Preparation and characterization of Hep-PDA-rGO nanosheets
A facile two-step method was developed to type the Hep-PDA-rGO nanosheets (Scheme 1A). Firstly, GO was chemically deoxidized by mixing it with heparin to generate heparin-adherent rGO (Hep-rGO). The functionalization of heparin on each side of the rGO floor occurred via non-covalent interactions, equivalent to hydrophobic and hydrogen bond interactions. The robust unfavorable cost density ensuing from the carboxyl and sulfonic teams in heparin prevented the Hep-rGO from aggregating as a consequence of electrostatic repulsion [22]. Secondly, Hep-rGO was added to the PDA answer (dopamine was pre-polymerized below oxidative and alkaline situation for 20 minutes), and additional lowered by PDA for 10 minutes to generate Hep-PDA-rGO. After that, the Hep-PDA complicated [23] self-assembled via ionic forces successfully immobilized onto the rGO floor, enhancing the soundness of the nanosheets. Subsequently, the Hep-PDA complicated served not solely as a robust decreasing agent but additionally as an efficient stabilizer for the rGO nanosheets. The composition of every rGO nanosheet is proven in Further file 1: Desk S1.
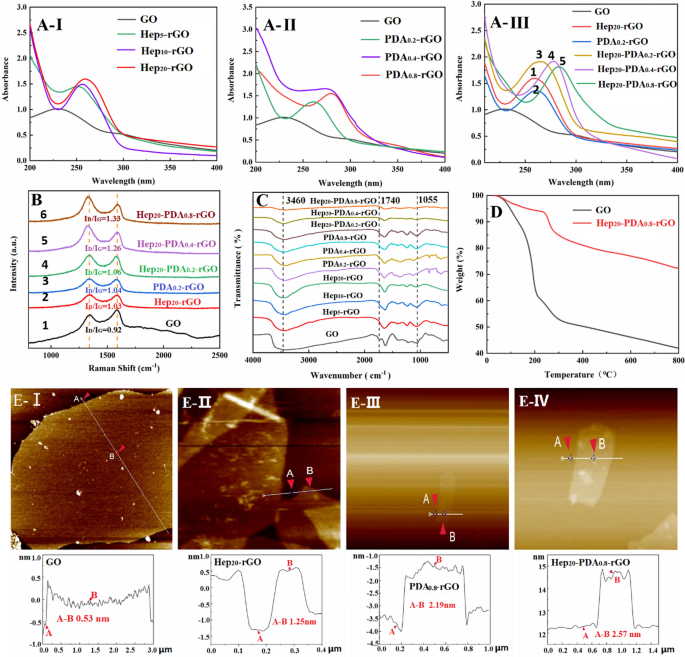
Spectral characterization of GO, Hep-rGO, PDA-rGO and Hep-PDA-rGO: A UV–seen absorption spectra, B Raman spectra, and C FT-IR spectra; D Thermal stability of GO and Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO was evaluated by way of TGA within the temperature vary of 0–800 °C at 10 °C/min; E AFM photos and the corresponding peak measurements of GO (I), Hep20-rGO (II), PDA0.8-rGO (III) and Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO (IV). The subscript represents the burden multiples relative to rGO
The discount levels of rGO had been characterised by utilizing UV–vis, Raman and FTIR spectra. The UV-vis spectrum of the GO suspension exhibited two attribute peaks (Fig. 1A–I) at 230 nm and 300 nm, comparable to the π-π* transitions of fragrant C=C bonds and n-π* transitions of the C=O bonds in GO, respectively. Because the proportion of heparin elevated, the absorption peak of Hep-rGO related to the π-π* transition regularly red-shifted to a better wavelength above 250 nm, indicating the gentle decreasing capability of heparin. However, the absorption spectrum of PDA-rGO peaked at 261–279 nm, and the redshift grew to become extra important with growing PDA dosage (Fig. 1A–II), demonstrating the robust decreasing functionality of PDA in direction of GO. Evaluating the height values of Fig. 1A–III-1, 2 and three, it may be noticed that the longer wavelengths exhibited by Hep20-PDA0.2-rGO point out a synergistic discount of GO facilitated by the HEP-PDA complicated. Moreover, Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO shifted right into a wavelength of round 283 nm, indicating a excessive diploma of discount of GO. The Raman spectra of GO displayed two distinguished peaks at 1589 and 1357 cm−1 (Fig. 1B-1), comparable to the G (the E2g mode of sp2 carbon atoms) and D (the symmetry A1g mode) bands, respectively. The depth ratio of the D and G peaks (ID/IG) signifies the diploma of dysfunction in graphene [24]. After the discount course of, the ID/IG elevated to various levels in comparison with GO (ID/IG= 0.92). Evaluating the spectra of Fig. 1B-2, 3 and 4, Hep20-PDA0.2-rGO confirmed a better ID/IG ratio (ID/IG=1.06) in comparison with Hep20-rGO and PDA0.2-rGO, indicating synergistic discount by the Hep-PDA complicated. Hep20-PDA0.8−rGO exhibited the very best ID/IG ratio, suggesting practically full discount of GO when the PDA content material within the Hep-PDA complicated reached 0.8 wt%. The infrared spectra (Fig. 1C) of GO and rGO revealed attribute peaks related to oxygen functionalities in GO, equivalent to O-H teams (3460 cm−1), C=O stretching (1740cm−1), and C–O stretching (1055 cm−1). With growing Hep, PDA, and Hep-PDA contents, these attribute peaks weakened or disappeared, indicating various levels of discount in GO. The above evaluation outcomes present that Hep-PDA complicated function an efficient decreasing agent to implement the controllable transformation of GO to rGO below reasonable response circumstances.
