
The Moscow-based cybersecurity firm Kaspersky says iOS units are being focused by a beforehand unknown malware. The agency found the menace whereas monitoring the community site visitors of its personal company Wi-Fi.
Kaspersky is asking the brand new marketing campaign Operation Triangulation. The marketing campaign report reveals how the assault works and particulars the exploitation’s technical properties. Kaspersky’s researchers guarantee the oldest hint of an infection dates again to 2019, with assaults nonetheless ongoing as of 2023 and affecting variations as much as iOS 15.7.
Kaspersky’s zero-click assault report has precipitated controversy, because the Russian Federal Safety Service claims hundreds of Russians, together with international diplomats and authorities officers, had been focused and compromised by the malware. Russia’s Federal Safety Service has accused Apple and the U.S. Nationwide Safety Company of masterminding the assaults; Apple has denied this declare.
Bounce to:
How this zero-click assault works
The brand new iOS safety vulnerability is a zero-click assault. Not like most malware assaults that require customers to take motion, like obtain a file or click on on a hyperlink, zero-click assaults are self-executable, requiring no motion from the customers.
Kaspersky reconstructed the an infection sequence by analyzing its compromised cellular units’ timeline.
The assault begins when the focused iOS machine receives a message by way of the iMessage service. The message despatched will embody an attachment, which accommodates the exploit. With no interplay from the consumer, when the message is acquired, it triggers a vulnerability that results in code execution.
The code inside the exploit downloads a number of subsequent phases from the Command and Management server managed by the cybercriminal, together with different exploits for privilege escalation.
As soon as the exploitation is profitable, a ultimate payload is downloaded from the C&C server. The malware deletes the preliminary message and the exploit attachment.
“The malicious software set doesn’t assist persistence, probably because of the limitations of the OS,” Kaspersky mentioned within the report. Nevertheless, evaluation of a number of iOS machine timelines alerts doable reinfection after rebooting the machine.
Kaspersky added that the ultimate evaluation of the payload shouldn’t be but full. The agency says the menace code runs with root privileges and implements a set of instructions to gather system and consumer info. It might probably additionally run arbitrary code downloaded as plug-in modules from the C&C server.
SEE: Safe your Mac from hackers with these eight finest practices.
Forensic evaluation with the Cellular Verification Toolkit
Kaspersky explains that, as a result of iOS units can’t be inspected from the within, with a view to uncover the menace, offline backups of the units should be created. The backups are inspected utilizing the Cellular Verification Toolkit, which allows forensic evaluation of Android and iOS units and is used to establish traces of compromise.
The cellular machine backup will include a partial copy of the filesystem and a few consumer knowledge and repair databases. The timestamps of the recordsdata, folders and database data permit customers to reconstruct the occasions taking place to the machine roughly. The MVT can generate a sorted timeline of occasions right into a file known as timeline.csv; this timeline can be utilized to establish the menace and its conduct.
Whereas the assault covers its tracks by deleting the preliminary message and the attachment exploit, it’s nonetheless doable to establish if a tool has been compromised by the timeline evaluation.
Based on Kaspersky, the malware may also be transferred from an iTunes backup.
“If a brand new machine was arrange by migrating consumer knowledge from an older machine, the iTunes backup of that machine will include the traces of compromise that occurred to each units, with right timestamps,” the agency mentioned.
Methods to examine iOS units for malware traces
Following a set of procedures, iOS units will be checked for traces of compromises.
First, to examine an iOS machine for any malware traces, a backup should be created. This may be accomplished utilizing iTunes or an open-source utility like idevicebackup2.
To create a backup with idevicebackup2, run the next command:
idevicebackup2 backup --full $backup_directory
Customers could must enter the safety code of their machine a number of instances. Relying on how a lot knowledge is saved on the iOS machine, the backup course of could take minutes or hours.
After the backup is full, the MVT should be put in to course of the backup. If Python 3 is put in within the system, run the next command:
pip set up mvt
If the iOS machine proprietor has enabled encryption, the backup copy will must be decrypted utilizing the next command.
mvt-ios decrypt-backup -d $decrypted_backup_directory $backup_directory
To run all of the checks utilizing the MVT, use the next command:
mvt-ios check-backup -o $mvt_output_directory $decrypted_backup_directory
The output listing will include a number of JSON and CSV recordsdata. To investigate the timeline, the file known as timeline.csv can be used.
Indicators of compromise within the timeline
When checking the file timeline.csv, Kaspersky discovered that essentially the most dependable indicator of a compromise was a course of named BackupAgent within the knowledge utilization traces. This course of shouldn’t seem in a timeline underneath regular circumstances.
