Dec 22, 2023
(Nanowerk Information) A pancake stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies carried via the sky by a balloon was in a position to take the world’s most correct image of a neutron star’s gamma ray beam. To attain this, Kobe College researchers mixed the oldest technique of capturing radioactive radiation with the most recent knowledge capturing methods and a intelligent time-recording machine.
The outcomes have been revealed in The Astrophysical Journal (“First emulsion γ-ray telescope imaging of the Vela pulsar by the GRAINE 2018 balloon-borne experiment”).
 A single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route. Equally, Kobe College researchers might precisely picture a gamma-ray-emitting pulsar (the sky’s lighthouses) with a stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies on a balloon. To have the ability to inform the orientation of the dangling gondola relative to the celebs, they added a star digicam and a tool to timestamp the gamma-rays’ impacts. (Picture: Kobe College)
The celebs shine their mild on us within the full vary of the spectrum of sunshine, from infra-red to gamma rays. For every of those bands, completely different sensing tools is required. Essentially the most difficult one is gamma rays, well-known for being a high-energy product of nuclear fission, as a result of their very brief wavelength implies that they do not work together with matter in the identical means as different types of mild and thus cannot be deflected with lenses or detected by normal sensors. Thus, there’s a hole in our capability to detect the sunshine coming from fascinating stellar objects reminiscent of supernovae and their remnants.
To resolve this subject, Kobe College astrophysicist AOKI Shigeki and his group turned to the very first materials that was used to detect radioactivity, photographic movies.
“Our group has been specializing in the superb functionality of emulsion movie to hint gamma rays with excessive precision and proposed that it might grow to be a wonderful gamma-ray telescope by introducing a number of fashionable knowledge seize and evaluation options,” explains Aoki.
Primarily based on the excessive sensitivity of those movies and a novel, automated, high-speed technique of extracting knowledge from them, the physicists’ thought was to stack up a number of of them to precisely seize the trajectory of the particles that the gamma ray produces on affect, similar to a single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route.
To scale back atmospheric interference, they then mounted the stack of movies onto a scientific statement balloon to elevate it to a peak between 35 and 40 kilometers. Nonetheless, since a balloon is swaying and twisting within the wind, the route of the “telescope” just isn’t secure, in order that they added a set of cameras to document the gondola’s orientation relative to the celebs at any time. However this created one other subject, as a result of as anyone who has ever taken {a photograph} with lengthy publicity is aware of, photographic movie doesn’t document the passage of time and so it isn’t straight potential to know at what time any given gamma ray affect occurred. To beat this downside, they made the underside three layers of movie transfer forwards and backwards at common however completely different speeds, similar to the palms of a clock. From the relative dislocation of the traces in these decrease plates they may then calculate the exact time of the affect and thus correlate it with the cameras’ footage.
They’ve now revealed the primary picture ensuing from this setup within the journal The Astrophysical Journal. It’s the most correct picture ever produced of the Vela pulsar, a fast-spinning neutron star that tasks a beam of gamma rays into the sky like a lighthouse at evening.
A single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route. Equally, Kobe College researchers might precisely picture a gamma-ray-emitting pulsar (the sky’s lighthouses) with a stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies on a balloon. To have the ability to inform the orientation of the dangling gondola relative to the celebs, they added a star digicam and a tool to timestamp the gamma-rays’ impacts. (Picture: Kobe College)
The celebs shine their mild on us within the full vary of the spectrum of sunshine, from infra-red to gamma rays. For every of those bands, completely different sensing tools is required. Essentially the most difficult one is gamma rays, well-known for being a high-energy product of nuclear fission, as a result of their very brief wavelength implies that they do not work together with matter in the identical means as different types of mild and thus cannot be deflected with lenses or detected by normal sensors. Thus, there’s a hole in our capability to detect the sunshine coming from fascinating stellar objects reminiscent of supernovae and their remnants.
To resolve this subject, Kobe College astrophysicist AOKI Shigeki and his group turned to the very first materials that was used to detect radioactivity, photographic movies.
“Our group has been specializing in the superb functionality of emulsion movie to hint gamma rays with excessive precision and proposed that it might grow to be a wonderful gamma-ray telescope by introducing a number of fashionable knowledge seize and evaluation options,” explains Aoki.
