Characterization of the synthesized Nano-Se
The synthesis of Nano-Se on this examine utilized ascorbic acid and chitosan to stop the aggregation of nanoparticles and enhance the bioavailability of Nano-Se [30]. The artificial course of was taken as full after resolution grew to become purple (Further file 1: Fig. S1A). As a way to examine the common particle measurement and form of the synthesized Nano-Se, SEM and TEM observations have been performed. Dynamic Gentle Scattering (DLS) evaluation was additionally used to outline the particle measurement distribution and polydispersity index (PDI) [31]. The floor traits and morphology of the synthesized Nano-Se have been studied by SEM and TEM. Sodium selenite was dispersed by chitosan and ascorbic acid, and the floor of Nano-Se was uniform and clear. SEM (Further file 1: Fig. S1B) and TEM (Further file 1: Fig. S1G, J) pictures monodisperse spherical Nano-Se with a measurement between 50 and 200 nm. The morphology was additional validated by AFM (Further file 1: Fig. S1K). DLS expertise outlined the everyday particle measurement distribution, which was estimated to be 72.4 nm (Further file 1: Fig. S1M). The polydispersity index (PDI) calculated from DLS information, the place PDI values < 0.05 are match greatest to the monodisperse mannequin, whereas PDI values > 0.7 are thought-about to point a polydispersity diffusion of particles [32]. In our examine, the synthesized Nano-Se has a PDI worth of 0.085, indicative of a medium dispersity. Power dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis is a technique used for elemental evaluation [33]. The fundamental construction and purity of the synthesized Nano-Se have been decided by EDX, as proven in Further file 1: Fig. S1D–J. The precise absorption peak of Nano-Se (1.74 keV) corresponds to Selenium, with no different aspect peak detected within the spectrum (Further file 1: Fig. S1E). EDX mapping confirmed the composition of the Nano-Se, indicating the presence of C, O and Se (Further file 1: Fig. S1H–J). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra have been in line with the Se section (Further file 1: Fig. S1N). Further file 1: Fig. S1O depicts the FTIR spectrum of the synthesized Nano-Se, which exhibits an expanded band width of 3266 cm−1 (≡C–H stretching band) indicating the existence of the alkyne. The medium-strong spike evident at 1637 cm−1 is attributable to carbonyl C = O, confirming the presence of an amide group.
Results of Nano-Se on the incidence of powdery mildew illness in melon leaves
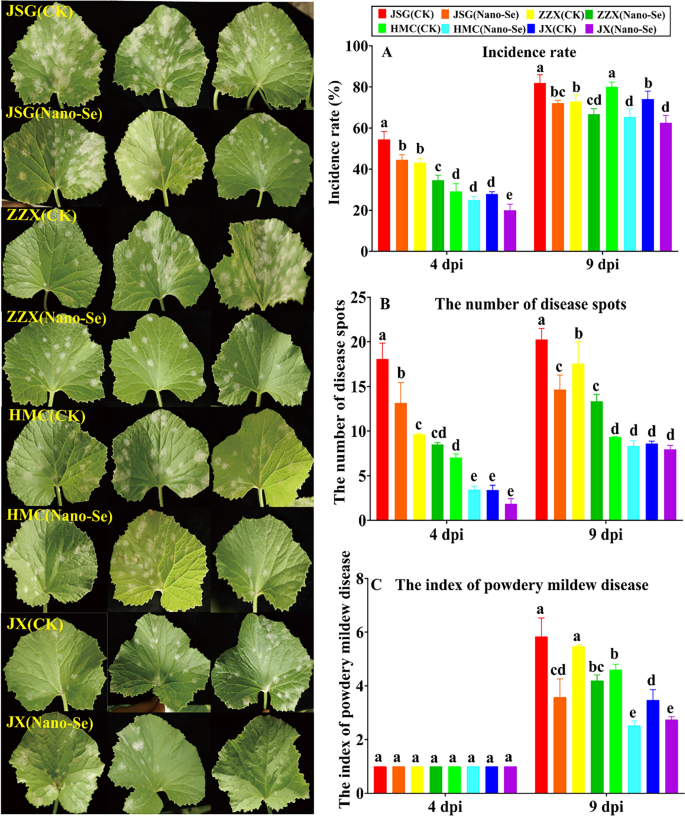
The results of the Nano-Se therapy on the incidence of powdery mildew in melon cultivars of differing resistances is proven in Fig. 1. At 4 dpi, the Nano-Se therapy considerably lowered the incidence of powdery mildew in JSG, ZZX and JX vegetation by 18, 20 and 28%, respectively. At 9 dpi, the incidence fee of powdery mildew in JSG, ZZX, HMC and JX vegetation have been considerably lowered by 12, 8, 18 and 16%, respectively (Fig. 1A). Relative to their controls, the Nano-Se therapy considerably lowered the variety of illness spots in JSG and HMC vegetation by 27 and 51%, respectively and at 9 dpi by 28 and 24% in JSG and ZZX vegetation, respectively (Fig. 1B). No important impact of the Nano-Se therapy on the index of powdery mildew illness may very well be detected at 4 dpi, whereas at 9 dpi, the index was considerably lowered in all 4 cultivars by 21–45% (Fig. 1C). Nano-Se was reported to an efficient and financial different to regulate fungal plant pathogens of faba bean [34].
Impact of Nano-Se on the incidence of powdery mildew in leaves of melon cultivars of differing resistance at totally different an infection levels. JSG, ZZX, HMC and JX symbolize the 4 melon cultivars with totally different resistances to powdery mildew, that are Jia shi, Zao zui xian (vulnerable) and Huang meng cui, Jun xiu (resistant), respectively. CK and Nano-Se symbolize the management leaves and people sprayed with 5.0 mg⋅L−1 Nano-Se, respectively. dpi: days put up inoculation. The totally different lowercase letters above the bars point out a big distinction (p< 0.05) between the remedies and the error bars symbolize normal deviations (n = 4)
Nano-Se remedies of soil or vegetation can improve plant resistance to fungal pathogens [35,36,37]. Nevertheless, how Nano-Se achieves this protecting impact stays unclear. On this examine, Nano-Se was proven to cut back the illness index in melon contaminated with a foremost agent of powdery mildew, P. xanthii by 21–45% (Fig. 1) and that this occurred with will increase in lively oxygen species scavenging, polyamine synthesis, phenylpropanoid metabolism and modifications in plant hormone ranges. The results of the foliar utility of Nano-Se on the melon stem weights within the 4 melon cultivars are proven in Further file 2: Desk S3. In contrast with the management group, the Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated the recent weight of stems in JSG, ZZX and JX vegetation at 0 dpi by 62, 76 and 24%, respectively, and elevated dry weight of stems in JSG, ZZX and HMC vegetation by 79, 23 and 93%, respectively.