Determine 1D exhibits the thermogravimetric evaluation (TGA) outcomes. GO displays a speedy weight lack of 58.1% at 800 °C, primarily as a result of elimination of water molecules and the combustion of oxygen-containing purposeful teams [25]. In distinction, Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO demonstrates improved thermal stability, with a decrease weight lack of solely 27.8% between 100 and 800 °C. This means a big discount in oxygen-containing purposeful teams after the discount of GO. Moreover, the soundness of Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO in aqueous answer was evaluated over 3 months (Further file 1: Fig. S1). In contrast to Hep20-rGO and PDA0.8−rGO, Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO confirmed no indicators of aggregation after three months. This enhanced stability is attributed to the synergistic results of heparin and PDA. PDA aids within the absorption of heparin on the rGO floor and imparts a robust unfavorable cost density (− 33 ± 0.60 mV), as confirmed by DLS (Further file 1: Fig. S2) and proven in Further file 1: Desk S2. This unfavorable cost prevents aggregation via electrostatic repulsion interactions, making certain the soundness of the Hep-PDA-rGO nanosheets. Determine 1E presents cross-sectional AFM photos and corresponding peak measurements of single-layered GO and rGO. The typical thickness of the single-layer GO sheet was discovered to be 0.53 nm (Fig. 1E–I), in step with earlier literature [26]. After discount and functionalization with heparin/PDA, the common thickness elevated to 1.25 nm/2.19 nm, respectively. Notably, an extra enhance in common thickness to 2.57 nm was noticed in Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO (Fig. 1E–IV), indicating profitable immobilization of the Hep-PDA complicated on the rGO floor.
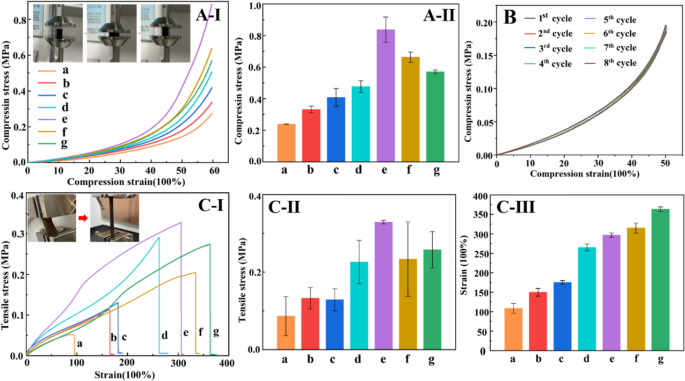
Compressive stress-strain curve (A-I) and compressive energy histogram of hydrogel (A-II); 8 cycles compressive stress-strain curve of Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel at 50% of most pressure (B); Tensile stress-strain curve (C-I), tensile stress histogram (C-II) and tensile pressure histograms of the hydrogels (C-III) (a–g are as follows: (a) PAM (b) GO-PAM (c) Hep20-rGO-PAM (d) PDA0.8-rGO-PAM (e) Hep20-PDA0.2-rGO-PAM (f) Hep20-PDA0.4-rGO-PAM (g) Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM)
Preparation and mechanical characterization of Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel
Versatile hydrogel sensors face periodic loading in sensible purposes, necessitating glorious mechanical properties to keep up secure sensing efficiency. The incorporation of rGO within the hydrogel performs a vital function in reaching optimum properties. On this examine, GO/rGO was added at a ratio of 1.0 wt% to the PAM community. The composition of every conductive hydrogel is proven in Further file 1: Desk S2. Functionalizing the rGO sheets with PDA or heparin led to improved compressive and tensile energy of the hydrogel (Fig. 2A/C-I, II-c, d relative to b). Significantly, the Hep20-PDA0.2−rGO-PAM hydrogel demonstrated increased compressive and tensile energy than Hep20-rGO-PAM and PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogels, owing to the synergistic motion of the Hep-PDA complicated nanosheets (Fig. 2A/C-I, II-e relative to c, d). This enhancement could be attributed to the homogeneous dispersion of Hep20-PDA0.2-rGO throughout the polymer matrix, which reinforces mechanical properties as a result of nanomaterial’s massive facet ratio and interplay with the polymer chains [27]. Nonetheless, growing the PDA content material resulted in a lower within the mechanical energy of the Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel (Fig. 2A/C-I, II-e, f, g) as a consequence of elevated discount of oxygen-containing teams on the GO nanosheets, weakening their interplay with the PAM community [21]. Cyclic compressive checks demonstrated that the compression efficiency of the Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel remained secure after eight cycles (Fig. 2B). Moreover, the Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel displayed excessive stretchability, with a most pressure exceeding 350% (Fig. 2C-III-g) and a tensile energy of roughly 250 kPa (Fig. 2C–II-g), matching the elastic modulus of the pores and skin. Thus, as a 2D nanomaterial, Hep-PDA-rGO successfully transfers masses and reinforces the mechanical properties of nanocomposite hydrogels, laying the muse for the event of high-performance hydrogel sensors.
