(Picture courtesy NIST)
The Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise (NIST) right this moment revealed the AI Danger Administration Framework, doc meant to assist organizations voluntarily develop and deploy AI programs with out bias and different unfavourable outcomes. The doc has an excellent shot at defining the usual authorized method that organizations will use to mitigate the dangers of AI sooner or later, says Andrew Burt, founding father of AI legislation agency BNH.ai.
Because the tempo of AI improvement accelerates, so too do the potential harms from utilizing AI. The NIST, on the request of the USA Congress, devised the AI Danger Administration Framework (RMF) to plot a repeatable method to creating accountable AI programs.
“With out correct controls, AI programs can amplify, perpetuate, or exacerbate inequitable or undesirable outcomes for people and communities,” states the RMF govt abstract. “With correct controls, AI programs can mitigate and handle inequitable outcomes.”
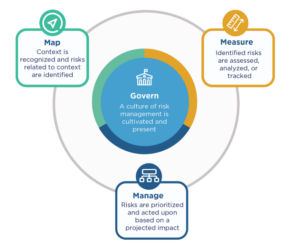
The 48-page doc, which you’ll entry right here, seeks to assist organizations method AI threat administration in 4 methods, dubbed the RMF Core features, together with Map, Measure, Handle, and Govern.
First, it encourages customers to map out the AI system in its totally, together with meant enterprise objective and the potential harms that may end result from utilizing AI. Imagining the totally different ways in which AI programs can have optimistic and unfavourable outcomes is important to the entire course of. Enterprise context is crucial right here, as is the group’s tolerance for threat.
Second, the RMF asks the moral AI practitioner to make use of the maps created in step one to find out measure the impacts that AI programs are having, in each a quantitative and a qualitative method. The measurements needs to be carried out repeatedly, cowl the AI programs’ performance, examinability, and trustworthiness (avoidance of bias), and the outcomes needs to be in comparison with benchmarks, the RMF states.
Third, organizations will use the measurements from step two to assist it handle the AI system in an ongoing vogue. The framework offers customers the instruments to handle the dangers of deployed AI programs and to allocate threat administration assets based mostly on assessed and prioritized dangers, the RMF says.
The map, measure, and handle features come collectively beneath an overarching governance framework, which provides the consumer the insurance policies and procedures to implement all the required elements of a threat mitigation technique.
The RMF doesn’t have the drive of legislation, and certain by no means will. But it surely does lay out a workable method to managing threat in AI, says Burt, who co-founded BNH.ai in 2019 after working as Immuta’s chief authorized counsel
“A part of the benefit of the NIST framework is that it’s voluntary, not regulatory,” Burt tells Datanami in an interview right this moment. “That being stated, I feel it’s going to set the usual of care.”
The present state of American legislation with regards to AI is “the Wild West,” Burt says. There are not any clear authorized requirements, which is a priority each to the businesses trying to undertake AI in addition to residents hoping to not be harmed by it.
The NIST RMF has the potential to develop into “a concrete, particular commonplace” that everyone within the U.S. can agree on, Burt says.
“From a authorized perspective, if folks have practices in place which might be wildly divergent from the NIST RMF, I feel it will likely be simple for a plaintiff to say ‘Hey what you’re doing is negligent or irresponsible’ or ‘Why didn’t you do that?’” he says. “This can be a clear commonplace, a transparent finest follow.”
BNH.ai conducts AI audits for a variety of purchasers, and Burt foresees the RMF method turning into the usual approach to conduct AI audits sooner or later. Corporations are shortly awakening to the truth that they should audit their AI programs to make sure that they’re not harming customers or perpetuating bias in a harmful manner. In some ways, the AI cart is getting manner out in entrance of the horse.
“The market is adopting these applied sciences lots sooner than they’ll mitigate their hurt,” Burt says. “That’s the place we are available in as a legislation agency. That’s the place rules are beginning to are available in. That’s the place the NIST framework is available in. There are all types of sticks and carrots which might be going to, I feel, assist to right this misbalance. However proper now, I’d say there’s a reasonably extreme imbalance between the worth that individuals are getting out of those instruments and the precise threat that they pose.”
A lot of the chance stems from the speedy adoption of instruments like ChatGPT and different giant language and generative AI fashions. Since these programs are educated on a corpus of information that’s nearly equal to the complete Web, the quantity of bias and hate-speech contained within the coaching knowledge is probably staggering.
“Within the final three months, the massive massive change for the potential of AI to inflect hurt , pertains to how many individuals are utilizing these programs,” Burt says .”I don’t know the numbers for ChatGPT and others, however they’re skyrocketing. These programs are beginning to be deployed outdoors of laboratory environments in methods which might be actually vital. And that’s the place the legislation is available in. That’s the place threat is available in and that’s the place actual harms begin to be generated.”
The RMF in some methods will develop into the American counter to the European Union’s AI Act. First proposed in 2021, the EU’s AI Act is more likely to develop into legislation this yr, and–with its gradations of ranges of acceptable threat–can have a dramatic influence on the aptitude of firms to deploy AI programs.
There are massive variations between the 2 approaches, nevertheless. For starters, the AI Act can have the drive of legislation, and can impose fines for transgressions. The RMF, then again, is totally voluntary, and can impose change by turning into the business commonplace that attorneys can cite in civil courtroom.
The RMF can also be common and versatile sufficient to adapt to the fast-changing AI panorama, which additionally places it at odds with the AI Act, Burt says.
“I’d say [the EU]s method tends to be fairly systematic and fairly rigid, just like the GDPR,” Burt says. “They’re making an attempt to actually deal with everting all of sudden. It’s a valiant effort, however the NIST RMF is much more versatile. Smaller organizations with minimal assets can apply it. Giant organizations with an enormous quantity of assets can apply it. I’d say it’s much more of a risk-based, context-specific versatile method.”
You’ll be able to entry extra details about the RMF at www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework.
Associated Gadgets:
Europe’s New AI Act Places Ethics Within the Highlight
Organizations Wrestle with AI Bias
New Regulation Agency Tackles AI Legal responsibility