Impact of the Nano-Se therapy on structural alterations in melon leaves contaminated with P. xanthii
The alterations in melon leaf anatomical group after powdery an infection are lowered in Nano-Se handled vegetation
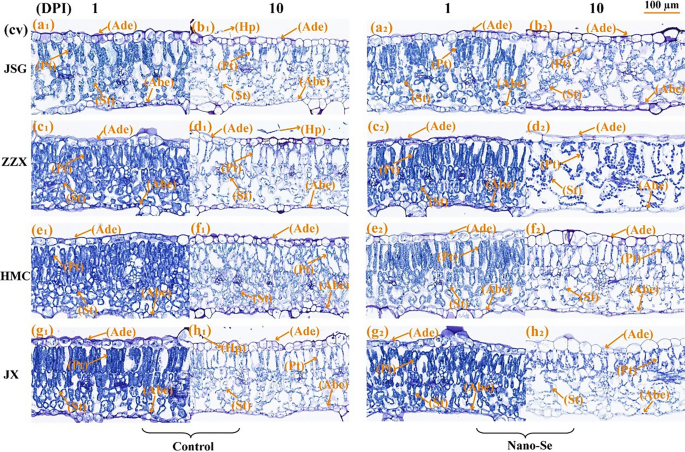
Leaf construction is affected by and might adapt to altering environments [38, 39]. As proven in Fig. 2, the anatomical construction of melon leaves largely consists of the (high to backside) adaxial dermis (Ade), palisade tissue (Pt), spongy tissues (St) and the abaxial dermis (Abe). The Ade and Abe are each mobile monolayers. The Ade cells have been flat and almost rectangular, whereas these of the Abe have been small, irregular in form and tightly packed. The tissue compactness after the Nano-Se therapy was greater than that of the management group (Further file 2: Desk S4), and a considerable amount of mycelium was connected to the adaxial dermis of the management leaves of the vulnerable cultivar at 10 dpi. The tissue sections of inoculated melon leaves (Fig. 2b1, d1, h1) clearly confirmed numerous hyphae (Hp) connected to the higher floor of leaf epidermal cells at 10 dpi, whereas no invading hyphae have been noticed within the Pt or St. At 1 dpi, the tissue construction of melon leaves (Fig. 2a1–h1) confirmed an orderly association to the Pt cells and a comparatively compact St. Nevertheless, at 10 dpi (Fig. 2a2–h2), the Pt and St have been loosely organized.
Anatomical structural traits of leaf mesophyll cells contaminated with powdery mildew at 1 and 10 dpi in vulnerable and resistance cultivars with or with out Nano-Se therapy. The panels (a1, a2, b1, b2), (c1, c2, d1, d2) and (e1, e2, f1, f2), (g1, g2, h1, h2) symbolize the paraffin part pictures of powdery mildew vulnerable (JSG, ZZX) and resistant cultivars (HMC, JX) at 1, 10 dpi within the management and Nano-Se therapy group, respectively. Key: Ade: adaxial dermis; Abe: abaxial dermis; Pt: Palisade tissue; Sp: Spongy tissue; Hp: Hyphae
The anatomical traits of contaminated melon leaves at 1 dpi have been proven in Further file 2: Desk S4. Leaf thickness, stomatal density and spongy tissue thickness considerably affected the resistance of loquat leaf spot illness [40]. The leaf thickness of all 4 cultivars have been considerably elevated within the Nano-Se handled vegetation by 11–34%. The thickness of the Ade of HMC and JX leaves was additionally considerably elevated after Nano-Se therapy by 33 and 31%, respectively. The palisade tissue thickness of ZZX and JX Nano-Se handled leaves considerably elevated by 17 and 21%, respectively. The anatomical traits at 10 dpi melon leaves are proven in Further file 2: Desk S4. Relative to their controls, the Nano-Se therapy resulted in considerably elevated leaf thickness in JSG, HMC and JX cultivars by 12, 17 and 42%, respectively. The Ade thickness of JSG after Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated by 41%. Within the Nano-Se group, the thickness of the Abe and Pt layers in HMC and JX leaves confirmed important will increase of 53, 17, 37 and 73%, respectively. In ZZX, HMC and JX, the Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated the Pt to St ratio by 63, 33 and 20%, and the tissue compactness by 50, 17 and 24%, respectively.
Results of Nano-Se foliar therapy on fungal growth and melon leaf cell ultrastructural modifications after an infection with P. xanthii
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations of melon leaves at totally different levels of powdery mildew an infection are proven in Further file 1: Fig. S2. To spotlight the ultrastructural results of P. xanthii and the amelioration of such by Nano-Se, solely the vulnerable cultivars have been studied. Because the an infection progresses the mycelial community turns into denser, with larger hyphal leaf penetration and the manufacturing of many conidiophores. When the mycelium invades into the leaves, it produced haustoria, which can have an effect on leaves. In contrast with the management vegetation, the mycelial density on the leaf floor of Nano-Se handled vegetation was lowered. Within the current analysis, Nano-Se was proven to assist preserve the construction of the palisade and spongy tissue layers and to cut back the variety of mycelia detected by SEM in these vegetation (Further file 1: Fig. S2a2–f2).
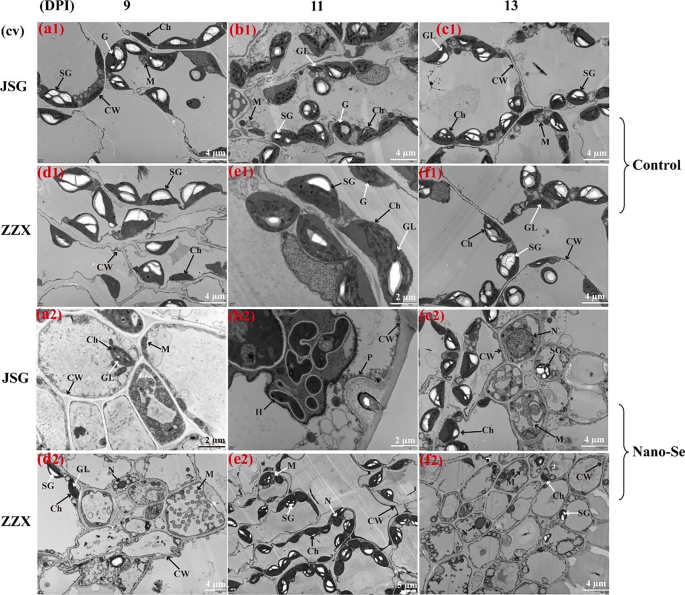
The cell ultrastructural traits of melon leaf cells have been studied with transmission electron microscope (TEM) at totally different levels of powdery mildew an infection (Fig. 3). Because the an infection progressed, the palisade chloroplasts swelled, grew to become extra spherical and clumped collectively. With the rise in chloroplast deformation, the starch granules modified from lengthy strips to oval or triangular, the osmiophilic granules in cells elevated, and the grana lamellar construction modified considerably (panels b1, c1–2, f1). The cell wall serves as a major protection towards fungal invasion and is quickly and domestically modified in response to fungal an infection, together with the formation of encapsulating papillae [41]. Within the early stage of fungal contact and cell penetration, vegetation cells type a papilla between the cell wall and the plasma membrane to impede fungal penetration. An instance of that is given in panel b2. Nevertheless, no papillae have been present in JSG leaves of the management group, which was in line with the SEM outcomes. The intrusion plugs of powdery mildew penetrate the papillae to type haustoria. The epidermal cells of JSG leaves handled by Nano-Se have been crammed by a number of haustoria at 11 dpi. The papilla construction was noticed in Nano-Se handled vegetation by TEM (Fig. 3b2), which indicated that the Nano-Se pretreatment enhanced the resistance of melon vegetation.
