
A brand new malware marketing campaign that emerged in March 2023 used JavaScript internet injections to attempt to steal the banking knowledge of over 50,000 customers of 40 banks in North America, South America, Europe, and Japan.
IBM’s safety staff found this evasive risk and reported that the marketing campaign has been underneath preparation since no less than December 2022, when the malicious domains had been bought.
The assaults unfolded through scripts loaded from the attacker’s server, focusing on a particular web page construction widespread throughout many banks to intercept person credentials and one-time passwords (OTPs).
By capturing the above info, the attackers can log in to the sufferer’s banking account, lock them out by altering safety settings, and carry out unauthorized transactions.
A stealthy assault chain
The assault begins with the preliminary malware an infection of the sufferer’s gadget. IBM’s report does not delve into the specifics of this stage, but it surely might be through malvertizing, phishing, and so forth.
As soon as the sufferer visits the attackers’ compromised or malicious websites, the malware injects a brand new script tag with a supply (‘src’) attribute pointing to an externally hosted script.
The malicious obfuscated script is loaded on the sufferer’s browser to switch webpage content material, seize login credentials, and intercept one-time passcodes (OTP).
IBM says this additional step is uncommon, as most malware performs internet injections immediately on the internet web page.
This new strategy makes the assaults extra stealthy, as static evaluation checks are unlikely to flag the easier loader script as malicious whereas nonetheless allowing dynamic content material supply, permitting attackers to change to new second-stage payloads if wanted.
It is also value noting that the malicious script resembles reliable JavaScript content material supply networks (CDN), utilizing domains like cdnjs[.]com and unpkg[.]com, to evade detection. Moreover, the script performs checks for particular safety merchandise earlier than execution.
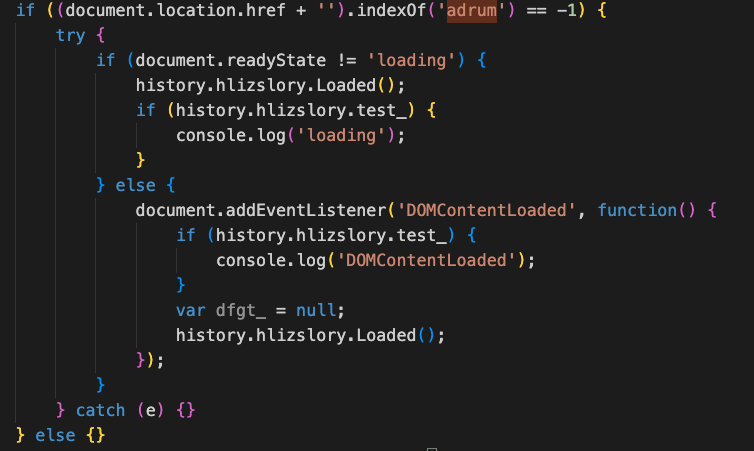
The script is dynamic, consistently adjusting its conduct to the command and management server’s directions, sending updates, and receiving particular responses that information its exercise on the breached gadget.
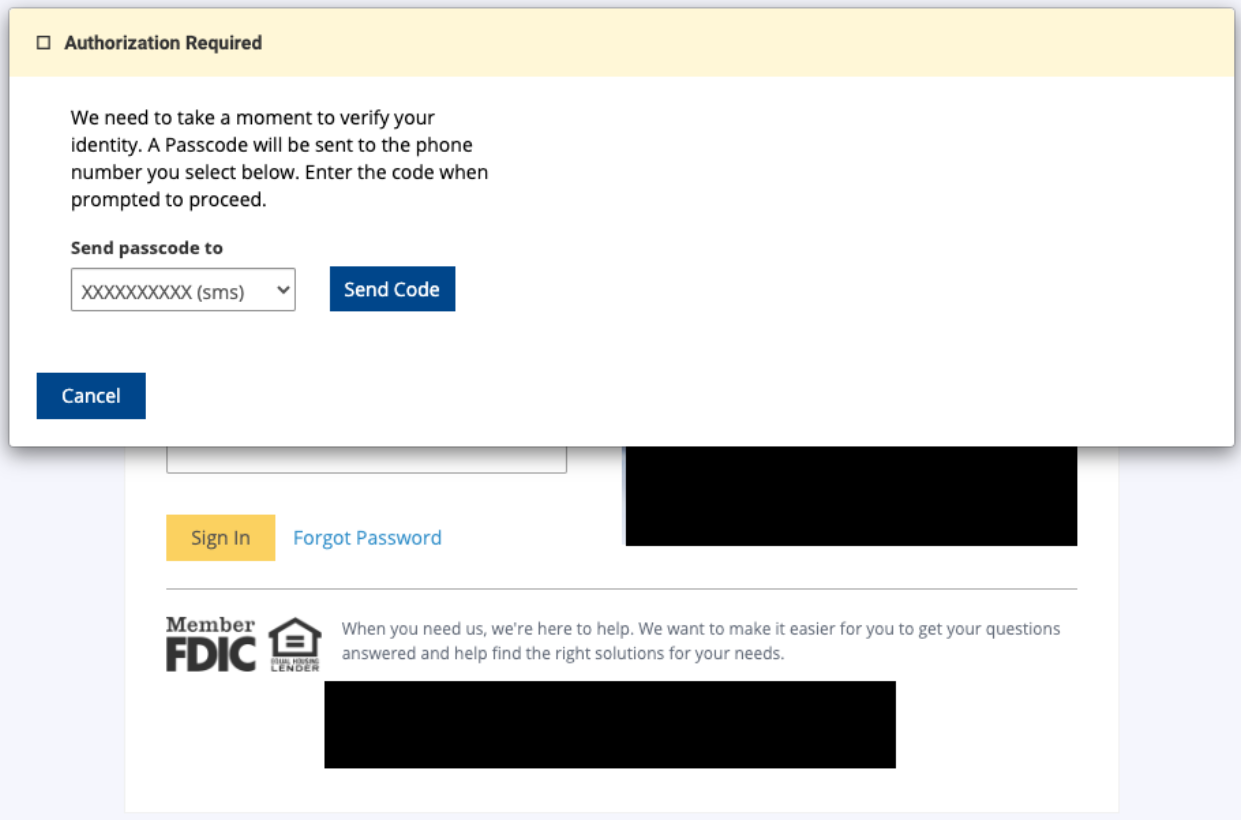
It has a number of operational states decided by a “mlink” flag set by the server, together with injecting prompts for cellphone numbers or OTP tokens, displaying error messages, or simulating web page loading, all a part of its data-stealing technique.
