Deep reinforcement studying (RL) continues to make nice strides in fixing real-world sequential decision-making issues similar to balloon navigation, nuclear physics, robotics, and video games. Regardless of its promise, considered one of its limiting elements is lengthy coaching instances. Whereas the present method to velocity up RL coaching on advanced and tough duties leverages distributed coaching scaling as much as a whole lot and even 1000’s of computing nodes, it nonetheless requires using important {hardware} sources which makes RL coaching costly, whereas rising its environmental influence. Nonetheless, latest work [1, 2] signifies that efficiency optimizations on current {hardware} can cut back the carbon footprint (i.e., complete greenhouse gasoline emissions) of coaching and inference.
RL also can profit from comparable system optimization methods that may cut back coaching time, enhance {hardware} utilization and cut back carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. One such approach is quantization, a course of that converts full-precision floating level (FP32) numbers to decrease precision (int8) numbers after which performs computation utilizing the decrease precision numbers. Quantization can save reminiscence storage value and bandwidth for sooner and extra energy-efficient computation. Quantization has been efficiently utilized to supervised studying to allow edge deployments of machine studying (ML) fashions and obtain sooner coaching. Nonetheless, there stays a chance to use quantization to RL coaching.
To that finish, we current “QuaRL: Quantization for Quick and Environmentally Sustainable
Reinforcement Studying”, printed within the Transactions of Machine Studying Analysis journal, which introduces a brand new paradigm known as ActorQ that applies quantization to hurry up RL coaching by 1.5-5.4x whereas sustaining efficiency. Moreover, we show that in comparison with coaching in full-precision, the carbon footprint can be considerably lowered by an element of 1.9-3.8x.
Making use of Quantization to RL Coaching
In conventional RL coaching, a learner coverage is utilized to an actor, which makes use of the coverage to discover the setting and accumulate information samples. The samples collected by the actor are then utilized by the learner to constantly refine the preliminary coverage. Periodically, the coverage educated on the learner aspect is used to replace the actor’s coverage. To use quantization to RL coaching, we develop the ActorQ paradigm. ActorQ performs the identical sequence described above, with one key distinction being that the coverage replace from learner to actors is quantized, and the actor explores the setting utilizing the int8 quantized coverage to gather samples.
Making use of quantization to RL coaching on this trend has two key advantages. First, it reduces the reminiscence footprint of the coverage. For a similar peak bandwidth, much less information is transferred between learners and actors, which reduces the communication value for coverage updates from learners to actors. Second, the actors carry out inference on the quantized coverage to generate actions for a given setting state. The quantized inference course of is way sooner when in comparison with performing inference in full precision.
 |
| An summary of conventional RL coaching (left) and ActorQ RL coaching (proper). |
In ActorQ, we use the ACME distributed RL framework. The quantizer block performs uniform quantization that converts the FP32 coverage to int8. The actor performs inference utilizing optimized int8 computations. Although we use uniform quantization when designing the quantizer block, we imagine that different quantization methods can substitute uniform quantization and produce comparable outcomes. The samples collected by the actors are utilized by the learner to coach a neural community coverage. Periodically the realized coverage is quantized by the quantizer block and broadcasted to the actors.