Transmission electron microscopic (TEM) of management and Nano-Se handled melon leaves at totally different an infection levels of powdery mildew an infection. (a), (b), (c), (d), (e) and (f) symbolize the cultivars JSG and ZZX at 9. 11 and 13 dpi, respectively. Panels 1 and a couple of symbolize the management and handled leaves (5.0 mg L-1), respectively
Results of Nano-Se on melon leaf chitinase (CHT) and β-1, 3-glucanase (GLU) after an infection with P. xanthii
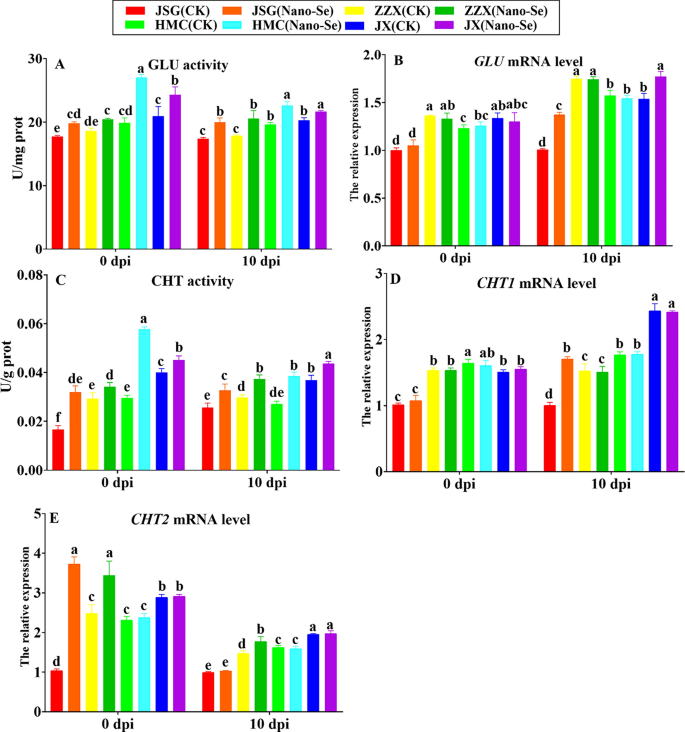
Pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins are essential parts of plant protection [42]. Members of the GLU and CHI PR households catalyze the degradation of fungal cell partitions [43]. The affect of Nano-Se on melon leaf CHT and GLU on the ranges of enzyme and transcriptional exercise is proven in Fig. 4. Previous to an infection (0 dpi), Nano-Se therapy resulted in considerably greater GLU actions in all 4 cultivars (10–36%). At 10 dpi, Nano-Se therapy additionally considerably elevated GLU exercise (7–15%) in 4 cultivars. Earlier than an infection (0 dpi), the degrees of GLU mRNA have been largely unaffected by Nano-Se therapy in all 4 cultivars. At 10 dpi, GLU mRNA ranges in ZZX and HMC remained largely unaffected, whereas GLU mRNA ranges in JSG and JX have been considerably elevated by 15–36%. GLU exercise was proven to induce the systemic response in vegetation by releasing polymers from the fungal cell wall [44].
Results of Nano-Se on leaf protection enzyme exercise and mRNA ranges at 0 and 10 dpi. The determine structure, cultivars and situations utilized are as in Fig. 1
Chitin is without doubt one of the foremost parts of fungal cell partitions consisting of a homopolymer of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine linked by means of β (1–4) bonds and might induce the plant defensive response [45]. Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated CHT actions at 0 dpi (12–95%) and at 10 dpi, (19–42%) within the 4 cultivars. At 10 dpi, Nano-Se considerably upregulated the expressions of CHT1 in JSG and CHT2 in ZZX by 70% (D) and 20% (E), respectively. Conversely, Nano-Se therapy group considerably elevated CHT2 expression in JSG and ZZX at 0 dpi by 259 and 38%, respectively. On this examine, Nano-Se was proven to extend the actions and mRNA ranges of GLU and CHI (Fig. 4), indicating they may play a task within the Nano-Se mediated enhanced resistance to P. xanthii. Sugar signaling is intently associated with cell proliferation, plant development and growth and interacts with many different sign pathways [46].
Results of Nano-Se therapy on LOX and plant hormones in melon leaves contaminated with P. xanthii
The results of Nano-Se therapy teams on LOX exercise and mRNA ranges of melon leaves contaminated with powdery mildew weren’t important (Further file 1: Fig. S3). The results of Nano-Se on plant hormone ranges in melon leaves inoculated with powdery mildew pathogens are proven in Further file 1: Fig. S4. An infection was seen to lower the IAA ranges in management vegetation with out the Nano-Se therapy. Conversely, Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated the IAA content material within the 4 cultivars at each 0 dpi (28–124%) and 10 dpi cultivars (43–172%). IAA therapy elevated the resistance of kiwifruit to Botrytis cinerea, with the promotion of excessive actions of pathogen resistance-related protection enzymes [47].
