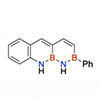
(Nanowerk Information) A workforce of researchers led by Professor Younger S. Park at UNIST’s Division of Chemistry has achieved a major breakthrough within the discipline of natural semiconductors. Their profitable synthesis and characterization of a novel molecule known as “BNBN anthracene” has opened up new prospects for the event of superior digital gadgets.
Natural semiconductors play a vital function in bettering the motion and lightweight properties of electrons in carbon-centered natural digital gadgets. The workforce’s analysis centered on enhancing the chemical range of those semiconductors by changing carbon-carbon (C−C) bonds with isoelectronic boron-nitrogen (B−N) bonds. This substitution permits for exact modulation of the digital properties with out vital structural adjustments.
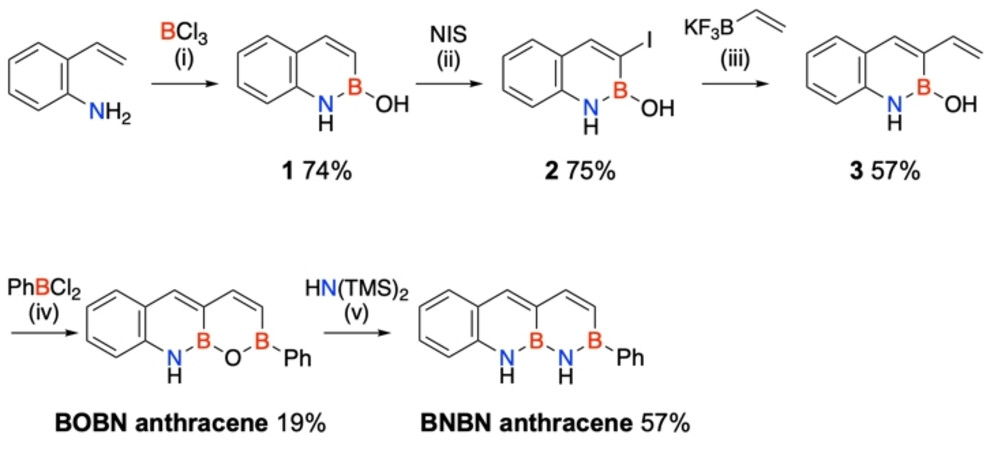 Schematic picture, displaying the syntheses of BOBN anthracene and BNBN anthracene. (Picture: UNIST)
The researchers efficiently synthesized the BNBN anthracene spinoff, which comprises a steady BNBN unit fashioned by changing the BOBN unit on the zigzag edge. In comparison with typical anthracene derivatives composed solely of carbon, the BNBN anthracene exhibited vital variations within the C−C bond size and a bigger highest occupied molecular orbital–lowest unoccupied molecular orbital vitality hole.
Along with its distinctive properties, the BNBN anthracene spinoff demonstrated promising potential for software in natural electronics. When used because the blue host in an natural light-emitting diode (OLED), the BOBN anthracene exhibited a remarkably low driving voltage of three.1V, together with increased effectivity when it comes to present utilization, vitality effectivity, and lightweight emission.
The analysis workforce additional confirmed the properties of the BNBN anthracene spinoff by finding out its crystal construction utilizing an X-ray diffractometer. This evaluation revealed structural adjustments, comparable to bonding size and angle, ensuing from the boron-nitrogen (BN) bonding.
Schematic picture, displaying the syntheses of BOBN anthracene and BNBN anthracene. (Picture: UNIST)
The researchers efficiently synthesized the BNBN anthracene spinoff, which comprises a steady BNBN unit fashioned by changing the BOBN unit on the zigzag edge. In comparison with typical anthracene derivatives composed solely of carbon, the BNBN anthracene exhibited vital variations within the C−C bond size and a bigger highest occupied molecular orbital–lowest unoccupied molecular orbital vitality hole.
Along with its distinctive properties, the BNBN anthracene spinoff demonstrated promising potential for software in natural electronics. When used because the blue host in an natural light-emitting diode (OLED), the BOBN anthracene exhibited a remarkably low driving voltage of three.1V, together with increased effectivity when it comes to present utilization, vitality effectivity, and lightweight emission.
The analysis workforce additional confirmed the properties of the BNBN anthracene spinoff by finding out its crystal construction utilizing an X-ray diffractometer. This evaluation revealed structural adjustments, comparable to bonding size and angle, ensuing from the boron-nitrogen (BN) bonding.