Observe: The binary course of BackupAgent2 shouldn’t be an indicator of compromise.
When analyzing the timeline file, Kaspersky discovered the method BackupAgent is preceded by the method IMTransferAgent (Determine A).
Determine A
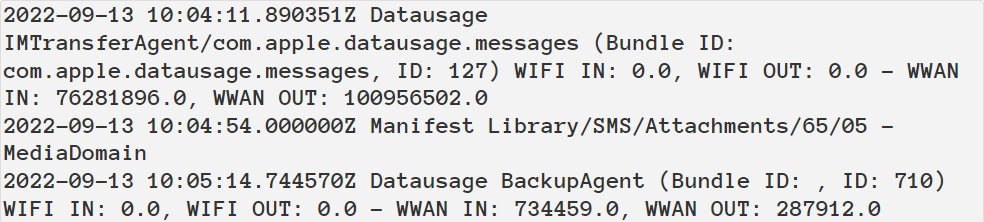
The IMTransferAgent course of downloads the attachment, which on this case is the exploit. This obtain results in the modification of the timestamps of a number of directories within the Library/SMS/Attachments. The attachment is then deleted, leaving solely modified directories with out precise recordsdata inside them.
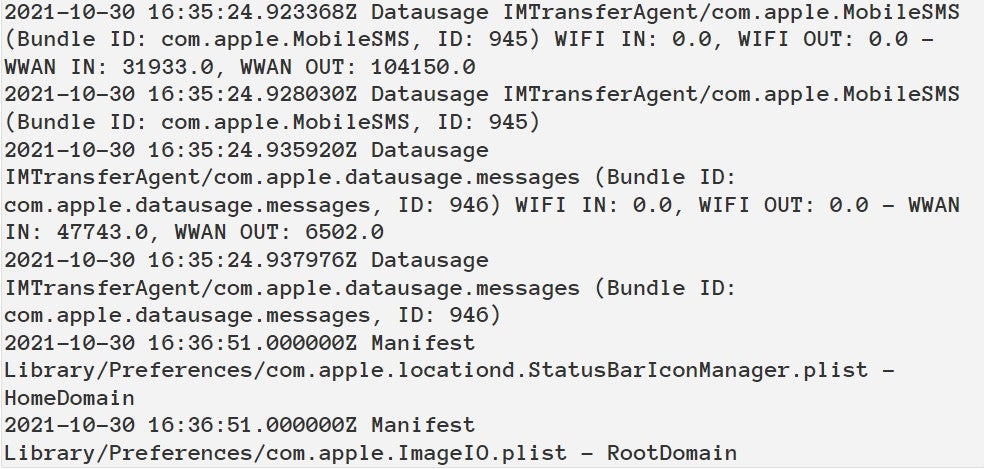
Different indicators of compromises, if a number of are discovered to have occurred inside minutes of the timeframe, embody:
- Modification of 1 or a number of recordsdata:
com.apple.ImageIO.plist,com.apple.locationd.StatusBarIconManager.plist,com.apple.imservice.ids.FaceTime.plist. - Information utilization info of the companies:
com.apple.WebKit.WebContent,powerd/com.apple.datausage.diagnostics,lockdownd/com.apple.datausage.safety(Determine B).
Determine B
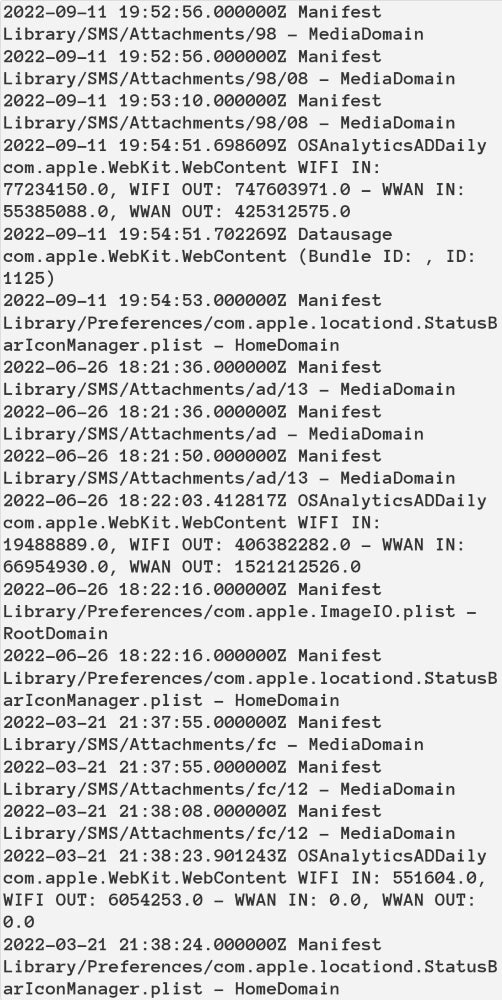
One other string of occasions taking place inside one to 3 minutes reveals the profitable zero-click compromise by way of the iMessage attachment, starting with the modification of an SMS attachment listing (however no attachment filename), adopted by knowledge utilization of com.apple.WebKit.WebContent, adopted by modification of com.apple.locationd.StatusBarIconManager.plist (Determine C).