The JA and SA signaling pathways have been reported to play key and built-in roles within the poplar response to fungal an infection [48]. The leaf SA content material was additionally elevated in response to an infection within the management group with out the Nano-Se therapy. Nevertheless, relative to the management ranges, the SA ranges in Nano-Se handled vegetation have been considerably elevated the SA content material within the 4 cultivars at each 0 dpi (61–122%) and 10 dpi (24–73%). Chitosan enhanced the resistance of apple to Glomerella leaf spot by means of the SA sign pathways [49], which was in line with this examine (Further file 1: Fig. S4). The synthesis and sign transduction of JA pathway have been inhibited throughout the an infection of Botrytis cinerea [50]. In distinction, though an infection with P. xanthii induced greater JA ranges, the Nano-Se therapy had no additional important impact. On this examine, there was no important distinction in gene expression concerned in JA synthesis, together with LOX1, LOX2, LOX8, LOX9 and LOX10 (Further file 1: Fig. S3). The upregulation of gene expression in plant hormone sign pathways, together with these of SA and JA, has been reported to be concerned in fruit protection towards molds [51]. SA was proven to activate catechin and proanthocyanidins biosynthesis in poplar bushes towards rust an infection [52].
Results of Nano-Se on antioxidant capability of melon leaves contaminated with P. xanthii
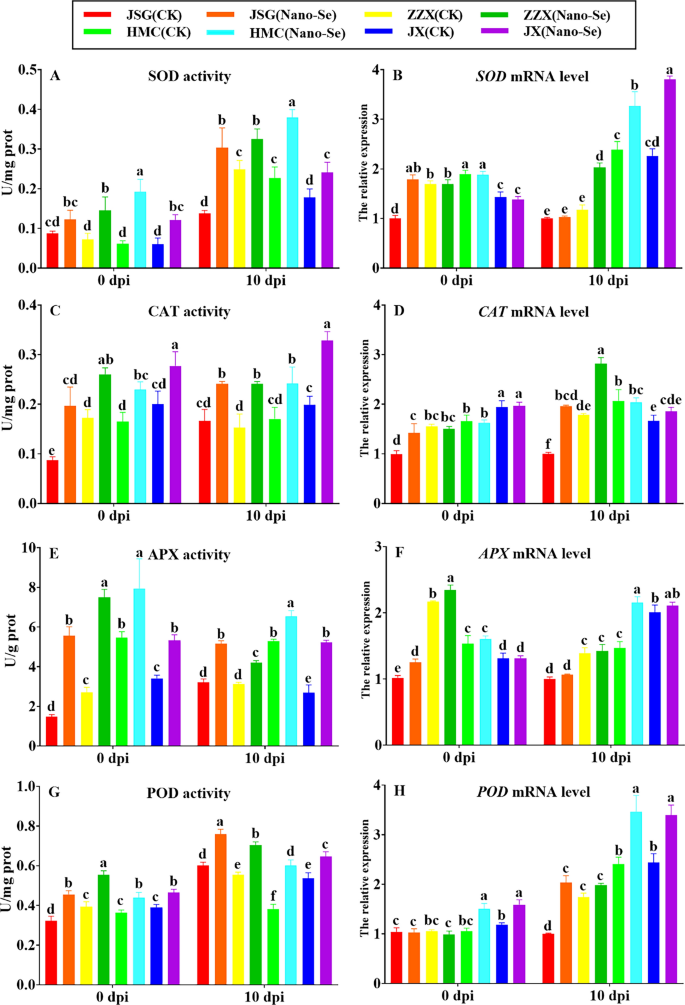
The results of Nano-Se on the leaf antioxidant enzyme actions earlier than (0 dpi) and after (10 dpi) P. xanthii an infection are proven in Fig. 5. Nano-Se therapy resulted in a big enhance in SOD exercise in all 4 cultivars. Each previous to (41–215%) and following an infection (31–120%; A). Earlier than an infection (0 dpi), SOD mRNA ranges have been largely unaffected by Nano-Se in ZZX, HMC, and JX, however considerably elevated in JSG by 44%. In distinction, at 10 dpi, Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated SOD mRNA ranges in ZZX, HMC and JX (37–72%; B). Quiterio-Gutierrez et al. [53] confirmed that the mixed utility of Nano-Se and Nano-Cu lowered the incidence of Alternaria solani in tomato vegetation, with the induction of upper leaf actions of SOD, APX, glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and PAL. Nano-Se therapy elevated CAT exercise each earlier than (38–126%) and after an infection (42–65%; C) within the 4 cultivars. Earlier than an infection (0 dpi), the CAT mRNA ranges have been largely unaffected by Nano-Se in ZZX, HMC and JX, however considerably elevated by 30% in JSG. At 10 dpi, the Nano-Se therapy resulted in important will increase (58–96%) in CAT mRNA ranges in JSG and ZZX, however not in HMC or JX (D). Nano-Se therapy elevated APX exercise (45–279%) within the 4 cultivars each earlier than (45–279%) and after an infection (24–94%; E).
Impact of Nano-Se on leaf antioxidant actions at 0 and 10 dpi. The determine structure, cultivars and situations utilized are as in Fig. 1
Earlier than an infection (0 dpi), Nano-Se therapy resulted in elevated APX mRNA ranges have been elevated by Nano-Se earlier than an infection in JSG and ZZX (8–23%). In distinction, at 10 dpi, Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated APX mRNA ranges solely in HMC (32%; F). POD exercise was elevated by Nano-Se in all 4 cultivars previous to (19–41%) and following an infection (21–58%; G). Will increase in enzymes concerned in ROS scavenging, together with POD, has been linked to the improved illness resistance of loquat fruit to C. gloeosporioides [54]. Nevertheless, earlier than an infection (0 dpi), Nano-Se therapy resulted in elevated POD mRNA ranges have been solely elevated previous to an infection in HMC and JX (34–43%) and after an infection in JSG, HMC and JX (28–51%; H). Following an infection, the antioxidant capability of disease-resistant cultivars was stronger than in disease-susceptible cultivars within the management group with out Nano-Se utility. The antioxidant capability of melon seedlings handled with Nano-Se elevated each earlier than and after an infection with P. xanthii powdery mildew, however to totally different levels.