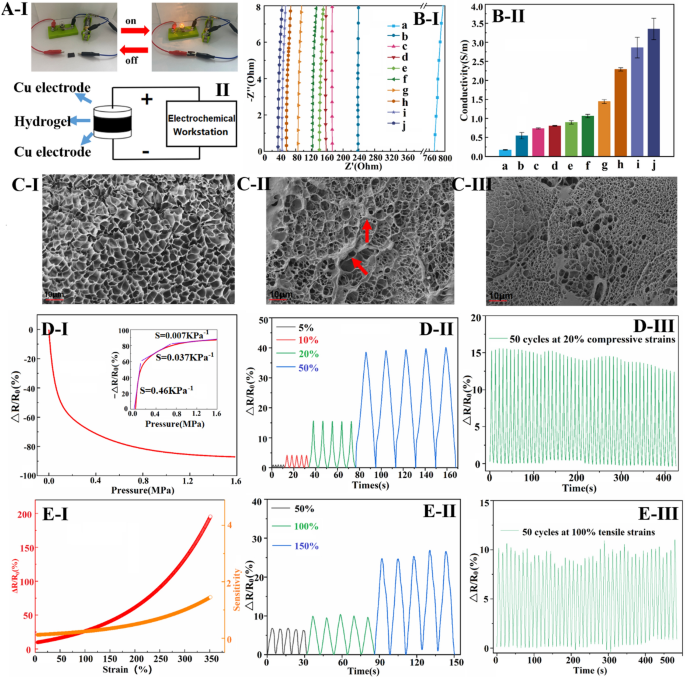
Diagram exhibiting conductive hydrogels related to a circuit with a lighted bulb (A-I) and schematic diagram of the hydrogel conductivity take a look at (A-II); Nyquist plots (B-I) and conductivity histograms (B-II) of various conductive hydrogels; Microscopic morphology of a (C-I), g (C-II) and j (C-II) hydrogels (a–j are as follows: (a) GO-PAM (b) Hep5-rGO-PAM (c) Hep10-rGO-PAM (d) Hep20-rGO-PAM (e) PDA0.2-rGO-PAM (f) PDA0.4-rGO-PAM (g) PDA0.8-rGO-PAM (h) Hep20-PDA0.2-rGO-PAM (i) Hep20-PDA0.4-rGO-PAM (j) Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM); ΔR/R0 and sensitivity of conductive hydrogels below compressive stress (D-I) and tensile pressure (E-I); ΔR/R0 for five cycles at totally different compressive stress (D–II) and tensile strains (E–II); ΔR/R0 at 20% compressive pressure (D-III) and 100% tensile pressure for 50 cycles (E–III)
Electrical conductivity and compression/pressure sensing of hydrogels
rGO incorporation enhances {the electrical} conductivity of PAM hydrogel, which is essential for sensing efficiency. In Fig. 3A-I, a Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel-connected circuit with a lighted bulb demonstrates conductivity. Conductivity measurements utilizing a two-probe technique (Fig. 3A-II) present that the hydrogels exhibit totally different conductivities. Nyquist plots in Fig. 3B-I and corresponding conductivity ends in Fig. 3B-II point out that the hydrogel conductivity aligns with the rGO discount diploma. GO-PAM hydrogels have very low conductivity (0.16 S/m), however with elevated PDA and Hep content material, the diploma of GO discount and hydrogel conductivity enhance. Notably, Hep-PDA-rGO composite hydrogel displays considerably enhanced conductivity in comparison with Hep-rGO and PDA-rGO hydrogels as a consequence of synergistic discount by the Hep-PDA complicated. Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel, with just one.0 wt% rGO, achieves a conductivity of three.63 S/m, surpassing many reported ionic gel conductors [28, 29]. SEM micrographs reveal that the GO-PAM scaffold has clean pore partitions (Fig. 3C–I), whereas PDA-rGO nanosheets cluster on the scaffold (Fig. 3C–II). In distinction, Hep-PDA-rGO is uniformly scattered, forming an built-in digital transmission pathway within the matrix (Fig. 3C–III). Such a giant rise in conductivity is expounded to the upper content material of sp2 carbon, lowered structural defects, and the integrity of the conductive community throughout the Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel.
Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel displays excessive sensitivity to compressive stress, as proven in Fig. 3D-I. The relative resistance change (ΔR/R0) decreases because the pattern is compressed. That is attributed to the lowered interlayer spacing and elevated contact space between graphene nanosheets below compression, resulting in extra environment friendly electron transmission and a lower within the hydrogel’s resistance at a macroscopic stage [30]. The hydrogel exhibits a strain sensitivity of 0.464 KPa−1 at low strain (< 0.2 MPa) and maintains a sensitivity of 0.037 KPa−1 at excessive strain (round 1.0 MPa), protecting a variety of sensing working strain. In Fig. 3D-II, it’s proven that the △R/R0 worth of the hydrogel displays a secure and incremental response to utilized compression ranges starting from 5–50%. The repeatability of the compression-sensitive electrical efficiency is evaluated in Fig. 3D-III, the place the hydrogel demonstrates comparatively secure (a slight discount as a consequence of water loss within the hydrogel materials) and repeatable response alerts with well-preserved amplitude even after present process 50 consecutive cycles of 20% compression. Moreover, Fig. 3E-I illustrates the △R/R0 response of Hep20-PDA0.8−rGO-PAM hydrogel below utilized tensile pressure. The sensitivity of ΔR/R0 will increase because the hydrogel is stretched. This may be attributed to the discount in conductivity pathways for electrons on the graphene when the hydrogel is stretched, leading to a lower in electron mobility. The sensitivity worth reaches 0.24 at 100% pressure and 1.45 at 350% pressure, indicating a large possible pressure vary of 0-350%. Determine 3E-II exhibits equivalent waveforms obtained in every cycle when most strains of fifty%, 100%, and 150% are utilized for five cycles, indicating the soundness of the hydrogel’s response. Equally, Fig. 3E-III demonstrates secure and repeatable pressure response alerts obtained when subjecting the hydrogel to a cyclic tensile pressure of 100% for 50 consecutive cycles. Based mostly on these findings, Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel holds promise as a wearable sensor as a consequence of its secure resistive response to each compressive stress and tensile pressure.
PDA-HEP-rGO-PAM hydrogels for the epidermal sensor
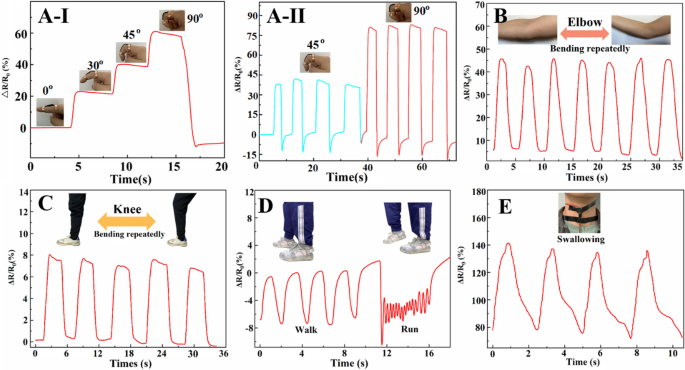
Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogels had been utilized to totally different elements of the human physique to guage their sensible utility as wearable sensors. Determine 4A–I exhibits that the ΔR/R0 will increase because the finger is bent, and {the electrical} alerts exhibit excessive repeatability and stability, as depicted in Fig. 4A–II. Equally, when the hydrogel sensors are hooked up to joints equivalent to elbows (Fig. 4B) and knees (Fig. 4C), they display delicate and repeatable detection of joint bending. Furthermore, the hydrogel sensors can precisely establish human strolling and working by analyzing distinguishable resistance change frequencies and sign waveforms, as proven in Fig. 4D. Apparently, even refined human motions like swallowing could be simply detected by observing corresponding ΔR/R0 variations (Fig. 4E). The sensing sensitivity is dependent upon the extent of adjustments within the conductive community throughout the pressure course of [31]. These findings display the potential of Hep20-PDA0.8−rGO-PAM hydrogel as a wearable sensor for monitoring numerous human actions in actual time. Its means to detect and distinguish actions in several physique elements makes it a promising candidate for purposes in healthcare and movement monitoring.
