
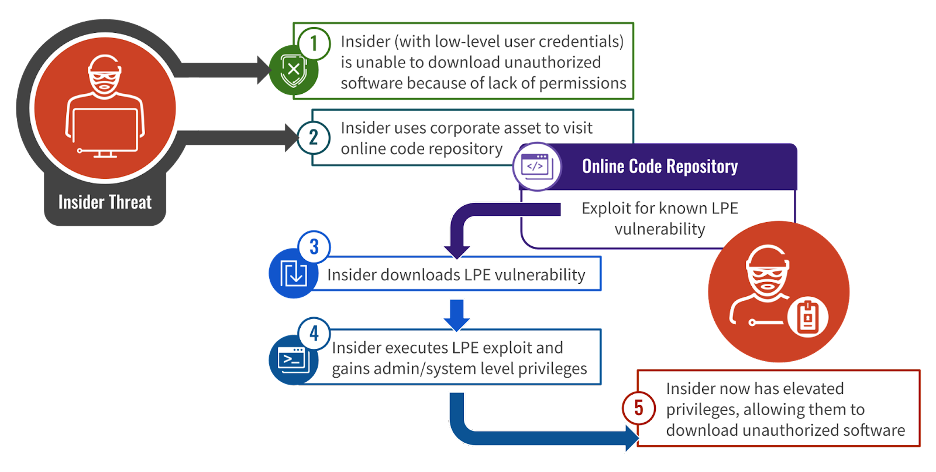
Elevation of privilege flaws are the most typical vulnerability leveraged by company insiders when conducting unauthorized actions on networks, whether or not for malicious functions or by downloading dangerous instruments in a harmful method.
A report by Crowdstrike based mostly on information gathered between January 2021 and April 2023 reveals that insider threats are on the rise and that utilizing privilege escalation flaws is a major factor of unauthorized exercise.
In keeping with the report, 55% of insider threats logged by the corporate depend on privilege escalation exploits, whereas the remaining 45% unwittingly introduce dangers by downloading or misusing offensive instruments.
Rogue insiders usually flip in opposition to their employer as a result of they’ve been given monetary incentives, out of spite, or as a result of variations with their supervisors.
CrowdStrike additionally categorizes incidents as insider threats when they aren’t malicious assaults in opposition to an organization, akin to utilizing exploits to put in software program or carry out safety testing.
Nonetheless, in these instances, although they aren’t used to assault the corporate, they’re generally utilized in a dangerous method, probably introducing threats or malware to the community that menace actors may abuse.
Crowdstrike has discovered that assaults launched from inside focused organizations value a mean of $648,000 for malicious and $485,000 for non-malicious incidents. These figures could also be even greater in 2023.
Moreover the numerous monetary value of insider threats, Crowdstrike highlights the oblique repercussions of name and status damages.
A typical insider assault
Crowdstrike explains that using privilege escalation vulnerabilities to achieve administrative privileges is essential to many insider assaults, as most often, rogue insiders begin with low-level entry to their community environments.
Greater privileges enable the attackers to carry out actions akin to downloading and putting in unauthorized software program, wiping logs, and even diagnosing issues on their laptop utilizing instruments that require administrator privileges.
Probably the most exploited flaws for native privilege escalation by rogue insiders are the next, in keeping with CrowdStrike’s observations:
- CVE-2017-0213: Home windows flaw permits for elevating privileges by COM infrastructure exploitation.
- CVE-2022-0847 (DirtyPipe): Linux kernel pipe operations administration flaw.
- CVE-2021-4034 (PwnKit): Linux flaw impacting the Polkit system service.
- CVE-2019-13272: Linux vulnerability associated to improper dealing with of consumer privileges in kernel processes.
- CVE-2015-1701: Home windows bug involving the kernel-mode driver ‘win32k.sys’ for unauthorized code execution.
- CVE-2014-4113: Additionally targets ‘win32k.sys’ however includes a distinct exploitation technique.
The above flaws are already listed in CISA’s Identified Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog (KEV) as they’ve been traditionally utilized in assaults by menace actors.
Even when a system has been patched for these flaws, insiders can acquire elevated privileges by different means, akin to DLL hijacking flaws in apps working with elevated privileges, insecure file system permissions or service configurations, or Carry Your Personal Susceptible Driver (BYOVD) assaults.
Supply: Crowdstrike
Crowdstrike has seen a number of instances of exploitation of CVE-2017-0213 impacting a retail agency in Europe, the place an worker downloaded an exploit through WhatsApp to put in uTorrent and play video games. One other case considerations a terminated worker of a media entity within the U.S.
PwnKit exploitation was noticed by an worker of an Australian tech firm who tried to achieve administrative rights for laptop troubleshooting functions.
An instance of CVE-2015-1701 exploitation considerations a U.S. tech agency worker who tried to bypass current controls to put in an unauthorized Java digital machine.
Whereas virtually all of those insider menace incidents wouldn’t be thought-about malicious assaults, they introduce danger by modifying how a tool ought to run or by probably working malicious or insecure packages on the community.
Insider errors introduce danger
Almost half of the insider incidents recorded by Crowdstrike concern unintentional mishaps like exploit testing getting uncontrolled, executing offensive safety instruments with out applicable safety measures, and by downloading unvetted code.
For instance, CrowdStrike says some incidents have been attributable to safety professionals testing exploits and exploit kits instantly on a manufacturing workstation reasonably than by a digital machine that’s segmented from the remainder of the community.
The analysts report that almost all instances of this sort contain instruments just like the Metasploit Framework and the ElevateKit, whereas the vulnerabilities launched most frequently because of careless actions are the next:
- CVE-2021-42013: Path traversal vulnerability in Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49 and a couple of.4.50.
- CVE-2021-4034 (PwnKit): Out-of-bounds vulnerability in Polkit system service.
- CVE-2020-0601: Spoofing vulnerability in Home windows CryptoAPI.
- CVE-2016-3309: Privilege escalation challenge in Home windows kernel.
- CVE-2022-21999: Elevation of privilege vulnerability in Home windows Print Spooler.
Introducing these flaws into company networks can improve the general safety danger by offering menace actors who have already got a foothold within the community with extra vectors for exploitation.
Nonetheless, much more necessary, it’s not unusual for menace actors to create pretend proof-of-concept exploits or safety instruments that set up malware on gadgets.
For instance, in Could, menace actors distributed pretend Home windows proof-of-concept exploits that contaminated gadgets with the Cobalt Strike backdoor.
In one other assault, Rapid7 found that menace actors have been distributing pretend PoCs for zero-day exploits that put in Home windows and Linux malware.
In each eventualities, putting in the pretend exploit on a workstation would enable preliminary entry to a company community, which may result in cyber espionage, information theft, or ransomware assaults.

