What significant alternatives will metaverse applied sciences supply manufacturing?
As a New Yr dawns, the resounding cry from producers is: The place are the individuals? Far and away, the highest problem going through producers in 2023 would be the ongoing expert labor scarcity. Consultants say there merely aren’t sufficient individuals to fill manufacturing roles, particularly amidst reshoring efforts. The labor scarcity is one in all many transferring items shaping the manufacturing workforce—and the workforce as a complete—and these shifts, mixed with the convergence of know-how tendencies in Trade 4.0 and the IoT (Web of Issues) and nationwide manufacturing tendencies like reshoring efforts, are all coming to a head.
In the meantime, the metaverse is trending not solely within the social media-verse but additionally in enterprise circles. What significant alternatives will metaverse applied sciences supply within the manufacturing area? How will what’s taking place in metaverse intersect with what’s taking place within the manufacturing workforce?
2023 Manufacturing Tendencies to Watch
Within the subsequent yr, Mark Schuerman, senior supervisor of enterprise growth for Molex, says tendencies impacting the manufacturing area will embrace the workforce’s need for flexibility, rising prices of labor because of shortages and affect of inflation, the supply of and have to spend money on good manufacturing applied sciences, an consciousness inside manufacturing firms of their vulnerability to disruptions (largely due to the pandemic), and a basic scarcity of staff, each expert and unskilled. “All of the above components are driving the need and requirement for rising ranges of automation at manufacturing firms to mitigate danger publicity to labor and provide chain disruptions whereas driving operational efficiencies greater,” Schuerman says. “The development is towards utilizing automation to supply extra with a smaller workforce.”
And whereas automation and Trade 4.0 are essential tendencies in manufacturing, Jeannine Kunz, chief workforce growth officer at SME, stresses producers nonetheless want individuals to allow their digital transformations. “There merely aren’t sufficient individuals to fill roles,” Kunz says. “Automation and Trade 4.0 (have gotten) essential elements of rethinking how we do issues. Nonetheless, we nonetheless want individuals for automation and digitization. And people individuals must be a part of the change.”
Kunz says proper now, there’s a vital shift in what individuals count on from their employers. “I personally suppose we’re overlooking what is occurring with the ‘employee’ themselves,” she explains. “Particular person priorities, beliefs, and existence are altering. Their expectations and social contract with their employer are altering. […] The character of labor was already shifting with the brand new generations getting into the workforce, and with the modifications associated to Covid, the workforce challenges have grown. This creates a myriad of challenges to deal with to find, creating, and retaining a talented and engaged workforce to drive our trade ahead.”
The pandemic, the altering employee-employer relationship, the financial system—it’s all a part of what’s taking place in workforce as a complete, however the manufacturing area particularly is struggling. A 2021 research by Deloitte and The Manufacturing Institute anticipated that 2.1 million manufacturing jobs may go unfilled by 2030 because of expert labor shortages and a wave of baby-boomer retirements.
Tony Schmitz, professor on the College of Tennessee, Knoxville and joint school at Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory, says this actuality is partly as a result of manufacturing has not been promoted as a viable profession to highschool college students in latest a long time. “This has produced a scarcity of scholars getting into four-year and two-year manufacturing teaching programs,” Schmitz explains. “Second, manufacturing has modified considerably in latest a long time. It’s now principally a digital enterprise that requires new ability units than the coaching obtained by the newborn boomers that make up a lot of the manufacturing workforce. We have to recruit, however we’d like to ensure we’re recruiting utilizing an correct illustration of the sector and its alternatives.”
Manufacturing is a high-tech, high-reward profession that leverages the newest applied sciences, and it issues lots. U.S. manufacturing influences the nation’s financial system and its international viability as a aggressive drive. Schmitz factors to competitions just like the SEC Machining Competitors held in November as examples of how universities are working to elevate up the brand new era of producing workforce.