Quantization Improves RL Coaching Time and Efficiency
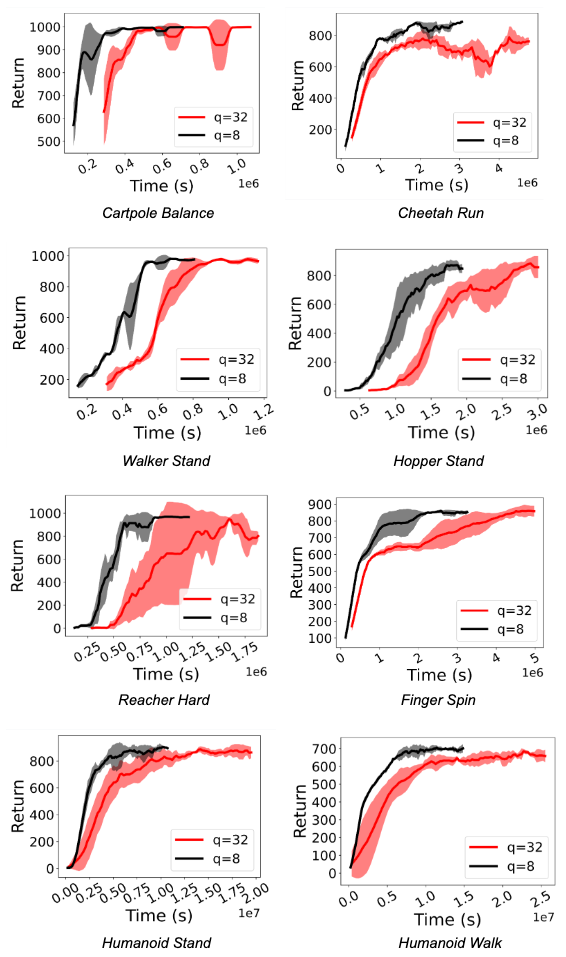
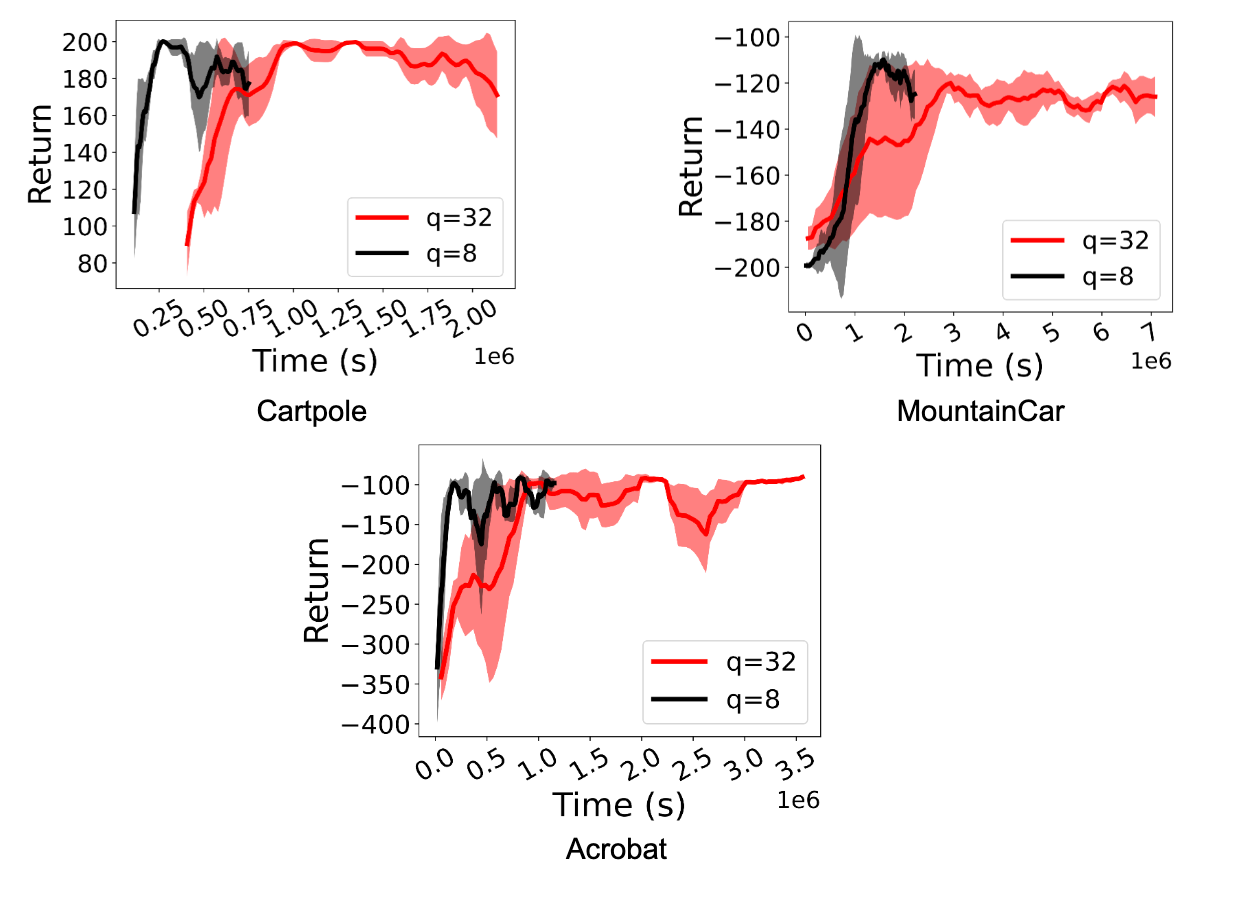
We consider ActorQ in a spread of environments, together with the Deepmind Management Suite and the OpenAI Gymnasium. We show the speed-up and improved efficiency of D4PG and DQN. We selected D4PG because it was one of the best studying algorithm in ACME for Deepmind Management Suite duties, and DQN is a extensively used and commonplace RL algorithm.