Determine C
Community exercise throughout exploitation
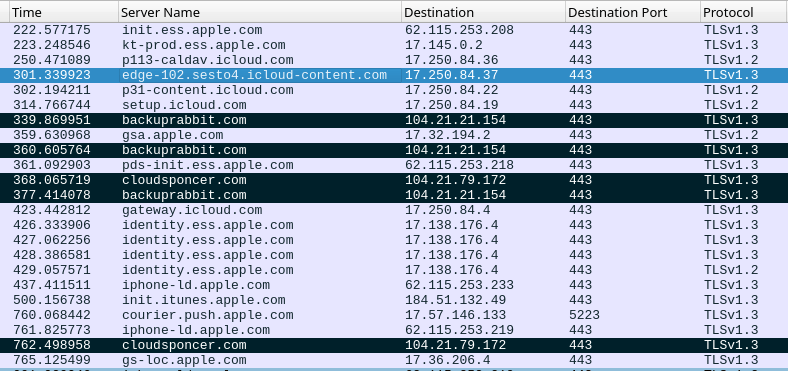
The assault additionally generates traces that may be recognized on the community stage. These traces present up as a sequence of a number of HTTPS connection occasions.
Evaluation of the community reveals exercise because of the interplay with iMessage service within the domains *.ess.apple.com, icloud-content.com, content material.icloud.com to obtain the iMessage attachment containing the exploit and a number of connections with computer systems managed by the cybercriminal with a major quantity of outgoing site visitors (Determine D).
Determine D
The listing of domains utilized by the exploits embody:
- addatamarket[.]web
- backuprabbit[.]com
- businessvideonews[.]com
- cloudsponcer[.]com
- datamarketplace[.]web
- mobilegamerstats[.]com
- snoweeanalytics[.]com
- tagclick-cdn[.]com
- topographyupdates[.]com
- unlimitedteacup[.]com
- virtuallaughing[.]com
- web-trackers[.]com
- growthtransport[.]com
- anstv[.]web
- ans7tv[.]nett of outgoing site visitors
Methods to keep secure from zero-click spyware and adware
Kaspersky founder Eugene Kaspersky mentioned on Twitter that the assault “transmits personal info to distant servers: microphone recordings, photographs from prompt messengers, geolocation and knowledge about plenty of different actions.”
This is able to align the malware with different zero-click spyware and adware equivalent to Pegasus.
Following Kaspersky’s report on Operation Triangulation printed on June 2, the agency launched a particular triangle_check utility that mechanically searches for the malware an infection. The software is publicly shared on GitHub and out there for macOS, Home windows and Linux.
“Immediately, we’re proud to launch a free public software that enables customers to examine whether or not they had been hit by the newly emerged refined menace,” Igor Kuznetsov, head of the EEMEA unit at Kaspersky World Analysis and Evaluation Workforce, mentioned in a press launch. “With cross-platform capabilities, the ‘triangle_check’ permits customers to scan their units mechanically. We urge the cybersecurity group to unite forces within the analysis of the brand new APT to construct a safer digital world.”
Whereas your complete goal of spyware and adware is to behave within the background with out the consumer noticing it, there are a number of clear indicators to maintain a watch out for equivalent to:
- Slowed-down community connection or suspicious excessive reminiscence utilization: Spy ware wants to speak with the attacker, transmit and ship knowledge, which may trigger your telephone to decelerate, freeze or shut down.
- Telephone battery drains extra quickly than regular: This is because of additional exercise taking place with out your consent.
Sadly, defending an iOS machine in opposition to zero-click assaults remains to be difficult, as these are extremely refined malware. The very best follow is to preserve your iOS updated. It’s additionally really useful to profit from your built-in privateness and safety settings.