Liz Caught, senior director of workforce growth at MxD, says one consequence of the crucial abilities scarcity that shouldn’t be missed is the corresponding safety danger to the manufacturing sector. “The rising abilities hole turns into much more regarding when contemplating that manufacturing is probably the most focused sector for cyber-attacks,” she says. “Thirty-five % of cyber-espionage assaults within the U.S. are focused at manufacturing, the most important of any single sector.”
Reshoring is compounding the workforce downside. Conrad Leiva, vice chairman of ecosystem and workforce schooling at CESMII – The Good Manufacturing Institute, says: “On the whole, we’ve had a rise of producing coming again to the nation by reshoring. And a number of that has been pushed by the belief that we’ve had overexposure to danger in our provide chain throughout the pandemic disruption. […] Manufacturing fell out of style as a result of we have been sending it offshore for therefore a few years, and now that we’re attempting to make issues once more, the labor’s not there. It takes just a few years to construct up the curiosity and the expertise pipeline.”
With boomers retiring and never sufficient staff coming in, the talents hole between the brand new era and the previous, and all of this amidst reshoring, it’s no marvel specialists cite workforce points time and again as the highest manufacturing development to observe in 2023. Nonetheless, no development occurs in a vacuum. Tendencies evolve concurrently and infrequently intersect to kind new tendencies. One instance is how workforce tendencies in manufacturing and the excitement concerning the metaverse are creating an enchanting dialogue about what may very well be.
Making Means for the Industrial Metaverse
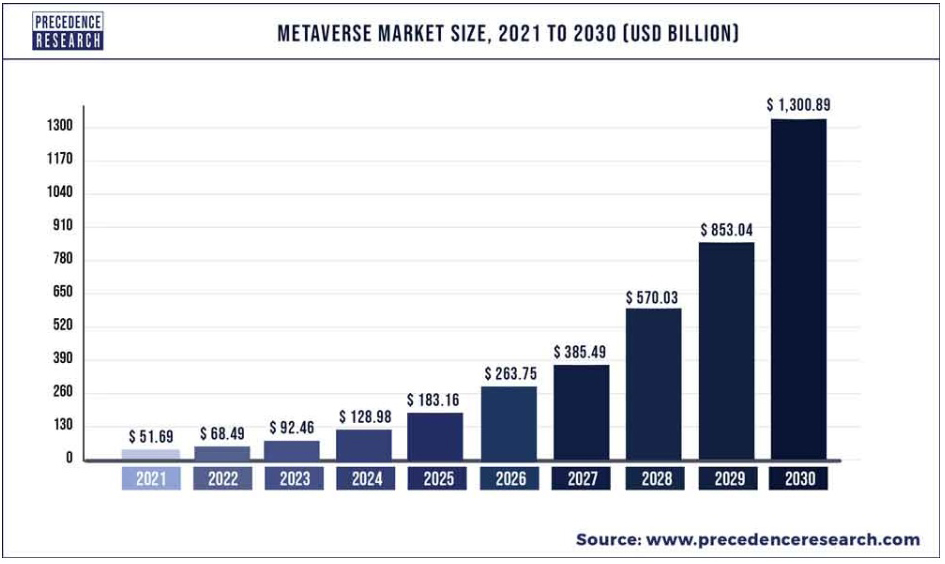
Priority Analysis estimates the worldwide metaverse market will exceed $1.3 trillion by 2030, which is up from $51.69 billion in 2021. MxD’s Caught defines the commercial metaverse as the power to mix digital applied sciences like VR (digital actuality), AR (augmented actuality), and digital twins with actual life to enhance processes and improve efficiencies. She says: “The industrial metaverse permits collaboration between a digital setting and a real-world setting in a approach that may doubtlessly stop issues from taking place to start with by analyzing the information and outputs from the digital setting and making use of them to the real-world setting.”
John Liu, principal investigator at MIT’s LEAP (Studying Engineering and Follow) Group, a lecturer in MIT’s Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, and a scientist on the MITx Digital Studying Lab, describes the commercial metaverse as an evolution of the digital illustration of complete methods composed of environments, merchandise, processes.