We observe a major speedup (between 1.5x and 5.41x) in coaching RL insurance policies. Extra importantly, efficiency is maintained even when actors carry out int8 quantized inference. The figures under show this for the D4PG and DQN brokers for Deepmind Management Suite and OpenAI Gymnasium duties.
Quantization Reduces Carbon Emission
Making use of quantization in RL utilizing ActorQ improves coaching time with out affecting efficiency. The direct consequence of utilizing the {hardware} extra effectively is a smaller carbon footprint. We measure the carbon footprint enchancment by taking the ratio of carbon emission when utilizing the FP32 coverage throughout coaching over the carbon emission when utilizing the int8 coverage throughout coaching.
In an effort to measure the carbon emission for the RL coaching experiment, we use the experiment-impact-tracker proposed in prior work. We instrument the ActorQ system with carbon monitor APIs to measure the power and carbon emissions for every coaching experiment.
In comparison with the carbon emission when operating in full precision (FP32), we observe that the quantization of insurance policies reduces the carbon emissions wherever from 1.9x to three.76x, relying on the duty. As RL techniques are scaled to run on 1000’s of distributed {hardware} cores and accelerators, we imagine that absolutely the carbon discount (measured in kilograms of CO2) will be fairly important.
Conclusion and Future Instructions
We introduce ActorQ, a novel paradigm that applies quantization to RL coaching and achieves speed-up enhancements of 1.5-5.4x whereas sustaining efficiency. Moreover, we show that ActorQ can cut back RL coaching’s carbon footprint by an element of 1.9-3.8x in comparison with coaching in full-precision with out quantization.
ActorQ demonstrates that quantization will be successfully utilized to many elements of RL, from acquiring high-quality and environment friendly quantized insurance policies to lowering coaching instances and carbon emissions. As RL continues to make nice strides in fixing real-world issues, we imagine that making RL coaching sustainable can be essential for adoption. As we scale RL coaching to 1000’s of cores and GPUs, even a 50% enchancment (as now we have experimentally demonstrated) will generate important financial savings in absolute greenback value, power, and carbon emissions. Our work is step one towards making use of quantization to RL coaching to attain environment friendly and environmentally sustainable coaching.
Whereas our design of the quantizer in ActorQ relied on easy uniform quantization, we imagine that different types of quantization, compression and sparsity will be utilized (e.g., distillation, sparsification, and many others.). We hope that future work will think about making use of extra aggressive quantization and compression strategies, which can yield further advantages to the efficiency and accuracy tradeoff obtained by the educated RL insurance policies.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank our co-authors Max Lam, Sharad Chitlangia, Zishen Wan, and Vijay Janapa Reddi (Harvard College), and Gabriel Barth-Maron (DeepMind), for his or her contribution to this work. We additionally thank the Google Cloud group for offering analysis credit to seed this work.