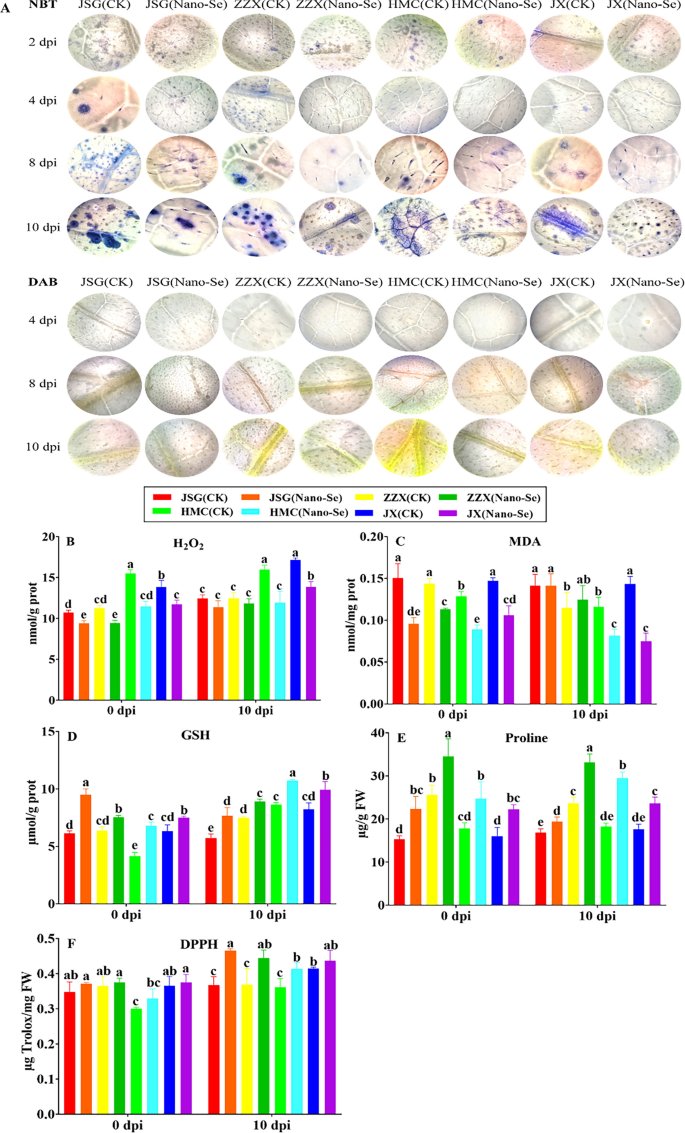
The immune response of vegetation to pathogens can contain callose deposition, the buildup of ROS and cell loss of life [55]. The impact of Nano-Se on ROS accumulation in leaves at totally different ages of powdery mildew an infection are proven in Fig. 6. Tissue observations of H2O2 and O2− at 2, 4, 8 and 10 dpi (Fig. 6A) confirmed that each ROS have been induced to greater ranges after an infection, indicating the next degree of oxidative stress, however that will increase in O2− have been detectable after 2 dpi, whereas will increase in H2O2 have been seen solely after 8 dpi. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) quickly accumulate in vegetation contaminated by microbial pathogens, and are essential parts of the plant protection response [56]. Notably, the buildup of each ROS was lowered by the Nano-Se therapy in all cultivars. To additional study the impact of Nano-Se on the antioxidant capability, radical scavenging and lipid peroxidation actions in melon leaves throughout powdery mildew an infection, the degrees of H2O2, MDA, GSH, proline and free radical scavenging/antioxidant exercise (utilizing DPPH) have been decided (Fig. 6B–F). Fungal ROS metabolism is central to the an infection course of, and essential in plant colonization [57]. Nano-Se was seen to extend leaf actions of SOD, CAT, APX and POD in addition to their gene expression (Fig. 5), which occurred with a discount in H2O2, O2− and MDA and a rise in GSH, proline and radical scavenging capability (Fig. 6).
Impact of Nano-Se on leaf ROS accumulation and lipid peroxidation at 0 and 10 dpi. The determine structure, cultivars and situations utilized are as in Fig. 1
The regulation of ROS ranges in pathogen-challenged vegetation performs a decisive position between vulnerable and resistant interactions [58]. In affirmation of histological commentary (Fig. 6A), Nano-Se therapy considerably lowered H2O2 accumulation in leaves at 0 and 10 dpi in all cultivars by 12–26% and 9–25%, respectively (B). Bai et al. [59] confirmed that H2O2 accumulation elevated considerably with the lower of complete antioxidant capability. Nano-Se considerably elevated the degrees of GSH at each 0 and 10 dpi within the all 4 cultivars by 18–63% and 19–34%, respectively (D). Nano-Se additionally promoted a big enhance in proline ranges at each 0 and 10 dpi in all cultivars by 39–46% and 16–61%, respectively (E). Based mostly on the DPPH assay, Nano-Se considerably elevated the antioxidant exercise at each 0 and 10 dpi in all cultivars by 3–10% and 5–27%, respectively (F). Nano-Se lowered the leaf MDA content material by 21–36% at 0 dpi, and by 30 and 48% at 10 dpi in cultivars HMC and JX, respectively (C). Wang et al. [60] reported that Na2SeO3 lowered H2O2 and MDA ranges in alfalfa and Cunha et al. [61] demonstrated that Na2SeO4 enhanced enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant metabolism in peanut vegetation.
Results of Nano-Se on the first metabolism of P. xanthii contaminated melon leaves
Sugar content material
Increased sugar contents have been reported to induce greater pathogen resistance in vegetation by selling cell wall lignification, flavonoids synthesis and the degrees of PR proteins [62]. Previous to the onset of an infection (0 dpi), Nano-Se handled vegetation of all cultivars confirmed important will increase in leaf soluble sugar, lowering sugar and sucrose contents by 16–36%, and 17–40% and 22–65%, respectively (Further file 1: Fig. S5A, B, C). The elevated ranges of sucrose have been accompanied by will increase in each sucrose phosphate synthase (52–206%) and sucrose synthase (24–91%) actions (D, E). At 10 dpi, the contents of soluble sugar, lowering sugar, sucrose and sucrose synthase exercise have been all decreased, however not considerably totally different between the management therapy with out Nano-Se utility and the Nano-Se therapy. In our examine, on the early stage of powdery mildew an infection, Nano-Se was seen to advertise will increase in soluble and lowering sugars, sucrose and associated enzyme actions (Further file 1: Fig. S5).
Results of Nano-Se on amino acid metabolism in melon leaves contaminated with P. xanthii
Amino acid homeostasis is interconnected with plant immune signaling pathways [63]. Relative to their controls, Nano-Se therapy had no discernable impact on complete free amino acid contents of the 4 cultivars both previous to or following an infection with powdery mildew (Further file 1: Fig. S6A). Nevertheless, Nano-Se handled vegetation of all cultivars confirmed a considerably greater content material of glutamate of at 0 dpi (52–107%; B) and people of ZZX, HMC and JX additionally confirmed important will increase of 44–56% at 10 dpi. Nano-Se additionally promoted will increase in glutamine synthase actions in all cultivars previous to an infection (16–24%) and in JSG and JX at 10 dpi by 32% and 17%, respectively (C). Vital will increase in leaf GABA content material have been noticed in all cultivars examined previous to an infection (21–88%) and at 10 dpi (50–199%) (D). The appliance of GABA was reported to extend plant tolerance to emphasize by regulating the expression of genes concerned in plant sign transduction, hormone, ROS and polyamine metabolism [64]. Hydroxyproline ranges have been additionally considerably elevated by Nano-Se in all 4 cultivars by 17–86% at 0 dpi and by 8–37% at 10 dpi (E). Within the current examine, the noticed enhance in amino acid content material of melon leaf after Nano-Se therapy occurred with will increase within the ranges of glutamate, GABA and GS exercise (Further file 1: Fig. S6).
