(Nanowerk Information) In recent times, ultrasmall steel nanoclusters have unlocked advances in fields starting from bioimaging and biosensing to biotherapy because of their distinctive molecular-like properties. In a examine printed within the journal Polyoxometalates (“Steel ion-induced alloying and dimension transformation of water-soluble steel nanoclusters”), a analysis group from Qingdao College of Science and Expertise proposed a design to synthesize atomically exact, water-soluble alloy nanoclusters.
“The novelty of this examine is in a brand new technique for the synthesis of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters and an extra contribution to the elemental understanding of the alloying mechanism of steel nanoclusters,” stated examine writer Xun Yuan from Qingdao College of Science and Expertise.
“The last word objective is to develop such alloy nanoclusters as novel nanomedicine,” Yuan stated.
 Scientists from Qingdao College of Science and Expertise developed a novel path to synthesize atomically exact, water-soluble alloy nanoclusters. (Picture: Xun Yuan, Faculty of Supplies Science and Engineering, Qingdao College of Science and Expertise)
Nanoclusters are product of just a few to tens of atoms, and the scale of their cores is normally beneath 2 nanometers (nm). For the reason that ultra-small dimension of the clusters is near the Fermi wavelength of electrons, the continual band turns to discontinuous and turns into molecule-like with discrete vitality ranges. Consequently, the nanoclusters exhibit distinctive optical and digital traits.
Latest research have demonstrated how alloy nanoclusters — synthesized by combining two or extra totally different metals right into a monometallic nanocluster framework — can generate new geometric constructions and extra performance. Researchers can “tune” the bodily and chemical properties (e.g., optical, catalytic, and magnetic) of steel nanoclusters. Furthermore, alloy nanoclusters usually exhibit synergistic or new properties, which transcend these of monometallic nanoclusters.
Heightened curiosity in potential alternatives has spurred current exercise to develop new strategies to synthesize alloy nanoclusters. However, whereas the correlations between dimension, morphology, and composition of alloy nanoclusters and their physicochemical properties have been effectively demonstrated, points surrounding doping processes and the dynamic responses are usually not effectively understood, in keeping with Yuan.
“These unresolved points are primarily because of the technical limitations in characterizing the alloy atom distribution on the atomic degree, particularly in real-time monitoring of the dynamic heteroatom motion within the alloy nanoparticles in the course of the reactions,” Yuan stated.
As well as, most of these strategies had been exploited for hydrophobic alloy nanoclusters, which can preclude synthesis for water-soluble alloy nanoclusters. Given the huge utility of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters in biomedicine and environmental safety, creating novel artificial methods of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters on the atomic degree is considerably vital.
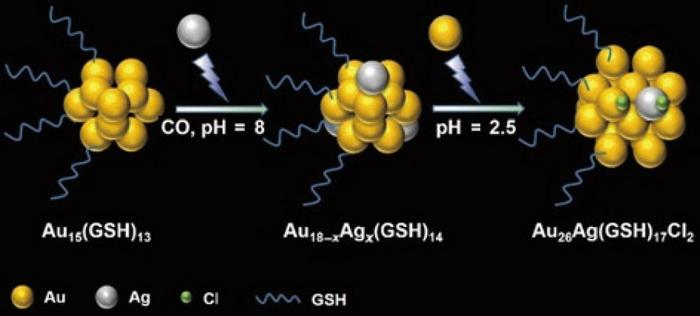
With this objective in thoughts, Yuan and collaborators discovered that seeding silver (Ag) ions may set off the transformation from gold (Au)-based nanoclusters into alloy Au18-xAgx(GSH)14 nanocluster which will be additional reworked to composition-fixed Au26Ag(GSH)17Cl2 nanoclusters by gold (Au) ions— with GSH denoting water-soluble glutathione. Furthermore, the place of the one Ag atom of Au26Ag(GSH)17Cl2 nanoclusters may very well be recognized on the floor.
“Our outcomes may obtain the atom-level modulation of steel nanoparticles, and supply a platform for producing alloy practical nanomaterials for particular purposes,” stated Yuan. “Moreover, the acquired alloying mechanism could deepen the understanding on the properties-performance of alloy nanomaterials, contributing to the era of latest data within the fields of nanomaterials, chemistry, and nanocluster science.”
In future research, the researchers will use these alloy nanoclusters for biomedical purposes.
Scientists from Qingdao College of Science and Expertise developed a novel path to synthesize atomically exact, water-soluble alloy nanoclusters. (Picture: Xun Yuan, Faculty of Supplies Science and Engineering, Qingdao College of Science and Expertise)
Nanoclusters are product of just a few to tens of atoms, and the scale of their cores is normally beneath 2 nanometers (nm). For the reason that ultra-small dimension of the clusters is near the Fermi wavelength of electrons, the continual band turns to discontinuous and turns into molecule-like with discrete vitality ranges. Consequently, the nanoclusters exhibit distinctive optical and digital traits.
Latest research have demonstrated how alloy nanoclusters — synthesized by combining two or extra totally different metals right into a monometallic nanocluster framework — can generate new geometric constructions and extra performance. Researchers can “tune” the bodily and chemical properties (e.g., optical, catalytic, and magnetic) of steel nanoclusters. Furthermore, alloy nanoclusters usually exhibit synergistic or new properties, which transcend these of monometallic nanoclusters.
Heightened curiosity in potential alternatives has spurred current exercise to develop new strategies to synthesize alloy nanoclusters. However, whereas the correlations between dimension, morphology, and composition of alloy nanoclusters and their physicochemical properties have been effectively demonstrated, points surrounding doping processes and the dynamic responses are usually not effectively understood, in keeping with Yuan.
“These unresolved points are primarily because of the technical limitations in characterizing the alloy atom distribution on the atomic degree, particularly in real-time monitoring of the dynamic heteroatom motion within the alloy nanoparticles in the course of the reactions,” Yuan stated.
As well as, most of these strategies had been exploited for hydrophobic alloy nanoclusters, which can preclude synthesis for water-soluble alloy nanoclusters. Given the huge utility of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters in biomedicine and environmental safety, creating novel artificial methods of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters on the atomic degree is considerably vital.
With this objective in thoughts, Yuan and collaborators discovered that seeding silver (Ag) ions may set off the transformation from gold (Au)-based nanoclusters into alloy Au18-xAgx(GSH)14 nanocluster which will be additional reworked to composition-fixed Au26Ag(GSH)17Cl2 nanoclusters by gold (Au) ions— with GSH denoting water-soluble glutathione. Furthermore, the place of the one Ag atom of Au26Ag(GSH)17Cl2 nanoclusters may very well be recognized on the floor.
“Our outcomes may obtain the atom-level modulation of steel nanoparticles, and supply a platform for producing alloy practical nanomaterials for particular purposes,” stated Yuan. “Moreover, the acquired alloying mechanism could deepen the understanding on the properties-performance of alloy nanomaterials, contributing to the era of latest data within the fields of nanomaterials, chemistry, and nanocluster science.”
In future research, the researchers will use these alloy nanoclusters for biomedical purposes.