A analysis workforce led by The Hong Kong College of Science and Expertise (HKUST) has developed an optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled Floor-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) platform that makes use of on-and-off management of sunshine to probe varied amylin species in mixtures on the single-molecule stage, unveiling the heterogeneous constructions of pH-dependent amylin species, and the secrets and techniques behind amyloid aggregation mechanisms related to sort 2 diabetes.
By eradicating ensemble averaging, single-molecule methods discern the sign of particular person molecules to unveil hidden particulars and revolutionize our understanding of advanced and heterogeneous molecular methods. Present single-molecule approaches are restricted to ultra-dilution and/or molecular immobilization as a result of the diffraction-limited detection quantity can’t be additional diminished.
Whereas, sure biomolecules interact in varied interactions which can be considerably affected by concentrations. For instance, as a typical intrinsically disordered protein, human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (amylin, hIAPP) lacks secure secondary constructions however possesses aggregation propensity ruled by environmental components, equivalent to focus and pH, to type completely different oligomeric intermediates and amyloid fibrils in sort II diabetes sufferers.
The molecular mechanism stays unclear, because of the challenges of detecting the uncommon, transient, and heterogeneous amylin species in a dynamic combination, calling for the event of superior single-molecule strategies.
In a current breakthrough, the analysis workforce led by Prof. Huang Jinqing, Assistant Professor at HKUST’s Division of Chemistry has efficiently developed a novel single-molecule platform combining optical plasmonic manipulation and SERS measurement to scale back detection quantity and elevate sign enhancement, enabling environment friendly and high-throughput single-molecule characterization to check pH-dependent amylin species at physiological concentrations.
Particularly, the workforce constructed a plasmonic junction between two Ag nanoparticle-coated silica microbeads to lure a further Ag nanoparticle to type a dynamic nanocavity upon laser irradiation, which may encapsulate a single or a couple of molecules for delicate SERS characterizations.
Since each optical plasmonic trapping and SERS phenomena are spatially confined within the nanometer scale, it surpasses the optical diffraction restrict to allow exact place management, reduce detection quantity, and enhance SERS enhancement concurrently.
Moreover, the constructed Ag nanoparticle-coated silica microbead dimers are extra secure than the standard Ag nanoparticle assembles in options, making it simpler to look at and find the plasmonic junction on common microscopes to enhance effectivity and reproducibility. By switching the laser gentle between “on” and “off” states, the researchers can management the optical plasmonic trapping to modulate the meeting and disassembly of the dynamic nanocavity for high-throughput sampling and simultaneous SERS measurements.
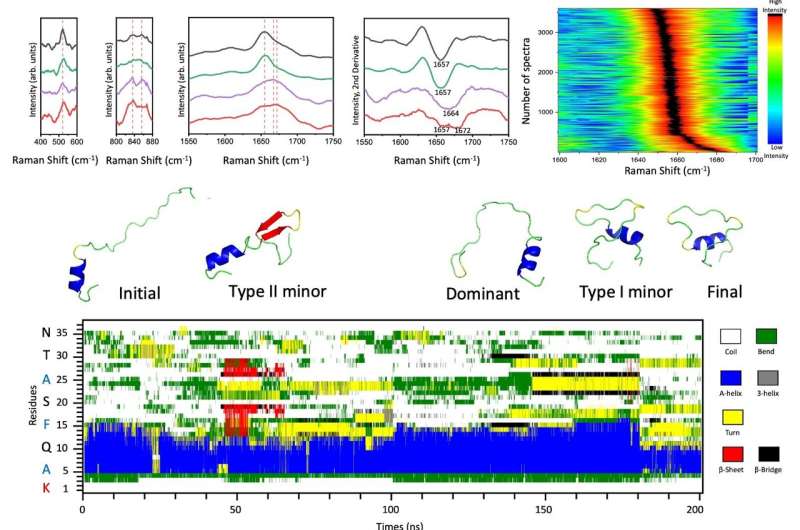
Utilizing this environment friendly single-molecule platform, the analysis workforce harnessed a statistically vital quantity of SERS spectra underlying the structural options of assorted amylin species below two distinct physiological circumstances: the secretory granules of pancreatic β-cells at pH 5.5 and the extracellular compartments at pH 7.4, respectively.
Two forms of low-populated amylin species had been recognized from their predominant monomers on the early stage of amyloid aggregation in impartial pH, containing a important flip construction or a brief β-hairpin with constrained C-terminal as supported by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations.
Such a slight shift within the equilibrium amongst completely different amylin species may drive irreversible amyloid growth even after the post-adjustment of pH from 7.4 to five.5. Therefore, the direct structural characterization of those amylin species inside heterogeneous mixtures signifies the impression of pH on their intra- and inter-molecular interactions and sheds gentle on the mechanism behind pH-regulated amyloid aggregation for understanding sort 2 diabetes.
“We current an easy-to-use technique that reduces detection quantity, enhances molecular sign, and will increase turnover effectivity,” defined Prof. Huang. “Our single-molecule platform can purchase a considerable amount of SERS spectra as molecular snapshots, corresponding to these obtained by means of MD simulations. By statistically analyzing the structural particulars on the single-molecule stage, we’re in a position to reconstruct the majority properties and achieve distinctive insights into the inhabitants and likelihood of particular molecule sorts inside the heterogeneous combination. It has the potential to uncover hidden mysteries in advanced methods.”
The research was just lately revealed in Nature Communications.
Extra data:
Wenhao Fu et al, Environment friendly optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled single-molecule SERS characterization of pH-dependent amylin species in aqueous milieus, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42812-3
Supplied by
Hong Kong College of Science and Expertise
Quotation:
Researchers develop environment friendly and accessible single-molecule platform for detecting varied amylin species (2024, January 4)
retrieved 6 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-efficient-accessible-molecule-platform-amylin.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


