(monticello/Shutterstock)
Should you deployed a brand new database in 2023, likelihood is good that it was Postgres or considered one of Postgres’ many derivatives for analytics and transactional workloads. There’s no denying the massive recognition of the database, which Michael Stonebraker began creating as a successor to Ingres greater than 35 years in the past. However can the great instances final? The newest launch, Postgres model 16, offers some clues.
As an alternative of a midlife disaster, Postgres at the moment is experiencing a midlife renaissance. At an age when most applied sciences have been given the dreaded “legacy” tag that indicators one thing to be moved away from, organizations as an alternative are gravitating to Postgres, which has found new life because the data-serving spine for hundreds of recent purposes.
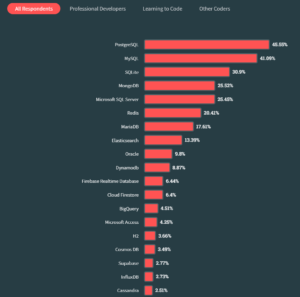
The open supply database had fairly a 12 months in 2023. It emerged because the primary database in Stack Overflow’s 2023 Developer Survey, besting database stalwarts MySQL, SQL Server, and MongoDB. Greater than 70% of the 76,000-plus builders who took the survey stated they used Postgres, which is thoughts blowing when you concentrate on it.
Tuesday, DB-Engines.com named Postgres (additionally known as PostgreSQL) because the DBMS of the 12 months for 2023, beating out Databricks and Google Cloud’s BigQuery. It was the fourth time successful the honour from DB-Engines, which makes use of various strategies to trace the recognition of assorted databases, and the primary victory since 2020 (Snowflake went back-to-back in 2021 and 2022).
Why is Postgres so common now, after so a few years of mediocre uptake? By all accounts, there are a number of causes for the recognition.
DB-Engines.com attributes Postgres’ lengthy successful streak to “excessive tempo of regular enhancements…that preserve the system on the forefront of DBMS expertise, whereas offering a dependable and steady platform on the similar time.” It added that Postgres is “one of the crucial profitable open supply initiatives ever.” To that checklist, one may add a historical past of stability, adherence to requirements, extensibility, broad help for knowledge varieties, and price ticket (it’s free).
Adoption by cloud giants has additionally performed an enormous function in Postgres’ sudden recognition. Amazon Internet Companies, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have every rolled out hosted Postgres companies that scale back the time and expense of implementing and operating a database. The truth is, again in 2021, AWS stated that Amazon Aurora, its Postgres-compatible database service, was its quickest rising service ever.
One other issue was the acquisition of rival database MySQL by Oracle. That occasion drove many would-be open supply database customers away from MySQL and into the Postgres camp, Stonebaker stated in a current interview.
So what does the longer term maintain for Postgres? Can the database preserve the recognition of the previous few years amid ferocious competitors? The Postgres neighborhood is betting on the current launch of model 16 to assist the database preserve the excessive degree of adoption in 2024 and the years to return.
Postgres 16 for Huge Knowledge
The brand new database, which was made usually obtainable in October 2023, options various new options geared toward serving to analytics in addition to transactional workloads, based on Charly Batista, the PostgreSQL tech lead at Percona, which sells tech help and upkeep plans to Postgres customers.
One of many huge sources of efficiency enhancements in V16 comes from the vacuum course of. Postgres makes use of the vacuum to scrub up previous data which were marked for deletion. When updating a database file, Postgres saves a duplicate of the previous document, and marks it for deletion, which happens when the vacuum course of runs.
The issue is that the vacuum course of was computationally costly, and required a freeze of the complete desk being cleaned up. With v16, the efficiency of the vacuum course of has been improved, eliminating the necessity for full-table freezes, Batista stated.
Postgres 16 helps CPU acceleration utilizing SIMD in each x86 and ARM architectures (emp-64GTX/Shutterstock)
Sharding has additionally been improved, which is necessary for storing massive knowledge units. The Postgres neighborhood has been engaged on sharding for the previous three or 4 releases, Batista stated. And whereas v16 doesn’t mark an enormous enchancment in that class, it does carry some enhancements, he stated.
“It’s now so much simpler to do sharding with Postgres,” he stated. “These enhancements, they assist. Should you ask me, if Postgres can be the only option for large knowledge, I’ll inform you the reply that everyone hates: It extremely relies upon.”
Whereas it could possibly shard knowledge throughout a number of nodes, Postgres isn’t a completely distributed database. Postgres customers that want a completely distributed database ought to most likely look to one thing like CockroachDB or Yugabyte, that are distributed database which might be wire-compatible with Postgres.
With that stated, Postgres does help parallelized operations. With model 16, the Postgres question planner now helps the parallelized execution of FULL and RIGHT JOINs, which might be helpful for operating sophisticated aggregation and windowing queries.
Model 16 additionally brings a number of new logical replication capabilities that may enhance how customers architect their database workloads. For instance, it now helps bidirectional replication, which permits knowledge to be replicated from a number of tables concurrently. Customers may also now apply massive transactions utilizing parallel staff.
One other replication options Postgres brings is help for cascading replication. In earlier releases, it was solely possible to copy knowledge from the first, Batista stated.

New parallelization capabilities will assist Postgres course of analytic queries quicker (MZinchenko/Shutterstock)
“Should you needed to have a cascading replication…let’s say from a main to a duplicate and one other reproduction…it was not attainable,” he stated. “On v16, they made it attainable, so that you’re not overloading your main an excessive amount of anymore.”
The sprawling Postgres neighborhood additionally delivered enhancements for bulk loading, utilizing the COPY command for each single and concurrent operations. Based on the Postgres neighborhood, exams present as much as a 300% efficiency enchancment utilizing the brand new bulk load command.
Postgres 16 additionally helps CPU acceleration utilizing SIMD in each x86 and ARM architectures, the group provides, “leading to efficiency features when processing ASCII and JSON strings, and performing array and subtransaction searches.”
Postgres 16 additionally begins to put the groundwork for supporting direct I/O, whereby the information path bypasses the working system, offering an enormous speedup, stated Batista, who’s lively within the Postgres neighborhood.
“Postgres has an enormous overhead once you’re writing a knowledge level,” he stated. “Should you bypass the operational system with direct I/O, that’s one thing big. In order that can provide so much for efficiency and provides a whole lot of freedom to developer.”
Postgres doesn’t but help direct I/O, as MySQL does. However Postgres customers can make the most of extensions, equivalent to PG-Strom, to speed up workloads utilizing GPUs and SSDs, Batista identified.
Associated Objects:
Microsoft Benchmarks Distributed PostgreSQL DBs
Google Cloud Launches New Postgres-Suitable Database, AlloyDB