Researchers on the Korea Analysis Institute of Requirements and Science developed a poisonous fuel sensor with the world’s highest sensitivity. This sensor can exactly monitor nitrogen dioxide (NO2), a poisonous fuel within the environment, at room temperature with low energy consumption and ultra-high sensitivity. It may be utilized to numerous fields, similar to detection of residual gases throughout semiconductor manufacturing course of and analysis on electrolysis catalysts.
NO2, produced by the high-temperature combustion of fossil fuels and primarily emitted by means of car exhaust or manufacturing unit smoke, contributes to a rise in mortality as a consequence of air air pollution. In South Korea, the annual common focus of NO2 within the air is regulated to be 30 ppb or decrease by presidential decree. Extremely delicate sensors, subsequently, are required to precisely detect gases at extraordinarily low concentrations.
In current instances, the usage of poisonous gases which can be doubtlessly deadly to people has been on the rise because of the improvement of high-tech industries, together with semiconductor manufacturing. Whereas some laboratories and factories have adopted semiconductor-type sensors for security, the problem lies of their low response sensitivity, making them unable to detect poisonous gases which will even be perceptible to the human nostril. To extend the sensitivity, they devour a whole lot of vitality ultimately as a result of they need to function at excessive temperatures.
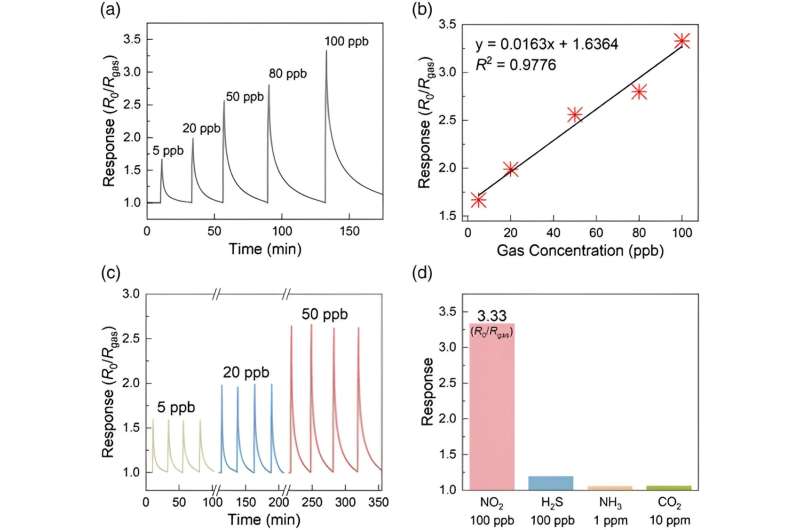
The newly developed sensor, a next-generation semiconductor-type poisonous fuel sensor primarily based on superior supplies, reveals considerably improved efficiency and value in comparison with standard sensors. With its excellent sensitivity to chemical reactions, the brand new sensor can detect NO2 rather more sensitively than beforehand reported semiconductor-type sensors, a sensitivity that’s 60 instances larger. Furthermore, the novel sensor consumes minimal energy working at room temperature, and its optimum semiconductor manufacturing course of allows large-area synthesis at low temperatures, thereby lowering fabrication prices.
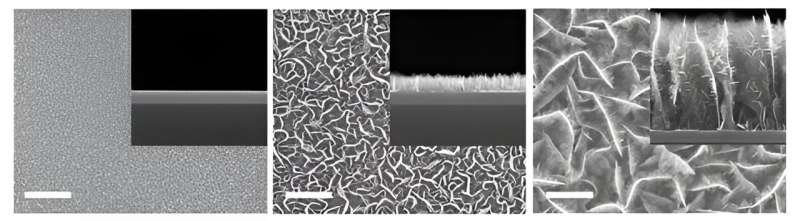
The important thing to the expertise lies within the MoS2 nanobranch materials developed by KRISS. Not like the traditional 2D flat construction of MoS2, this materials is synthesized in a 3D construction resembling tree branches, thereby enhancing the sensitivity. Apart from its power of uniform materials synthesis on a big space, it could possibly create a 3D construction by adjusting the carbon ratio within the uncooked materials with out further processes.
The KRISS Semiconductor Built-in Metrology Staff has experimentally demonstrated that their fuel sensor can detect NO2 within the environment at concentrations as little as 5 ppb. The calculated detection restrict of the sensor is 1.58 ppt, marking the world’s highest degree of sensitivity.
This achievement allows exact monitoring of NO2 within the environment with low energy consumption. The sensor not solely saves time and price but additionally presents wonderful decision. It’s anticipated to contribute to analysis on bettering atmospheric situations by detecting annual common concentrations of NO2 and monitoring real-time modifications.
One other attribute of this expertise is its means to regulate the carbon content material within the uncooked materials through the materials synthesis stage, thereby altering the electrochemical properties. This may be utilized to develop sensors able to detecting gases apart from NO2, similar to residual gases produced through the semiconductor manufacturing processes. The superb chemical reactivity of the fabric can be exploited to reinforce the efficiency of electrolysis catalysts for hydrogen manufacturing.
Dr. Jihun Mun, a senior researcher of the KRISS Semiconductor Built-in Metrology Staff, stated, “This expertise, which overcomes the restrictions of standard fuel sensors, won’t solely meet authorities rules but additionally facilitate exact monitoring of home atmospheric situations. We’ll proceed follow-up analysis in order that this expertise will be utilized to the event of varied poisonous fuel sensors and catalysts, extending past the monitoring of NO2 within the environment.”
Extra info:
Jeongin Track et al, MOCVD of Hierarchical C‐MoS2 Nanobranches for ppt‐Degree NO2 Detection, Small Constructions (2023). DOI: 10.1002/sstr.202200392
Quotation:
Novel poisonous fuel sensor improves the restrict of nitrogen dioxide detection (2023, December 29)
retrieved 29 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-toxic-gas-sensor-limit-nitrogen.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


