The Cisco Talos Yr in Assessment report launched Tuesday highlights new developments within the cybersecurity menace panorama. We’ll concentrate on three subjects lined: the ransomware cybercriminal ecosystem, community infrastructure assaults and commodity loader malware.
Extra ransomware actors switched to extortion relatively than encryption, whereas commodity loaders advanced to be stealthier and extremely efficient, though new main safety enhancements have seen the day in 2023, reminiscent of Microsoft Workplace disabling macros by default. Community gadgets are more and more impacted by cybercriminals and state-sponsored menace actors.
Soar to:
The ransomware cybercriminal ecosystem modified
Most focused vertical
When it comes to ransomware, essentially the most focused vertical, as noticed by Cisco Talos in 2023, was the healthcare and public well being sector, which isn’t shocking for the reason that organizations in that sector usually undergo from underfunded budgets for cybersecurity and low downtime tolerance (Determine A). As well as, these organizations are attention-grabbing targets as a result of they possess protected well being info.
Determine A
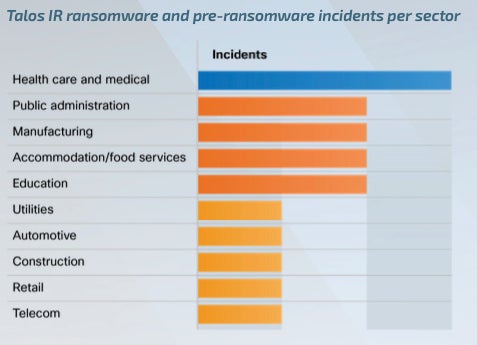
Some ransomware teams have been altering
Probably the most energetic ransomware group for the second yr in a row was LockBit (25.3% of the whole variety of posts made to information leak websites), adopted by ALPHV (10.7%) and Clop (8.2%).
But some ransomware teams saved altering in 2023; these constructions usually merged or rebranded in an try to confuse regulation enforcement and researchers monitoring them. The cybercriminals energetic within the subject usually work for a number of ransomware-as-a-service providers on the similar time.
A number of leaks of ransomware supply code and builders additionally affected the ransomware menace panorama as a result of these allowed extra individuals (even these with little technical data) to begin their very own operations.
Zero-days exploited at an unprecedented tempo
Extremely technical actors have been exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities at an unprecedented tempo. The Clop ransomware group specifically has been in a position to exploit a number of zero-day vulnerabilities, together with vulnerabilities within the GoAnywhere MFT platform, MOVEit and PaperCut.
Cisco Talos states that “Clop’s repeated efforts to take advantage of zero-day vulnerabilities is extremely uncommon for a ransomware group given the assets required to develop such capabilities,” but it’s nonetheless uncertain that they do develop exploits on their very own. When questioned about it in an electronic mail interview, a Cisco spokesperson informed TechRepublic, “Due to the murkiness within the relationships that represent the ransomware ecosystem, it may be tough to precisely parse out which personnel/organizations are chargeable for which actions. Due to this, we should not have direct perception into how Cl0p obtained the 0days and haven’t noticed any indications that they bought them. No matter whether or not they developed them themselves or bought them, the utilization suggests Cl0p is well-resourced, both in engineering expertise or in funds and connections that might permit them to acquire from a 3rd occasion.”
Extra associates are utilizing an information theft extortion mannequin
One other exceptional shift within the ransomware menace panorama is that extra associates at the moment are switching to an information theft extortion mannequin relatively than the standard encryption mannequin. In these assaults, cybercriminals don’t deploy ransomware; as an alternative, they steal organizations’ delicate info earlier than asking for a ransom.
The enhancements in ransomware detection capabilities from Endpoint Detection and Response and Prolonged Detection and Response software program is likely to be one cause for switching techniques and stopping deploying ransomware on the focused methods. Cisco Talos additionally suspects the aggressive pursuits from U.S. and worldwide regulation enforcement in opposition to ransomware actors is likely to be another excuse for that change.
Community infrastructure assaults elevated
Cisco Talos noticed a rise in assaults on networking gadgets in 2023, significantly assaults operated by China- and Russia-based teams trying to advance espionage targets and facilitate stealthy operations in opposition to secondary targets. The researchers noticed such exercise from different cybercriminals, together with preliminary entry brokers and ransomware menace actors.
Weak safety on community gadgets
Networking gadgets, though being key elements to any group’s IT infrastructure, usually are not usually examined from a safety perspective and are sometimes poorly patched, making them an attention-grabbing goal for cybercriminals. But these gadgets usually run on non-standard working methods, rendering their exploitation tougher by cybercriminals but in addition unmonitored by customary safety options.
