| Dec 19, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) A low-cost know-how involving nanoparticles loaded with antibiotics and different antimicrobial compounds that can be utilized in a number of assaults on infections by the bacterium liable for most instances of tuberculosis has been developed by researchers at São Paulo State College (UNESP) in Brazil and is reported in an article revealed within the journal Carbohydrate Polymers (“Antimicrobial peptides grafted onto the floor of N-acetylcysteine-chitosan nanoparticles can revitalize medicine in opposition to medical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis”). Outcomes of in vitro assessments counsel it may very well be the idea for a remedy technique to fight multidrug bacterial resistance.
|
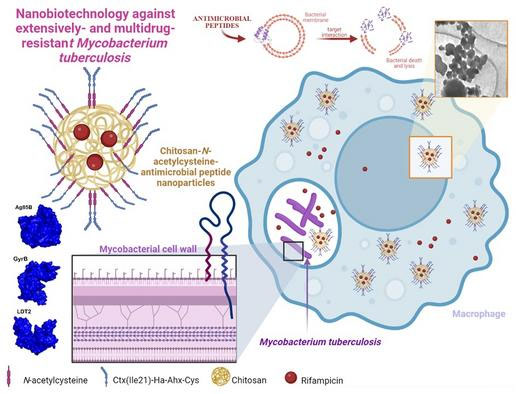 |
| Graphical summary of the examine. (Picture: Cesar Augusto Roque-Borda)
|
|
In line with Brazil’s Well being Ministry, some 78,000 instances of tuberculosis had been notified in 2022, 5% greater than within the earlier yr and greater than in some other nation within the Americas. Along with the rise in incidence, the variety of instances involving multidrug-resistant strains can be rising.
|
|
The primary agent of the illness is the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis, some of the deadly micro organism recognized to scientists. Transmission happens through inhalation of bacilli, which migrate to the pulmonary alveoli, inflicting irritation of the airways and ultimately destroying lung tissue.
|
|
The usage of nanotechnology is among the novel remedy methods thought of most promising by scientists world wide in opposition to multidrug-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis. The UNESP examine analyzed the antitubercular exercise of nanoparticles comprising N-acetylcysteine (an over-the-counter complement), chitosan (a pure compound derived from the outer skeleton of shellfish), an antimicrobial peptide initially remoted from the pores and skin of a Brazilian frog species, and rifampicin (an antibiotic generally used to deal with tuberculosis).
|
|
The outcomes confirmed that the nanoparticles considerably inhibited development of the illness and overcame resistance to the drug with out inflicting cell injury.
|
|
In vitro assays had been carried out with M. tuberculosis-infected fibroblasts, the principle cells energetic in connective tissue, and macrophages, cells of the innate immune system and a key element of first-line protection in opposition to pathogens.
|
|
“Rifampicin is taken into account out of date for sure strains of the bacillus, however in our examine, we revitalized and optimized it with antimicrobial peptides which were confirmed to assist fight the illness,” stated Laura Maria Duran Gleriani Primo, first writer of the article and an undergraduate pupil at UNESP’s College of Pharmaceutical Sciences with a scientific initiation grant.
|
|
“These peptides work together with numerous receptors in several elements of the bacterium, in each the membrane and periplasm. We discovered that they revitalized rifampicin, which turned much more energetic inside macrophages,” stated Cesar Augusto Roque-Borda, joint first writer of the examine and a PhD candidate in UNESP’s Program of Graduate Research in Biosciences and Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. The periplasm is a area of bacterial cells that lies between the interior cytoplasmic and outer bacterial membranes of the cell envelope.
|
Prospects
|
|
Standard remedy of tuberculosis entails concomitant use of a number of antiobiotics for six months to about two years relying on the affected person’s response and the bacterium’s resistance. The researchers count on their method to shorten this time.
|
|
“From the examine, we all know it’s doable to insert a substantial focus of antibiotic and peptides into macrophages – sufficient to spice up the impact of the remedy,” stated Fernando Rogério Pavan, final writer of the article and a professor at UNESP’s College of Pharmaceutical Sciences. “Our expectations for future analysis embody utilizing this kind of nanotechnology with different medicine and slow-release medicines in order that sufferers don’t must take their remedy on daily basis.”
|
|
The subsequent step might be to verify the in vitro findings by the use of in vivo trials and examine the usage of the nanoparticles to fight different ailments that require remedy for lengthy durations.
|