In vitro biocompatibility of hydrogels
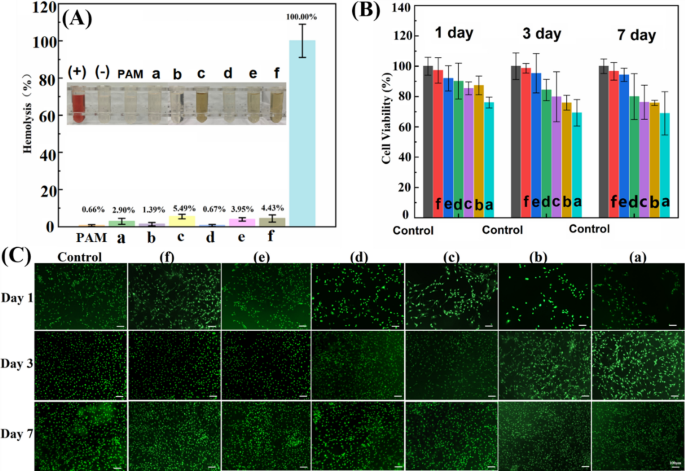
Hemolysis ratio and viability research on 3T3 cells had been carried out to evaluate the biocompatibility of GO and rGO-based hydrogels. The hemolytic property of GO/rGO hydrogel is primarily influenced by the interactions between the integrated nanosheets and blood elements. In Fig. 5A, it may be noticed that the GO-PAM hydrogel exhibited a better hemolysis ratio (2.90%) in comparison with the pure PAM hydrogel (0.66%), suggesting that GO brought on some disruption to the lipid bilayer of the blood cell membrane as a consequence of its surfactant and amphiphilic properties [32]. However, the Hep20-rGO-PAM hydrogel confirmed a decrease hemolysis ratio (1.39%) as a result of protecting impact of heparin, which acts as an electrical cost barrier and in addition alters the floor cost distribution of rGO [33]. Nonetheless, the PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel displayed seen launch of hemoglobin, with a excessive hemolysis fee of 5.49%, indicating a robust interplay between the PDA-adhered rGO and the blood cell membrane. This consequence aligns with the earlier report, indicating that pristine graphene exhibited the very best hemolysis fee, adopted by rGO and GO, in correlation with the diploma of floor oxidation [34]. Apparently, the Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel exhibited considerably lowered hemolysis in comparison with the PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel, which could be attributed to the affect of the Hep-PDA complicated on the floor modification of rGO. The hemolysis fee of the Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel fell throughout the hemolytic customary (5%), indicating acceptable hemocompatibility of the hydrogel.
A Hemolysis ratios of RBCs with photos of RBCs (inset) after the hydrogels incubated with RBCs for two h at 37 °C with shaking. The redness signifies that the RBCs had been destroyed and hemoglobin was launched. (+) represents constructive management, and (−) represents unfavorable management; Cell viability (B) and fluorescent staining (C) of 3T3 cells on hydrogel; GO-PAM (a), HEP20-rGO-PAM (b), PDA0.8-rGO-PAM (c), HEP20-PDA0.2-rGO-PAM (d), HEP20-PDA0.4-rGO-PAM (e), HEP20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM (f)
The cytotoxicity of GO and rGO-based hydrogels was assessed utilizing the CCK-8 technique in opposition to 3T3 cells, and the outcomes are offered in Fig. 5B. Cell viability on the Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel was constantly excessive, exceeding 90% all through the experiment. In distinction, different hydrogel teams confirmed a lower in cell viability over time, with the GO-PAM hydrogel group reaching as little as 70%. Significantly, the Hep20-PDA0.8−rGO-PAM hydrogel demonstrated glorious cell compatibility with a cell survival fee of 97%. These findings point out that cells had a better proliferation fee on the Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel, and the density and development of cells had been increased on hydrogels with a better PDA content material. AO/EB staining confirmed the cytotoxicity outcomes, exhibiting elevated cell density over time, notably within the Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM (Fig. 5C).
The outcomes point out that GO-PAM induces hemolysis and cytotoxicity as a consequence of its floor properties and interplay with the cell membrane. In distinction, the presence of PDA reduces electrostatic repulsion between rGO and the cell membrane, resulting in its partitioning into the lipid bilayer. Nonetheless, when PDA varieties a fancy with heparin, it enhances adhesion of the heparin layer to the rGO floor, leading to lowered hemolysis. Relating to cytotoxicity, cells cultured with PDA0.8-rGO-PAM and Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogels present improved spreading morphology on the primary day, possible as a consequence of PDA facilitating cell attachment [35]. Furthermore, the restricted aqueous stability of rGO causes sedimentation and compact mixture formation, limiting nutrient availability to cells [36]. Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel displays low cytotoxicity, probably as a result of increased aqueous stability of Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO nanosheets. It’s value noting that the soundness of various GO/rGO samples correlates with their corresponding hydrogel cell viability.
In vitro reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging actions of hydrogels
Throughout an harm or implantation, the physique responds quickly by accumulating cells and biomolecules to provoke the therapeutic course of on the affected website. Nonetheless, this response additionally triggers the technology of ROS and free radicals from neighboring tissues and immune reactions. Whereas ROS performs a vital function as a signaling molecule in regulating physiological processes, extreme ROS manufacturing as a consequence of irritation on the implant website can exacerbate mobile harm and compromise the soundness of sensor gadgets [37]. Moreover, the hindrance to diabetic wound therapeutic arises from an overabundance of inflammatory cytokines, ROS, and mobile dysfunction, compounded by the intrinsic antioxidative protection system’s lack of ability to rectify these imbalances. Consequently, the antioxidant properties that successfully counteract ROS oxidation reactions change into paramount not just for implanted versatile sensors but additionally for persistent wound dressing. On this examine, we investigated the ROS scavenging properties of hydrogels, assessing their means to inhibit hydroxyl radicals (OH·) and DPPH radicals, highlighting their potential as protecting and therapy elements throughout the realms of implantable sensors and wound dressing.