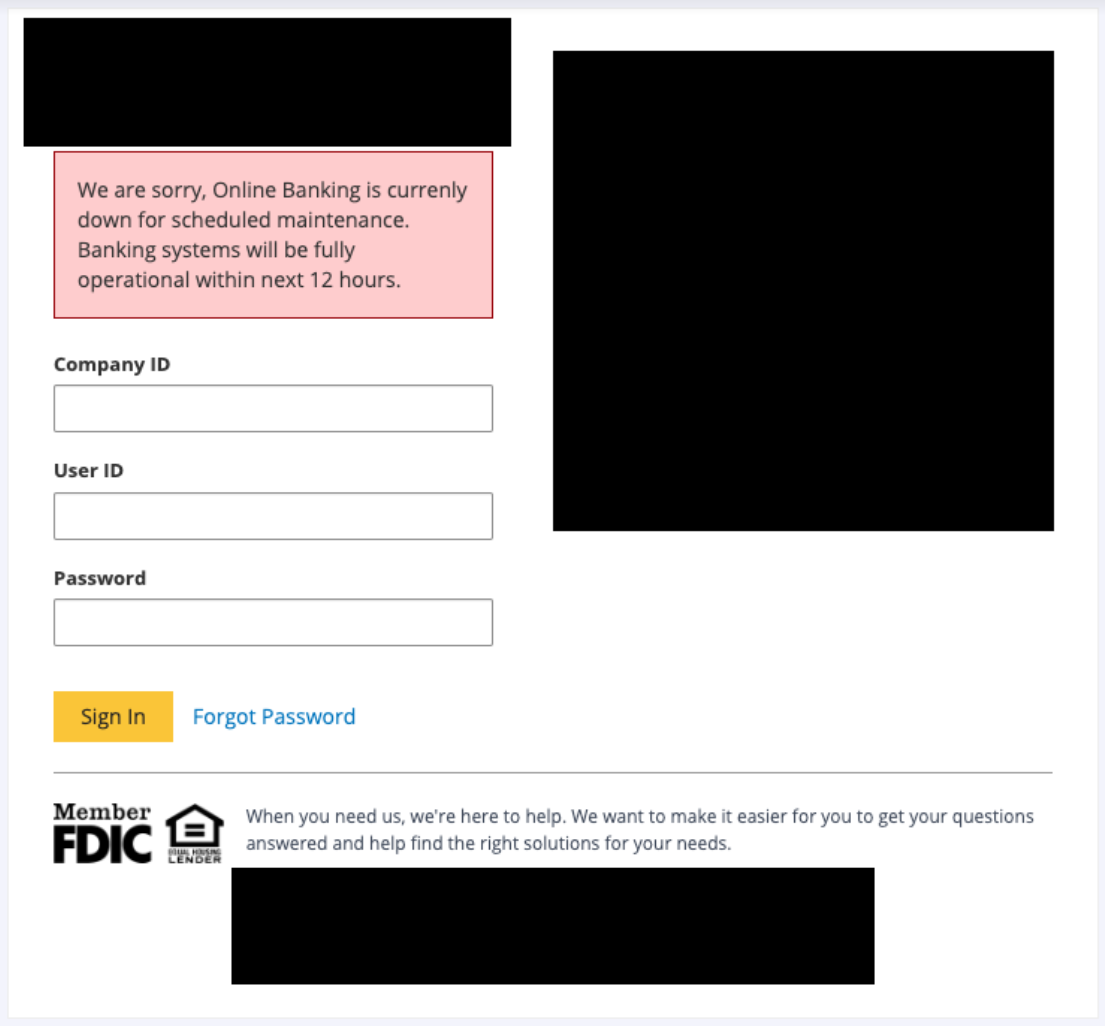
IBM says 9 “mlink” variable values may be mixed to order the script to carry out particular, distinct knowledge exfiltration actions, so a various set of instructions is supported.
The researchers have discovered free connections between this new marketing campaign and DanaBot, a modular banking trojan that has been circulated within the wild since 2018 and was not too long ago seen spreading through Google Search malvertising selling pretend Cisco Webex installers.
Based on IBM, the marketing campaign remains to be underway, so heightened vigilance is suggested when utilizing on-line banking portals and apps.