Results of Nano-Se on secondary metabolism
Polyamine metabolism
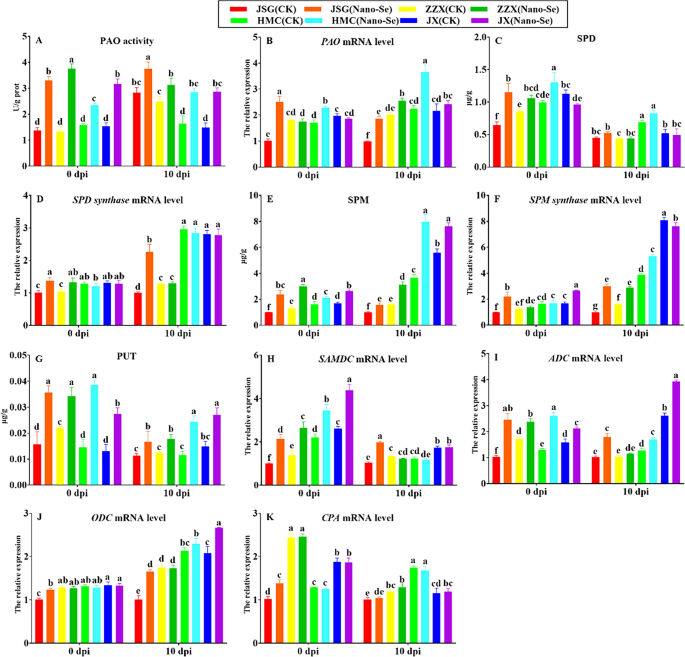
A attainable position free of charge polyamines and the regulation of polyamine catabolism in plant resistance has been proposed [65]. The PAO exercise in all cultivars was enhanced by the Nano-Se therapy at 0 and 10 dpi by 48–182% and 26–92%, respectively (Fig. 7A). These Nano-Se induced modifications have been accompanied by relative will increase in PAO expression in JSG (150%) and HMC (34%) previous to inoculation and in all contaminated cultivars at 10 dpi by 12–86% (B). At 0 dpi, the Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated SPD contents in JSG, ZZX and HMC by 78, 24 and 32%, respectively. Nevertheless, at 10 dpi, the modifications in SPD content material of 4 cultivars weren’t important (C). The Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated SPD synthase mRNA ranges in JSG, ZZX at 0 dpi by 36 and 27%, respectively (D).
In contrast with the management group, Nano-Se handled vegetation confirmed considerably elevated SPM ranges within the 4 cultivars at 0 and 10 dpi by 30–139% and 36–118%, respectively (E). At 0 dpi, the Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated SPM synthase mRNA ranges in JSG and JX by 122 and 58%, respectively and at 10 dpi, by 200, 78 and 37% within the JSG, ZZX and HMC cultivars, respectively (F). The Nano-Se therapy elevated PUT within the 4 cultivars at 0 and 10 dpi by 56–165% and 43–112%, respectively (G). Polyamines have been additionally urged to play an essential position in environmental stress responses [66] and the metabolism of primarily putrescine, spermine and spermidine can have an effect on the power of fungi to deal with environmental challenges [67].
S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase mRNA was elevated in all 4 cultivars at 0 dpi by 57–115%, whereas at 10 dpi, solely JSG confirmed a rise of 92% by Nano-Se (H). Aside from ZZX, Nano-Se therapy elevated arginine decarboxylase expression in three cultivars at 0 and 10 dpi by 34–140% and 34–76%, respectively (I). Conversely, no important results of Nano-Se therapy on the expression of ornithine decarboxylase and N-carbamyl putrescine hydrolase have been noticed (J, Okay). Conversely, the Nano-Se pretreatment potentiated PAO exercise, the degrees of SPD, SPM and PUT, in addition to the mRNA ranges of PAO, SPMS, S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase and arginine decarboxylase (Fig. 7).
Results of Nano-Se on melon leaf lignin metabolism
Further file 1: Fig. S7 exhibits that Nano-Se promoted will increase in lignin content material in all cultivars at each 0 and 10 dpi (17–49%; A). The buildup of phenylpropanoid-derived secondary metabolites, comparable to phenolic acids, flavonoids, and lignin have been related to citric plant protection towards fungi [68]. In our examine, the development of melon resistance to powdery mildew illness by Nano-Se was additionally proven to reinforce lignin synthesis (Further file 1: Fig. S7). In settlement, the buildup of lignin was proven to be linked to the development of antifungal exercise and the defensive response in citrus fruits [68]. Conversely, Nano-Se had no important impact on leaf CAD exercise or CAD and CCR mRNA ranges within the 4 cultivars at 0 or 10 dpi (B, C, D).
Alterations in phenylpropanoid metabolism in response to P. xanthii an infection and Nano-Se therapy
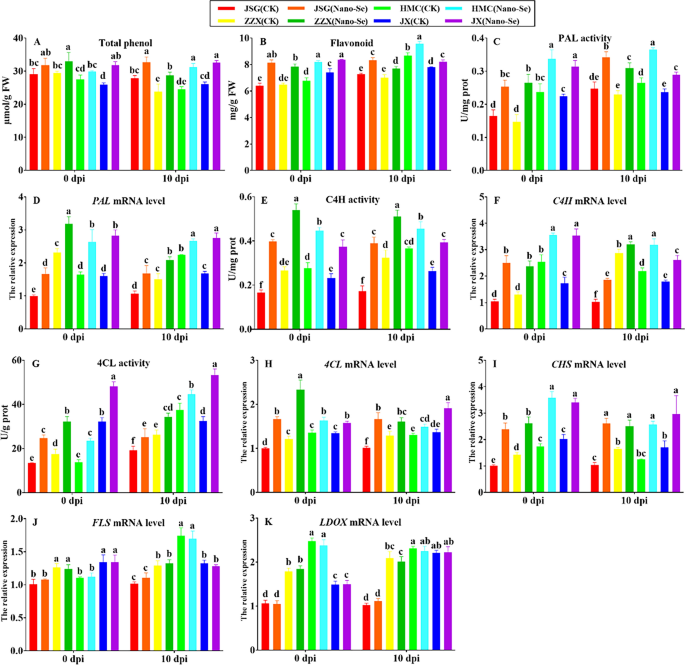
The affect of Nano-Se therapy teams on phenylpropanoid metabolism in melon leaves at totally different of P. xanthii an infection is depicted in Fig. 8. The Nano-Se therapy was seen to considerably enhance the full phenols in ZZX and JX cultivars at 0 dpi by 12–22%, respectively, whereas at 10 dpi, Nano-Se therapy teams considerably elevated the full phenol content material in all 4 cultivars by 17–27%, respectively (A). The flavonoid contents in all Nano-Se vegetation have been considerably elevated at 0 and 10 dpi by 13–27% and 5–15%, respectively (B). The Nano-Se therapy elevated PAL exercise within the 4 cultivars by 40–80% at 0 dpi and by 22–38% at 10 dpi (C). This was accompanied by important will increase in PAL mRNA ranges of in all 4 cultivars at 0 and 10 dpi by 37–76% and 18–64%, respectively (D). The flavonoids and phenolic acids have been proven linked to the development of antifungal exercise and the defensive response in citrus fruits [68]. Will increase in PAL exercise, flavonoid and complete phenol contents contribute to plant illness resistance [69].