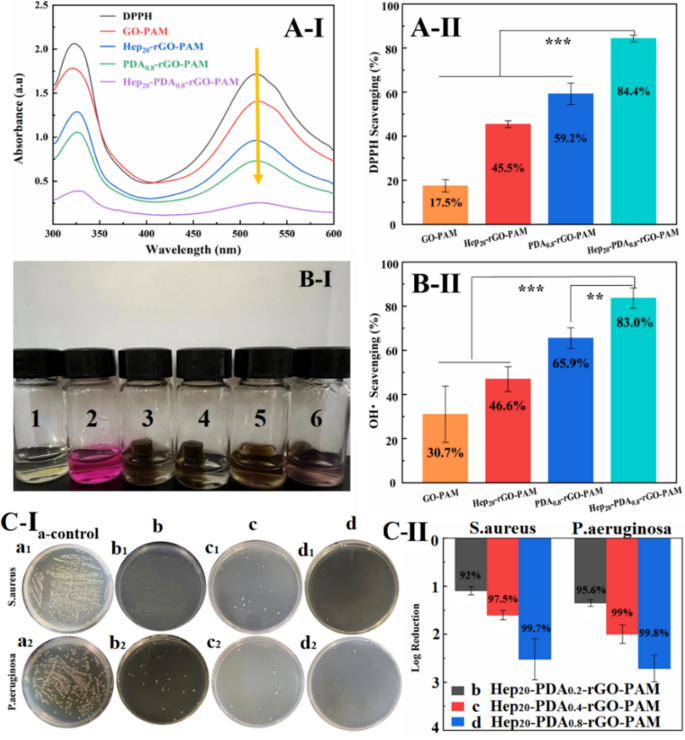
ROS scavenging property of hydrogels in opposition to Hydroxyl radicals and DPPH radicals. (A-I) UV − vis spectra of the DPPH response with totally different scaffolds after 120 min, (A-II) DPPH scavenging effectivity of the scaffolds; (B-I) The OH• scavenging actions of samples had been demonstrated by the colour change (1: clean, 2: management, 3: GO-PAM, 4: Hep20-rGO-PAM, 5: PDA0.8-rGO-PAM, 6: Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM group), (B-II) OH• scavenging effectivity of the scaffolds; (C-I) Development circumstances of S. aureus (a1-d1) and P. aeruginosa (a2-d2) on the clean tradition substrate (a1, a2), Hep20-PDA0.2-rGO-PAM (b1, b2), Hep20-PDA0.4-rGO-PAM (c1, c2) and Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM (d1, d2) hydrogel; (C-II) Antibacterial fee calculated by log discount of micro organism (CFU) on contact with the three hydrogels in accordance with the unfold plate outcomes (n = 3)
Within the free DPPH radicals scavenging assay, the depth of the DPPH radical was measured after 60 minutes of incubation with the hydrogel by monitoring the attribute UV-Vis absorption peak of DPPH radicals at 517 nm. As depicted in Fig. 6A–I, the height worth decreased from 1.71 to 0.25 within the presence of GO/rGO hydrogels. The GO-PAM hydrogel exhibited a reasonable scavenging capability in opposition to DPPH (17.5%), whereas the scavenging effectivity of Hep20-rGO-PAM and PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogels was enhanced to 45.5% and 59.2%, respectively (Fig. 6A–II). This enhancement suggests the essential function of reductive hydroxyl teams and catechol teams current on rGO as electron donors within the scavenging course of [38]. Importantly, the introduction of the Hep-PDA complicated considerably enhanced the DPPH scavenging capability of rGO hydrogels to 84.4%, attributed to the synergistic inhibition of heparin and PDA (Fig. 6A–II). Within the OH· scavenging assay, the Fenton response was employed to generate hydroxyl radicals. Hydrogen peroxide was lowered to OH· by ferrous ions, and the robust oxidizing means of OH· led to the oxidation and discoloration of the Safranin-O dye [39]. Thus, the darker the colour of the response answer, the stronger the hydrogel’s scavenging means in direction of OH·. It was noticed that the answer coloration of the GO-PAM hydrogel group was the lightest, and the colour regularly darkened with the introduction of Hep, PDA, and Hep-PDA, as proven in Fig. 6B–I. The Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel exhibited the very best scavenging capability in opposition to OH· at 83% (Fig. 6B–II). This may be attributed to the hydroxyl teams and phenolic compounds on the Hep-PDA complicated, which bind to OH· as electron donors and inhibit OH· technology.