The everyday compromise of these gadgets begins with menace actors exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities, weak or default credentials, or insecure gadget configuration.
A Cisco spokesman informed TechRepublic that “the continued prevalence of default credentials could also be partly defined by the sheer variety of distributors and merchandise mixed with the dearth of uniform requirements/finest practices. The transfer away from default credentials ought to actually assist enhance the state of affairs. It is very important word that weak credentials can be exploited if the actor is ready to brute-force or password-spray, and that entry brokers nonetheless obtain success in acquiring credentials and promoting them on the darkish net. Which means that even when organizations usually are not utilizing default credentials, it’s important they create distinctive and complicated passwords, make use of MFA the place doable, and emphasize extra safety measures reminiscent of segmentation and IR planning as properly.”
Focused gadgets had a excessive severity rating
Vulnerabilities affecting community gadgets in 2023 all had a excessive severity rating, which means these gadgets have been simply exploitable and had the potential to trigger vital operational influence, based on Cisco Talos.
As soon as compromised, these gadgets permit attackers to seize delicate community info, facilitating additional entry to the goal’s networks. Attackers additionally may plant malware on the gadgets to ascertain an preliminary foothold within the goal’s infrastructure with out the necessity for any authentication, or to redirect community site visitors to actor-controlled servers. Lastly, the gadgets are additionally usually utilized by attackers as anonymization proxies for conducting assaults on different targets.
Commodity loader malware advanced
Commodity loader malware reminiscent of Qakbot, Ursnif, Emotet, Trickbot and IcedID have been round for years. They have been initially banking trojans, searching for bank card info theft on contaminated computer systems.
In late 2023, new variants of IcedID and Ursnif appeared with a putting distinction as in comparison with their older variations: Their banking trojan capabilities had been eliminated, and their dropper functionalities had been improved. The IcedID new samples have been utilized by preliminary entry brokers identified for generally promoting community accesses to ransomware teams. The most recent Ursnif variants have been utilized by the Royal ransomware group.
Qakbot additionally advanced, deploying new options ideally suited to assist ransomware teams.
This evolution from banking trojan to loader is engaging for cybercriminals who need to be stealthier; the banking trojan operate removing renders these malware much less detectable.
The infecting vector for Qakbot, IcedID and Ursnif advanced, as Microsoft’s new safety measures on Workplace merchandise affected the malware menace panorama, forcing cybercriminals to seek out new methods to make use of macros undetected or keep away from utilizing them utterly (Determine B).
Determine B

Menace actors used completely different strategies in comparison with earlier years for spreading their malware and infecting gadgets, reminiscent of utilizing JavaScript, PowerShell, OneNote paperwork, or HTA recordsdata, to call just a few. Additionally they used the Google Adverts platform to deploy malware reminiscent of Ursnif, IcedID or Trickbot, totally avoiding macros.
Another menace actors deploying Emotet, IcedID and Ursnif have been noticed utilizing older strategies with macros, most likely as a result of the success price on unpatched enterprise legacy methods continues to be excessive.
Methods to defend your corporation from these cybersecurity threats
The menace panorama evolves to swimsuit cybercriminals’ wants, and your safety workforce wants to make sure its mitigation methods are maintaining with the developments. Listed here are some ideas for securing your corporation from these cyberthreats. As well as, all working methods and software program should be updated and patched to keep away from being compromised by widespread vulnerabilities.
Ransomware
Entry management mechanisms needs to be fastidiously reviewed in all company environments, and information segmentation needs to be utilized for storing delicate information as a result of ransomware menace actors are more and more attempting to steal delicate information relatively than encrypt it.
Community gadgets
Community gadgets should be updated and patched. Default passwords, if any, should be modified to sturdy passwords. All the gadgets’ configuration recordsdata needs to be fastidiously analyzed and tuned to keep away from any malicious exploitation. When doable, multifactor authentication should be deployed on these gadgets. Additionally, inbound and outbound communications from the gadgets needs to be monitored to detect malicious communication.
Commodity loaders
The primary households of commodity loaders have dropped their banking trojan capabilities to be lighter and stealthier, even with out utilizing macros — usually to facilitate ransomware operations. Organizations ought to educate their staff to deal with extra file varieties with warning, reminiscent of PDF recordsdata or ZIP archives which may include malicious recordsdata.
Disclosure: I work for Pattern Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.