Primarily based on the excessive sensitivity of those movies and a novel, automated, high-speed technique of extracting knowledge from them, the physicists’ thought was to stack up a number of of them to precisely seize the trajectory of the particles that the gamma ray produces on affect, similar to a single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route.
To scale back atmospheric interference, they then mounted the stack of movies onto a scientific statement balloon to elevate it to a peak between 35 and 40 kilometers. Nonetheless, since a balloon is swaying and twisting within the wind, the route of the “telescope” just isn’t secure, in order that they added a set of cameras to document the gondola’s orientation relative to the celebs at any time. However this created one other subject, as a result of as anyone who has ever taken {a photograph} with lengthy publicity is aware of, photographic movie doesn’t document the passage of time and so it isn’t straight potential to know at what time any given gamma ray affect occurred. To beat this downside, they made the underside three layers of movie transfer forwards and backwards at common however completely different speeds, similar to the palms of a clock. From the relative dislocation of the traces in these decrease plates they may then calculate the exact time of the affect and thus correlate it with the cameras’ footage.
They’ve now revealed the primary picture ensuing from this setup within the journal The Astrophysical Journal. It’s the most correct picture ever produced of the Vela pulsar, a fast-spinning neutron star that tasks a beam of gamma rays into the sky like a lighthouse at evening.
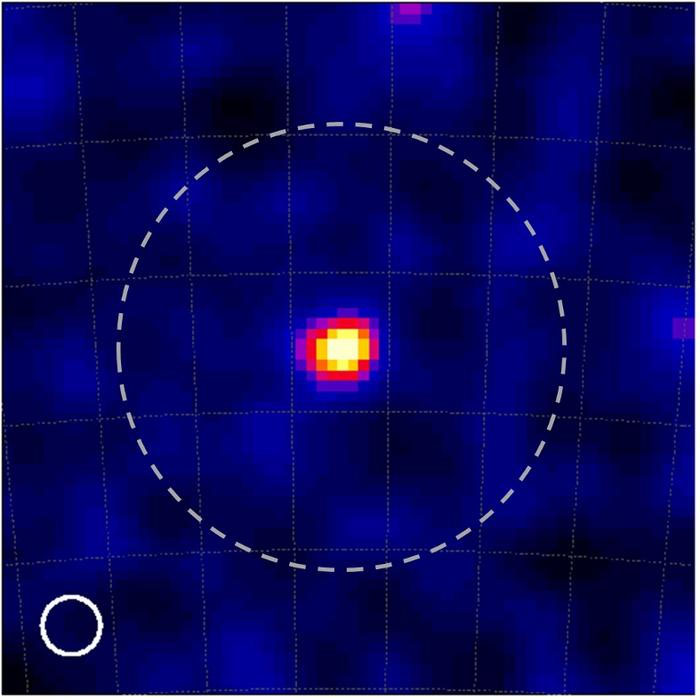 The picture of the Vela pulsar. The picture has a decision greater than 40 instances higher than what might be achieved beforehand: The circle on the backside left signifies the pulsar’s picture unfold for comparability with the picture unfold of the beforehand finest gamma ray picture (of a special stellar object), indicated by the dashed circle. (Picture: GRAINE collaboration)
“We captured a complete of a number of trillion tracks with an accuracy of 1/10,000 millimeters. By including time info and mixing it with perspective monitoring info, we have been in a position to decide ‘when’ and ‘the place’ the occasions originated with such precision that the ensuing decision was greater than 40 instances greater than that of typical gamma-ray telescopes,” Aoki summarizes his group’s achievements.
Whereas these outcomes are spectacular already, the brand new method opens the potential for capturing extra particulars on this frequency band of sunshine than ever earlier than. The Kobe College researcher explains, “By way of scientific balloon-borne experiments, we will try and contribute to many areas of astrophysics, and specifically to open up gamma-ray telescopy to ‘multi-messenger astronomy’ the place simultaneous measurements of the identical occasion captured via completely different methods are required. Primarily based on the success of the 2018 balloon experiment these knowledge have been generated with, we’ll develop the statement space and time in upcoming balloon flights and are wanting ahead to scientific breakthroughs within the area of gamma-ray astronomy.”