In vitro antibacterial actions of hydrogels
Power wound infections are extremely prevalent amongst diabetic sufferers, stemming from compromised immunity as a consequence of excessive blood sugar ranges, impaired circulation, and neuropathy, collectively leading to elevated susceptibility and delayed therapeutic. Standard conductive hydrogels have a downside of microbial absorption, which might result in irritation, wound infections, and immune responses, posing a danger to human well being. Graphene supplies have emerged as potential antibacterial brokers as a consequence of their low toxicity and broad-spectrum exercise [40]. Our earlier analysis has demonstrated that heparin enhances the antimicrobial exercise of PDA via the bactericidal results of cations and ROS [23, 41]. To judge the antibacterial exercise of the hydrogels, two consultant medical pathogens, specifically S. aureus and P. aeruginosa, had been cultured on the floor of the hydrogels at a focus of ~ 106 CFU/cm2 for 4 hours. The antibacterial exercise was assessed utilizing the plate colony counting technique with co-cultured bacterial suspensions. The clean tradition substrate served because the management (Fig. 6C–I-a). As depicted in Fig. 6C–I-b, c, d, Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel exhibited substantial discount in bacterial colonization, surpassing 90% eradication for each pathogens. Furthermore, an elevated PDA content material led to even decrease bacterial counts. Specifically, the Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel achieved practically full elimination of S. aureus (99.7% kill-log discount at 2.5) and P. aeruginosa (99.8% kill-log discount at 2.65), indicating its strong antibacterial efficacy (Fig. 6C–II). This synergistic impact between the Hep-PDA complicated and rGO nanosheets contributes to the antibacterial properties of the conductive hydrogel by disrupting microbial membranes.
In vivo wound therapeutic results
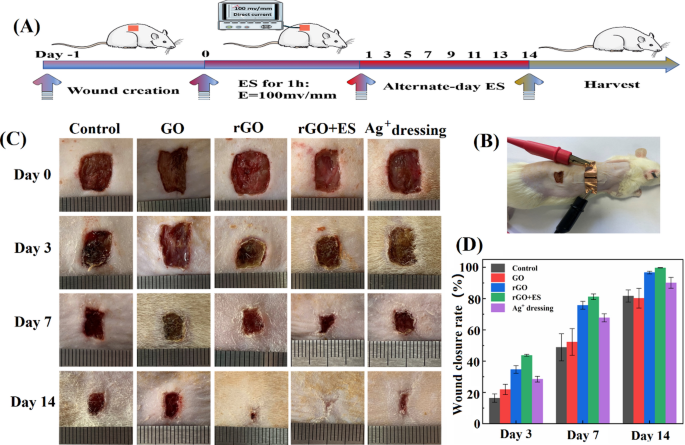
The Hep-PDA-rGO-PAM hydrogel has nice potential as a complicated dressing for electrotherapy (ES) within the therapy of persistent wounds as a consequence of its conductivity and multi-functionalities. To judge its wound therapeutic efficiency, the Hep20-PDA0.8-rGO-PAM hydrogel was in comparison with the GO-PAM hydrogel (referring to rGO and GO hydrogel within the following context) in a full thickness pores and skin defect mannequin on sort II diabetes mellitus Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. Within the examine, an exterior ES powered by a DC provide was utilized to the rGO hydrogel for one hour on alternate days within the rGO + ES group, to analyze the mixed results of rGO hydrogel dressings with ES (Fig. 7A, B). The management group acquired no therapy besides saline answer, whereas the Ag+ dressing group was handled with a business Ag+ dressing (AQUACEL®). All wounds had been inoculated with S. aureus to induce an infection. The macroscopic appearances of the injuries with totally different therapies on day 0, 3, 7, and 14 had been recorded (Fig. 7C). The wound space decreased over time in all teams albeit at totally different charges: rGO + ES group < rGO hydrogel group < Ag+ group < GO hydrogel group < management group. Significantly, the wound handled with ES via the rGO hydrogel confirmed the smallest wound space amongst all of the teams at any time level, reaching nearly full (99.7%) wound closure after 14 days (Fig. 7D). Moreover, a big discount in wound dimension was noticed within the rGO group with out ES, in comparison with the GO hydrogel group and Ag+ dressing group.
