Johns Hopkins researchers have recognized minuscule particles that supercharge therapeutic most cancers vaccines, which prepare the immune system to assault tumors. These new lipid nanoparticles—tiny constructions made from fats—not solely stimulate a two-pronged immune system response that enhances the physique’s skill to combat most cancers but additionally make vaccines more practical in focusing on tumors.
“This analysis marks a pivotal turning level in our understanding of how lipid nanoparticles could be harnessed to optimize anticancer immunity,” stated Hai-Quan Mao, director of Johns Hopkins’ Institute for NanoBioTechnology and professor within the Whiting College of Engineering’s Division of Supplies Science and Engineering. “Our findings unlock new avenues for enhancing the efficacy of RNA-based remedies for most cancers and infectious illnesses.”
The workforce’s outcomes seem in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
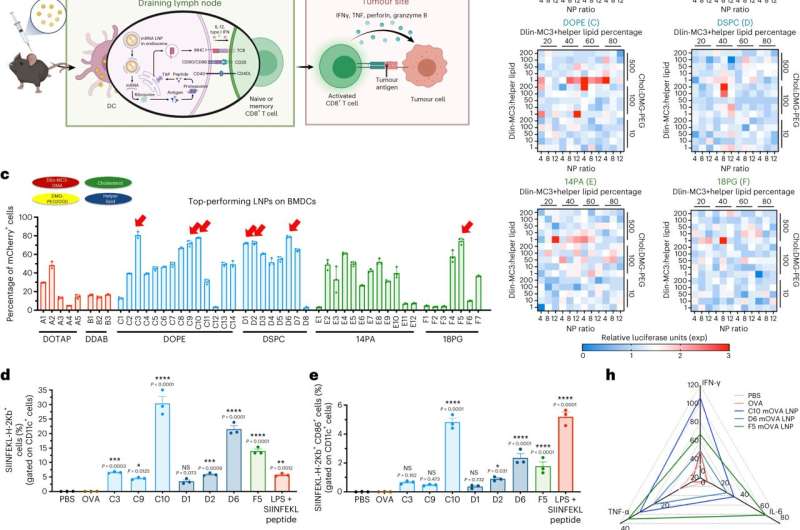
Lipid nanoparticles, made well-known for his or her use in delivering messenger RNA in COVID-19 vaccines, have gained consideration as carriers in most cancers immunotherapy. Earlier analysis targeted on optimizing lipid nanoparticles to set off a robust response by T helper 1 cells, cells that allow the immune system to determine and assault cancerous cells.
Utilizing a brand new screening technique, Mao and Yining Zhu, a biomedical engineering Ph.D. candidate, and collaborator Sean C. Murphy, professor of pathology on the College of Washington, fine-tuned the composition of lipid nanoparticles to customise and maximize immune-response activation. They recognized lipid nanoparticles that generated responses concurrently utilizing two parallel pathways to current tumor antigens to each Th1 and Th2 cells, one other kind of helper cell.
The workforce additionally mixed lipid nanoparticles with “checkpoint inhibitor therapy,” a kind of most cancers immunotherapy drug that helps the immune system acknowledge and assault most cancers cells. These inhibitors block “checkpoints:” molecules on immune cells that both stimulate or inhibit an immune response. Most cancers cells generally evade these checkpoints and thus go undetected by the immune system. The Mao workforce’s LNPs improve the therapeutics’ skill to scale back tumor dimension and prolong affected person survival time.
The researchers say that their examine is exclusive as a result of it demonstrates that lipid nanoparticles can enhance each Th1 and Th2 responses, producing coordinated assaults on most cancers by a number of immune cell sorts.
“This dual-attack method represents a brand new advance in most cancers therapy,” Zhu stated.
Extra info:
Yining Zhu et al, Screening for lipid nanoparticles that modulate the immune exercise of helper T cells in direction of enhanced antitumour exercise, Nature Biomedical Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41551-023-01131-0
Offered by
Johns Hopkins College
Quotation:
Nanoparticles amplify potential most cancers vaccine energy (2023, December 14)
retrieved 14 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-nanoparticles-amplify-potential-cancer-vaccine.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.