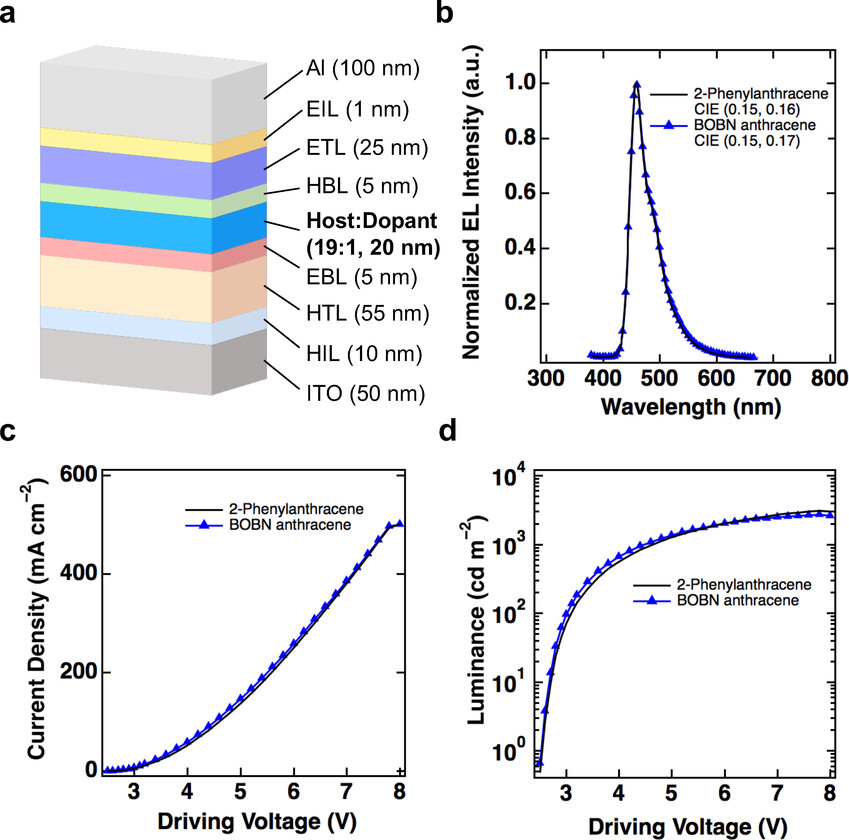 Traits of OLED gadgets utilizing BOBN anthracene (blue line) and 2-phenylanthracene (black line) because the blue host. (a) Machine structure of OLED. (b) Electroluminescence (EL) spectra of system recorded at 10 mA cm−2. (c) Present density–driving voltage traits. (d) Luminance–driving voltage traits. (Picture: UNIST)
“Our examine on anthracene, a kind of acene well known as an natural semiconductor, has laid the groundwork for future developments within the discipline,” commented Songhua Jeong (Mixed MS/Ph.D. Program of Chemistry, UNIST), the primary writer of this examine. “The continual BN bonding synthesized via this analysis holds nice potential for purposes in natural semiconductors.”
Professor Park emphasised the importance of this breakthrough, stating, “The synthesis and characterization of compounds with steady boron-nitrogen (BN) bonds contribute to basic analysis in chemistry. It offers a worthwhile software for synthesizing new compounds and controlling their digital properties.”
The analysis findings, which additionally contain the contributions of Professor Joonghan Kim’s workforce from the Catholic College of Korea, Professor Wonyoung Choe’s workforce from the Division of Chemistry at UNIST, and a analysis workforce from SFC Co., Ltd., have been revealed on-line in Angewande Chemie Worldwide Version (“Rising Chemical Range of B2N2 Anthracene Derivatives by Introducing Steady A number of Boron-Nitrogen Items”).
Traits of OLED gadgets utilizing BOBN anthracene (blue line) and 2-phenylanthracene (black line) because the blue host. (a) Machine structure of OLED. (b) Electroluminescence (EL) spectra of system recorded at 10 mA cm−2. (c) Present density–driving voltage traits. (d) Luminance–driving voltage traits. (Picture: UNIST)
“Our examine on anthracene, a kind of acene well known as an natural semiconductor, has laid the groundwork for future developments within the discipline,” commented Songhua Jeong (Mixed MS/Ph.D. Program of Chemistry, UNIST), the primary writer of this examine. “The continual BN bonding synthesized via this analysis holds nice potential for purposes in natural semiconductors.”
Professor Park emphasised the importance of this breakthrough, stating, “The synthesis and characterization of compounds with steady boron-nitrogen (BN) bonds contribute to basic analysis in chemistry. It offers a worthwhile software for synthesizing new compounds and controlling their digital properties.”
The analysis findings, which additionally contain the contributions of Professor Joonghan Kim’s workforce from the Catholic College of Korea, Professor Wonyoung Choe’s workforce from the Division of Chemistry at UNIST, and a analysis workforce from SFC Co., Ltd., have been revealed on-line in Angewande Chemie Worldwide Version (“Rising Chemical Range of B2N2 Anthracene Derivatives by Introducing Steady A number of Boron-Nitrogen Items”).