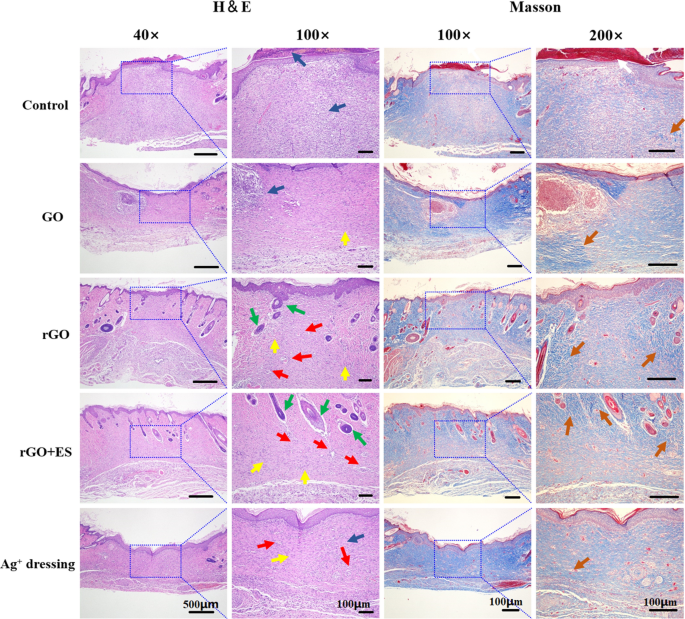
Hematoxylin & eosin and Masson staining of the sections of the regenerated tissues on the wound website on day 14 for the totally different handled teams. Scab (white arrow), blood vessels (crimson arrow), fibroblasts (yellow arrow), neutrophils (blue arrow), hair follicles (inexperienced arrow), and collagen deposition (orange arrow)
Histological evaluation of tissue sections from day 14 wounds was carried out utilizing H&E and Masson staining. The evaluation revealed distinct variations among the many totally different therapy teams (Fig. 8). The management group displayed incomplete wound closure, characterised by the presence of a scab and a excessive variety of blood cells and inflammatory cells. Within the Ag+ movie dressing group, fundamental formation of epithelium and dermis was noticed; nonetheless, the dermis was nonetheless present process restore with gentle irritation and the absence of hair follicles. The GO hydrogel group exhibited incomplete epithelium and dermis, with loosely distributed dermal tissue and a big infiltration of neutrophils. In distinction, the rGO hydrogel demonstrated common formation of epithelium and connective tissue, accompanied by an elevated density of fibroblasts, a lowered presence of neutrophils and new blood vessels and hair follicles formation. Usually, extreme irritation can delay the therapeutic, whereas the rGO group, as a consequence of its antibacterial and antioxidative properties, maintained an applicable inflammatory setting for selling wound therapeutic. Remarkably, the rGO + ES group exhibited essentially the most favorable wound therapeutic outcomes, together with considerable mature hair follicles and neoangiogenesis, in addition to well-proliferated fibroblasts, surpassing the outcomes of all different teams. Fibroblasts play a key function in producing collagen via their speedy proliferation [42]. Collagen, as the first constituent of the extracellular matrix, performs a vital function within the means of wound therapeutic. After a 14-day interval, the injuries handled with rGO hydrogel and ES exhibited the very best density of collagen (represented by the blue space) and a extra organized fibrous construction, facilitating connective tissue transforming in comparison with the opposite teams.
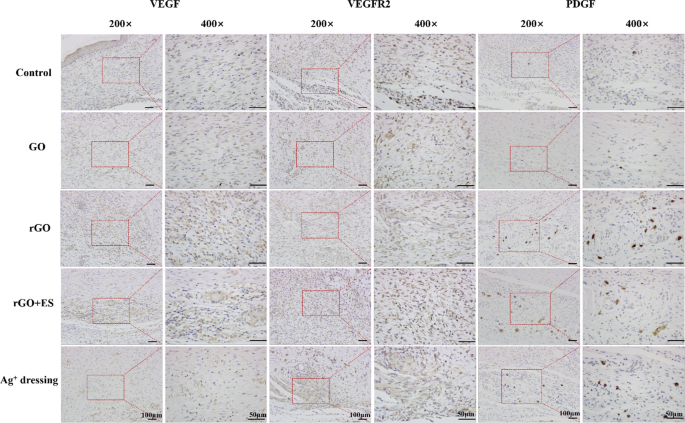
Angiogenesis, the formation of recent blood vessels, is important for wound restore because it contributes to the event of granulation tissue and provides vitamins and oxygen to rising tissues [43]. A number of development elements, together with VEGF, PDGF, and VEGFR2, are concerned in angiogenesis throughout wound therapeutic. VEGF enhances vascular permeability and attracts endothelial cells, initiating angiogenesis. PDGF stimulates the proliferation of clean muscle cells (SMCs) to reinforce vascular stability. VEGFR2, as a receptor for VEGF, binds to VEGF and prompts intracellular signaling pathways, selling the expansion, proliferation, and maturation of endothelial cells and facilitating neovascularization [44]. Subsequently, immunohistochemical evaluation of VEGF, PDGF and VEGFR2 can be utilized to guage angiogenesis throughout the wound therapeutic course of. As proven in Fig. 9, the expression ranges of VEGF, VEGFR2, and PDGF (indicated by the brownish-yellow staining) within the rGO teams had been clearly increased than within the different teams. Particularly, when uncovered to ES, the expression of the VEGFR2 within the rGO + ES group was notably increased in comparison with each the Ag+ dressing and rGO hydrogel handled teams. This implies {that electrical} stimulation by way of rGO hydrogel can promote angiogenesis and enhance the therapeutic fee of wound by upregulating the expression ranges of VEGF, VEGFR2, and PDGF. All above findings recommend that the electroactive rGO hydrogel alone can improve pores and skin wound therapeutic as a consequence of its intrinsic properties, equivalent to antibacterial and antioxidative results, and when mixed with ES, it displays accelerated therapeutic results, indicating a synergistic function between the rGO hydrogel and ES.