The picture of the Vela pulsar. The picture has a decision greater than 40 instances higher than what might be achieved beforehand: The circle on the backside left signifies the pulsar’s picture unfold for comparability with the picture unfold of the beforehand finest gamma ray picture (of a special stellar object), indicated by the dashed circle. (Picture: GRAINE collaboration)
“We captured a complete of a number of trillion tracks with an accuracy of 1/10,000 millimeters. By including time info and mixing it with perspective monitoring info, we have been in a position to decide ‘when’ and ‘the place’ the occasions originated with such precision that the ensuing decision was greater than 40 instances greater than that of typical gamma-ray telescopes,” Aoki summarizes his group’s achievements.
Whereas these outcomes are spectacular already, the brand new method opens the potential for capturing extra particulars on this frequency band of sunshine than ever earlier than. The Kobe College researcher explains, “By way of scientific balloon-borne experiments, we will try and contribute to many areas of astrophysics, and specifically to open up gamma-ray telescopy to ‘multi-messenger astronomy’ the place simultaneous measurements of the identical occasion captured via completely different methods are required. Primarily based on the success of the 2018 balloon experiment these knowledge have been generated with, we’ll develop the statement space and time in upcoming balloon flights and are wanting ahead to scientific breakthroughs within the area of gamma-ray astronomy.”
 A single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route. Equally, Kobe College researchers might precisely picture a gamma-ray-emitting pulsar (the sky’s lighthouses) with a stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies on a balloon. To have the ability to inform the orientation of the dangling gondola relative to the celebs, they added a star digicam and a tool to timestamp the gamma-rays’ impacts. (Picture: Kobe College)
The celebs shine their mild on us within the full vary of the spectrum of sunshine, from infra-red to gamma rays. For every of those bands, completely different sensing tools is required. Essentially the most difficult one is gamma rays, well-known for being a high-energy product of nuclear fission, as a result of their very brief wavelength implies that they do not work together with matter in the identical means as different types of mild and thus cannot be deflected with lenses or detected by normal sensors. Thus, there’s a hole in our capability to detect the sunshine coming from fascinating stellar objects reminiscent of supernovae and their remnants.
To resolve this subject, Kobe College astrophysicist AOKI Shigeki and his group turned to the very first materials that was used to detect radioactivity, photographic movies.
“Our group has been specializing in the superb functionality of emulsion movie to hint gamma rays with excessive precision and proposed that it might grow to be a wonderful gamma-ray telescope by introducing a number of fashionable knowledge seize and evaluation options,” explains Aoki.
Primarily based on the excessive sensitivity of those movies and a novel, automated, high-speed technique of extracting knowledge from them, the physicists’ thought was to stack up a number of of them to precisely seize the trajectory of the particles that the gamma ray produces on affect, similar to a single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route.
To scale back atmospheric interference, they then mounted the stack of movies onto a scientific statement balloon to elevate it to a peak between 35 and 40 kilometers. Nonetheless, since a balloon is swaying and twisting within the wind, the route of the “telescope” just isn’t secure, in order that they added a set of cameras to document the gondola’s orientation relative to the celebs at any time. However this created one other subject, as a result of as anyone who has ever taken {a photograph} with lengthy publicity is aware of, photographic movie doesn’t document the passage of time and so it isn’t straight potential to know at what time any given gamma ray affect occurred. To beat this downside, they made the underside three layers of movie transfer forwards and backwards at common however completely different speeds, similar to the palms of a clock. From the relative dislocation of the traces in these decrease plates they may then calculate the exact time of the affect and thus correlate it with the cameras’ footage.
They’ve now revealed the primary picture ensuing from this setup within the journal The Astrophysical Journal. It’s the most correct picture ever produced of the Vela pulsar, a fast-spinning neutron star that tasks a beam of gamma rays into the sky like a lighthouse at evening.
A single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route. Equally, Kobe College researchers might precisely picture a gamma-ray-emitting pulsar (the sky’s lighthouses) with a stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies on a balloon. To have the ability to inform the orientation of the dangling gondola relative to the celebs, they added a star digicam and a tool to timestamp the gamma-rays’ impacts. (Picture: Kobe College)
The celebs shine their mild on us within the full vary of the spectrum of sunshine, from infra-red to gamma rays. For every of those bands, completely different sensing tools is required. Essentially the most difficult one is gamma rays, well-known for being a high-energy product of nuclear fission, as a result of their very brief wavelength implies that they do not work together with matter in the identical means as different types of mild and thus cannot be deflected with lenses or detected by normal sensors. Thus, there’s a hole in our capability to detect the sunshine coming from fascinating stellar objects reminiscent of supernovae and their remnants.
