(Nanowerk Information) The demand to shrink the dimensions of semiconductors coupled with the issue of the warmth generated on the sizzling spots of the units not being successfully dispersed has negatively affected the reliability and sturdiness of contemporary units. Current thermal administration applied sciences haven’t been as much as the duty. Thus, the invention of a brand new means of dispersing warmth through the use of floor waves generated on the skinny metallic movies over the substrate is a crucial breakthrough.
KAIST introduced that Professor Bong Jae Lee’s analysis staff within the Division of Mechanical Engineering succeeded in measuring a newly noticed transference of warmth induced by ‘floor plasmon polariton’ (SPP) in a skinny metallic movie deposited on a substrate for the primary time on this planet.
The research was printed in Bodily Evaluate Letters (“Boosting Thermal Conductivity by Floor Plasmon Polaritons Propagating alongside a Skinny Ti Movie”).
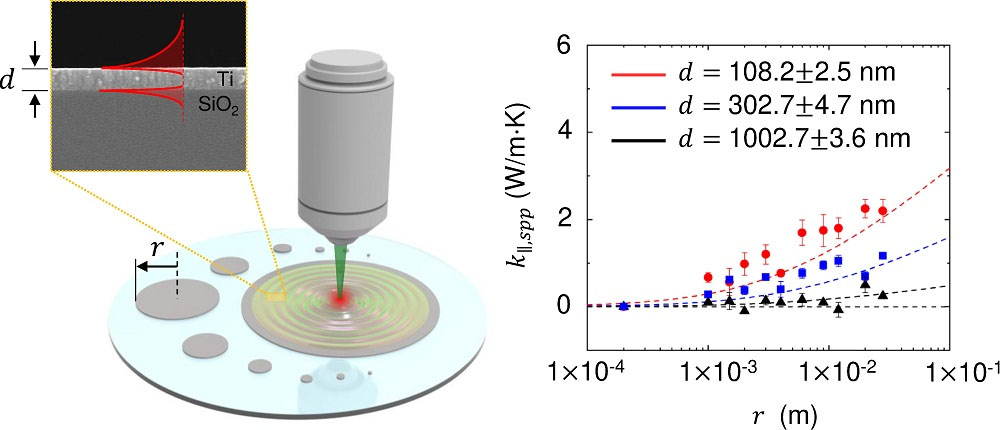 Schematic diagram of the precept of measuring the thermal conductivity of skinny Titanium (TI) movies and the thermal conductivity of floor plasmon polariton measured on the Ti movie. (Picture: KAIST)
Floor plasmon polariton (SPP) refers to a floor wave fashioned on the floor of a metallic because of robust interplay between the electromagnetic subject on the interface between the dielectric and the metallic and the free electrons on the metallic floor and comparable collectively vibrating particles.
The analysis staff utilized floor plasmon polaritons (SPP), that are floor waves generated on the metal-dielectric interface, to enhance thermal diffusion in nanoscale skinny metallic movies. Since this new warmth switch mode happens when a skinny movie of metallic is deposited on a substrate, it’s extremely usable within the system manufacturing course of and has the benefit of having the ability to be manufactured over a big space. The analysis staff confirmed that the thermal conductivity elevated by about 25% because of floor waves generated over a 100-nm-thick titanium (Ti) movie with a radius of about 3 cm.
KAIST Professor Bong Jae Lee, who led the analysis, stated, “The importance of this analysis is {that a} new warmth switch mode utilizing floor waves over a skinny metallic movie deposited on a substrate with low processing problem was recognized for the primary time on this planet. It may be utilized as a nanoscale warmth spreader to effectively dissipate warmth close to the recent spots for simply overheatable semiconductor units.”
The end result has nice implications for the event of high-performance semiconductor units sooner or later in that it may be utilized to quickly dissipate warmth on a nanoscale skinny movie. Specifically, this new warmth switch mode recognized by the analysis staff is predicted to unravel the basic drawback of thermal administration in semiconductor units because it permits much more efficient warmth switch at nanoscale thickness whereas the thermal conductivity of the skinny movie often decreases as a result of boundary scattering impact.
Schematic diagram of the precept of measuring the thermal conductivity of skinny Titanium (TI) movies and the thermal conductivity of floor plasmon polariton measured on the Ti movie. (Picture: KAIST)
Floor plasmon polariton (SPP) refers to a floor wave fashioned on the floor of a metallic because of robust interplay between the electromagnetic subject on the interface between the dielectric and the metallic and the free electrons on the metallic floor and comparable collectively vibrating particles.
The analysis staff utilized floor plasmon polaritons (SPP), that are floor waves generated on the metal-dielectric interface, to enhance thermal diffusion in nanoscale skinny metallic movies. Since this new warmth switch mode happens when a skinny movie of metallic is deposited on a substrate, it’s extremely usable within the system manufacturing course of and has the benefit of having the ability to be manufactured over a big space. The analysis staff confirmed that the thermal conductivity elevated by about 25% because of floor waves generated over a 100-nm-thick titanium (Ti) movie with a radius of about 3 cm.
KAIST Professor Bong Jae Lee, who led the analysis, stated, “The importance of this analysis is {that a} new warmth switch mode utilizing floor waves over a skinny metallic movie deposited on a substrate with low processing problem was recognized for the primary time on this planet. It may be utilized as a nanoscale warmth spreader to effectively dissipate warmth close to the recent spots for simply overheatable semiconductor units.”
The end result has nice implications for the event of high-performance semiconductor units sooner or later in that it may be utilized to quickly dissipate warmth on a nanoscale skinny movie. Specifically, this new warmth switch mode recognized by the analysis staff is predicted to unravel the basic drawback of thermal administration in semiconductor units because it permits much more efficient warmth switch at nanoscale thickness whereas the thermal conductivity of the skinny movie often decreases as a result of boundary scattering impact.