence microscopy, immediately’s gold commonplace in 3D mobile imaging.
|
Excessive-throughput screening of particular person cells
|
|
A necessary software of stain-free cell screening is liquid biopsies that enable the detection of circulating most cancers cells, used each to establish most cancers varieties in surgical procedure and as an early diagnostic device for most cancers metastasis.
|
|
One other is drug growth. Many ailments, corresponding to Parkinson’s, are related to cross-linked proteins. The method developed by Psaltis and his collaborators presents a extremely environment friendly, non-invasive strategy to consider the effectiveness of medicine designed to interrupt down these cross-linked proteins in real-time by repeatedly working handled cells via the imaging setup. In the identical approach, the method might be used to offer researchers new insights into the real-time results of pathogens on wholesome cells.
|
|
In accordance with Psaltis, future work will contain making use of machine studying instruments to extract biologically related info and concrete diagnoses from the estimated refractive index distribution.
|