To resolve this subject, Kobe College astrophysicist AOKI Shigeki and his group turned to the very first materials that was used to detect radioactivity, photographic movies.
“Our group has been specializing in the superb functionality of emulsion movie to hint gamma rays with excessive precision and proposed that it might grow to be a wonderful gamma-ray telescope by introducing a number of fashionable knowledge seize and evaluation options,” explains Aoki.
Primarily based on the excessive sensitivity of those movies and a novel, automated, high-speed technique of extracting knowledge from them, the physicists’ thought was to stack up a number of of them to precisely seize the trajectory of the particles that the gamma ray produces on affect, similar to a single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, nevertheless it takes a complete stack to document the straw’s route.
To scale back atmospheric interference, they then mounted the stack of movies onto a scientific statement balloon to elevate it to a peak between 35 and 40 kilometers. Nonetheless, since a balloon is swaying and twisting within the wind, the route of the “telescope” just isn’t secure, in order that they added a set of cameras to document the gondola’s orientation relative to the celebs at any time. However this created one other subject, as a result of as anyone who has ever taken {a photograph} with lengthy publicity is aware of, photographic movie doesn’t document the passage of time and so it isn’t straight potential to know at what time any given gamma ray affect occurred. To beat this downside, they made the underside three layers of movie transfer forwards and backwards at common however completely different speeds, similar to the palms of a clock. From the relative dislocation of the traces in these decrease plates they may then calculate the exact time of the affect and thus correlate it with the cameras’ footage.
They’ve now revealed the primary picture ensuing from this setup within the journal The Astrophysical Journal. It’s the most correct picture ever produced of the Vela pulsar, a fast-spinning neutron star that tasks a beam of gamma rays into the sky like a lighthouse at evening.
 The picture of the Vela pulsar. The picture has a decision greater than 40 instances higher than what might be achieved beforehand: The circle on the backside left signifies the pulsar’s picture unfold for comparability with the picture unfold of the beforehand finest gamma ray picture (of a special stellar object), indicated by the dashed circle. (Picture: GRAINE collaboration)
“We captured a complete of a number of trillion tracks with an accuracy of 1/10,000 millimeters. By including time info and mixing it with perspective monitoring info, we have been in a position to decide ‘when’ and ‘the place’ the occasions originated with such precision that the ensuing decision was greater than 40 instances greater than that of typical gamma-ray telescopes,” Aoki summarizes his group’s achievements.
Whereas these outcomes are spectacular already, the brand new method opens the potential for capturing extra particulars on this frequency band of sunshine than ever earlier than. The Kobe College researcher explains, “By way of scientific balloon-borne experiments, we will try and contribute to many areas of astrophysics, and specifically to open up gamma-ray telescopy to ‘multi-messenger astronomy’ the place simultaneous measurements of the identical occasion captured via completely different methods are required. Primarily based on the success of the 2018 balloon experiment these knowledge have been generated with, we’ll develop the statement space and time in upcoming balloon flights and are wanting ahead to scientific breakthroughs within the area of gamma-ray astronomy.”
The picture of the Vela pulsar. The picture has a decision greater than 40 instances higher than what might be achieved beforehand: The circle on the backside left signifies the pulsar’s picture unfold for comparability with the picture unfold of the beforehand finest gamma ray picture (of a special stellar object), indicated by the dashed circle. (Picture: GRAINE collaboration)
“We captured a complete of a number of trillion tracks with an accuracy of 1/10,000 millimeters. By including time info and mixing it with perspective monitoring info, we have been in a position to decide ‘when’ and ‘the place’ the occasions originated with such precision that the ensuing decision was greater than 40 instances greater than that of typical gamma-ray telescopes,” Aoki summarizes his group’s achievements.
Whereas these outcomes are spectacular already, the brand new method opens the potential for capturing extra particulars on this frequency band of sunshine than ever earlier than. The Kobe College researcher explains, “By way of scientific balloon-borne experiments, we will try and contribute to many areas of astrophysics, and specifically to open up gamma-ray telescopy to ‘multi-messenger astronomy’ the place simultaneous measurements of the identical occasion captured via completely different methods are required. Primarily based on the success of the 2018 balloon experiment these knowledge have been generated with, we’ll develop the statement space and time in upcoming balloon flights and are wanting ahead to scientific breakthroughs within the area of gamma-ray astronomy.”