Impact of Nano-Se on leaf phenylpropanoid metabolism at 0 and 10 dpi. The determine structure, cultivars and situations utilized are as in Fig. 1
Nano-Se therapy additionally elevated C4H exercise within the 4 cultivars at 0 and 10 dpi by 61–140% and 24–126%, respectively (E), which have been equally accompanied by respective will increase on the mRNA degree of 40–141% and 12–80% (F). Earlier than an infection (0 dpi), Nano-Se therapy elevated the 4CL exercise (50–84%) in 4 cultivars. At 10 dpi, Nano-Se therapy considerably elevated the 4CL exercise of the 4 cultivars by 19–64% (G). Nano-Se therapy teams considerably elevated 4CL mRNA ranges of all 4 cultivars at 0, 10 dpi by 18–67% and 14–65%, respectively (H). The Nano-Se therapy additionally elevated the CHS mRNA ranges within the 4 cultivars by 69–135% at 0 dpi and by 52–150% at 10 dpi (I). The Nano-Se therapy had no important impact on the mRNA ranges of FLS or LDOX in any cultivar (J, Okay). In our examine, the development of melon resistance to powdery mildew illness by Nano-Se was proven to reinforce phenylpropanoid metabolism (Fig. 8).
RNA-Seq evaluation of Nano-Se results on melon leaf gene expression in uninfected and P. xanthii contaminated seedlings
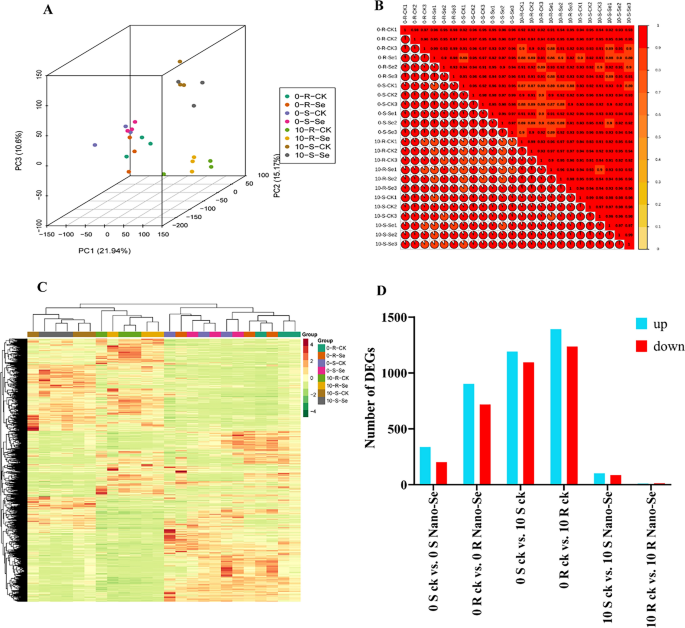
A PCA evaluation of leaf RNA-Seq information was performed with the samples of the vulnerable and resistant cultivars at 0 and 10 dpi, with and with out Nano-Se pretreatment. The PCA readily discriminated the 0 dpi and 10 dpi remedies, with PC1, PC2 and PC3 explaining 21.9%, 15.2% and 10.6% of the full variance, respectively. The melon leaf samples at 0 dpi and 10 dpi, in addition to the management and Nano-Se handled vegetation have been clearly distinguished (Fig. 9A). Based mostly on the correlation warmth map evaluation of FPKM values, it was discovered that there was correlation between the three organic replicates (Fig. 9B). A complete of 1,110,261,430 clear reads and 166.56 G clear bases have been obtained in all samples (Further file 2: Desk S5). As proven within the visualization of the warmth map, apparent hierarchical clustering of various kinds of samples may very well be seen (Fig. 9C). Previous to an infection (0 dpi), the numbers of DEGs detected in response to the Nano-Se therapy within the vulnerable (S; JSG) and resistant (R; HMC) cultivars have been 539 (338 up- and 201 down-regulated, Further file 1: Fig S8A) and 1621 (902 up- and 719 down-regulated, Further file 1: Fig S8B), respectively. In response to P. xanthii an infection (10 dpi), a bigger variety of DEGs have been detected in seedlings untreated with Nano-Se, the place 2285 (1191 up- and 1094 down-regulated) have been detected within the vulnerable cultivar JSG (Further file 1: Fig. S8C), and 2629 (1392 up- and 1237 down-regulated) have been detected within the resistant cultivar, HMC (Further file 1: Fig. S8D). Conversely, a lot fewer DEGs have been detected in contaminated seedlings that had been subjected to the Nano-Se pretreatment, the place 188 (102 up- and 86 down-regulated), and 23 (10 up- and 13 down-regulated) have been detected within the vulnerable and resistant cultivars, respectively. These outcomes are summarized in a bar chart in Fig. 9D.
A common transcriptomic evaluation of the melon seedling response to powdery mildew contaminated with or with out Nano-Se pretreatment. (A) Principal element evaluation, (B) Correlation evaluation, (C) Differential gene cluster evaluation and (D) Differential gene evaluation. The S and R symbolize the vulnerable cultivar JSG and resistant cultivar HMC at 0 and 10 dpi, respectively. CK, Nano-Se symbolize the management leaves and people sprayed with 5.0 mg⋅L−1 Nano-Se, respectively
The features of the DEGs recognized have been annotated from matched identifiers from 7 databases (KEGG, KOG, NR, Pfam, Swissprot, Tremble, and GO) (Further file 2: Desk S6). The organic features of DEGs have been subjected to GO enrichment evaluation. Within the comparability of management and Nano-Se therapy teams at 0 dpi, the principle enriched phrases indicated alterations in catalytic exercise, DNA polymerase exercise, monooxygenase exercise, nucleotidyl transferase exercise, RNA-directed DNA polymerase exercise, transferase exercise, chloroplast thylakoid, plastid thylakoid, coenzyme and tetrapyrrole binding. Between the situations of 0 and 10 dpi, each R and S cultivars primarily confirmed enrichment within the phrases chloroplast/thylakoid, photosynthetic membrane, plastid thylakoid, and thylakoid half (Further file 1: Fig S9). The principle differentially enriched phrases between the management and Nano-Se therapy group at 10 dpi have been bacterium and drug, secondary metabolic and biosynthetic course of and tetrapyrrole binding (Further file 1: Fig S10).
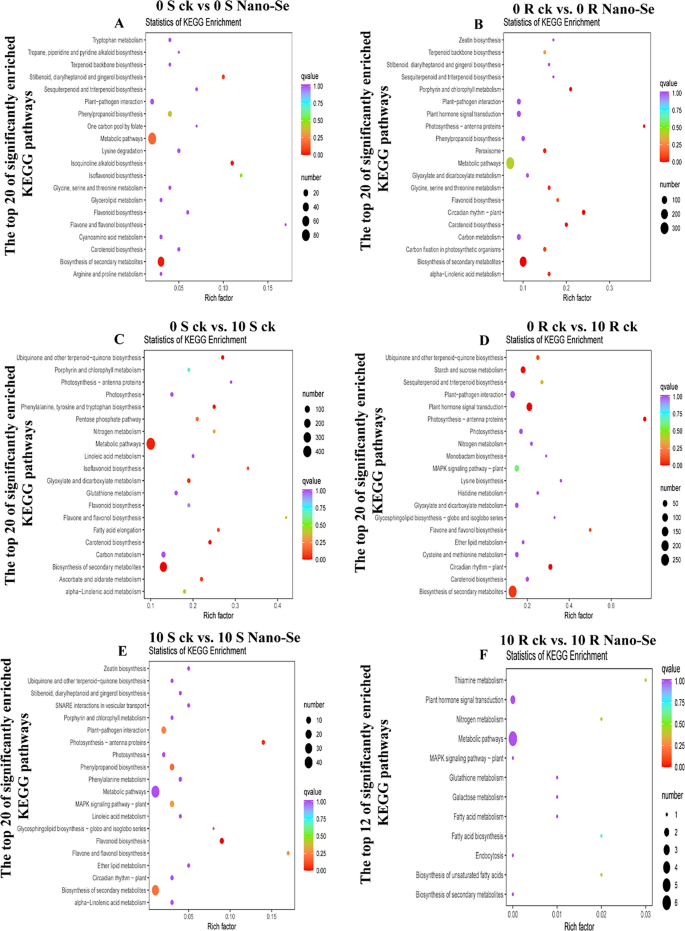
KEGG enrichment evaluation was additionally carried out. The DEGs obtained from the comparability teams of 0 S ck vs. 0 S Nano-Se, 0 R ck vs. 0 R Nano-Se, 0 S ck vs. 10 S ck, 0 R ck vs. 10 R ck, 10 S ck vs. 10 S Nano-Se, and 10 R ck vs. 10 R Nano-Se have been annotated on 78, 115, 123, 125, 64, and 126 KEGG pathways, respectively (Further file 2: Tables S7–S12), of which the 20 most importantly enriched pathways in every comparability are proven in Fig. 10. Particularly, the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites (ko01110) was considerably enriched in 4 comparisons (0 S ck vs. 0 S Nano-Se, 0 R ck vs. 0 R Nano-Se, 0 S ck vs. 10 S ck, and 0 R ck vs. 10 R ck). The flavonoid biosynthesis (ko00941; 0 R ck vs. 0 R Nano-Se), isoflavonoid biosynthesis (ko00943; 0 S ck vs. 10 S ck) and flavone and flavonol biosynthesis (ko00944; 0 R ck vs. 10 R ck) have been considerably enriched in two cultivars. KEGG pathway evaluation of tea vegetation handled with Na2SeO3 and Na2SeO4 revealed that many genes concerned in amino acid and glutathione metabolism have been up-regulated, and genes and proteins related to glutathione metabolism and biosynthesis of ubiquinone and terpenoid have been extremely expressed [70]. The DEGs related to the biosynthesis pathway of catechins, caffeine and theanine in tea have been affected by Nano-Se [71].
KEGG enrichment evaluation of the seedling leaf DEGs after powdery mildew an infection with or with out prior Nano-Se therapy. A: 0 S ck vs 0 S Nano-Se, B: 0 R ck vs 0 R Nano-Se, C: 0 S ck vs 10 S ck, D: 0 R ck vs 10 R ck, E: 10 S ck vs 10 S Nano-Se, F: 10 R ck vs 10 R Nano-Se. The Y-axis represents the enriched KEGG pathway, and the X-axis represents the wealthy issue. The dot measurement represents the variety of DEGs within the pathway, and the dot shade represents the q-value
Subsequently, the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, together with flavonoids and isoflavonoids would possibly play an essential position within the enhanced resistance to powdery mildew an infection displayed by Nano-Se handled vegetation. As well as, flavone and flavonol biosynthesis (ko00944) have been additionally enriched within the means of Nano-Se inducing resistance to P. xanthii an infection. After Na2SeO3 therapy, genes associated to phenylpropanoid, flavonoid and anthocyanin biosynthesis have been considerably up-regulated, ensuing within the accumulation of anthocyanin metabolites in grain wheat [72], which has similarities to the outcomes of this examine. The useful results of Nano-Se towards melon powdery mildew subsequently seems to be achieved by means of its results on a number of pathways. An inventory of the 18 most affected DEGs, together with genes for 2 antioxidant enzyme genes, 9 phenylpropanoid pathway genes, two flavonoid synthesis pathway genes and 5 glycosyl transferase genes, is offered in Further file 2: Desk S13 as genes worthy of additional investigation. The results of Nano-Se look like most evident previous to mildew an infection, indicating that Nano-Se largely impacts melon basal resistance, somewhat than reinforcing the plant response to an infection.
The focus of Nano-Se on this examine was 5.0 mg·L−1. We verified that the ready Nano-Se weren’t poisonous to vegetation. Melon seedlings at totally different levels of therapy with Nano-Se are proven in Further file 1: Fig S11. Low doses of selenium improved plant stress resistance by means of photosynthesis, whereas excessive doses of selenium interfered with nitrogen assimilation, leading to decreased nitrogen compound synthesis potential [73]. On this examine, the degrees of glutamate, GS and GABA related to the nitrogen cycle elevated after Nano-Se therapy, which additional indicated that 5 mg·L−1 Nano-Se just isn’t poisonous to melon. Low concentrations (20 μM) of selenates have been additionally proven to be useful for plant development, which was associated to the antioxidant impact of selenium [74].