“Suppose ‘digital twin’, however now, as an alternative of the standard single machine or course of, it may very well be a complete manufacturing facility, transportation system, or power grid,” Liu explains. “In fact, simulating and optimizing manufacturing traces has additionally been used within the trade for a while now. The commercial metaverse is a step ahead in that it consists of elevated complexity and energy. It is going to combine into one package deal elements resembling physics-based conduct, materials varieties, human ergonomics, and photo-realistic fashions.”
Liu imagines the commercial metaverse impacting the workforce in three areas: sort of labor, schooling and coaching, and pipeline. First, he says, the kind of work will change. “I think about we might see the emergence of latest occupations like digital thread or digital twin engineers or a larger concentrate on human ergonomics and productiveness to completely digital and hybrid interactions,” he says. “We’ll in all probability see within the subsequent 10 years the institution of finest practices on the right way to interpret and sift by richer and extra complicated knowledge and the right way to drive these insights in the direction of choices.”
Second, the commercial metaverse will affect schooling and coaching in manufacturing. Liu says as industries spawn new applied sciences at a dizzying tempo, firms can not thrive with out a nimble workforce, and one strategy to make a workforce nimbler is to leverage progressive options that enhance schooling, coaching, and productiveness. “The workforce must extra shortly adapt to new know-how, digitally upskill, and be taught to work higher with automation,” says Liu. “And the right way to do all of this at scale? Having a seamless integration between the digital and bodily worlds is ideal for the workforce to be taught these competencies. […] The metaverse may allow schooling and coaching for the workforce with an authenticity, connectedness, and scale we haven’t seen earlier than.”
Lastly, there’s the commercial metaverse’s potential affect on the manufacturing workforce pipeline. Liu says manufacturing is struggling to recruit new staff at a fee that matches retirement charges and native surges in demand, and a part of the problem is that manufacturing has “a picture downside”. Whereas manufacturing is advancing, the general public nonetheless thinks manufacturing is soiled, harmful, and darkish.
4 Methods the Metaverse Will Intersect with Manufacturing
Mark Schuerman of Molex lists 4 methods manufacturing and metaverse will intersect.
- In the course of the design course of, the commercial metaverse will function a instrument to optimize ergonomics and general employee well being and security. It is going to additionally enable manufacturing engineers to just about take a look at completely different manufacturing methods when it comes to selections of apparatus and use of handbook vs. automated methods to attain extra environment friendly manufacturing methods upon implementation.
- AR/VR instruments shall be used for employee coaching to assist them follow and enhance manufacturing, in addition to upkeep methods.
- AR/VR instruments can even be used to help staff throughout the manufacturing and upkeep processes themselves. For instance, AR goggles can direct staff by every stage of a producing course of, serving to to tell them of which steps must be carried out and when, in addition to performing a quality-control perform by monitoring and confirming all elements are put in within the appropriate order and to the correct manufacturing specs. If a step is missed or an element will not be put in correctly, the road will be stopped and corrective actions will be communicated to staff in realtime.
- The commercial metaverse additionally supplies alternatives for suppliers to supply distant, digital help to line staff when diagnosing and troubleshooting tools in want of restore. A specialist from a provider can remotely “go surfing” and work with a upkeep particular person just about within the metaverse to look at the issue and devise a corrective technique with the end-user upkeep group with out having to journey to the ability.
“I see the metaverse doubtlessly impacting the workforce pipeline in two methods,” Liu provides. “One, if you happen to can expertise manufacturing within the digital world with the identical realism as that of the bodily, job seekers and younger individuals can—not simply turn into conscious—however expertise for themselves the best manufacturing work has to supply. A baby may roleplay as a robotics engineer, or a highschool pupil may already start studying what it takes to reach manufacturing operations. Second—and that is extra of a moonshot—you would possibly be capable of open up distant work for bodily work. At the moment, distant work is usually accessible for work like software program growth or undertaking coordination. However in the case of bodily work, in fact you need to be there. Many individuals received’t transfer for a job, particularly in the event that they’re entry-level. That’s why the accessible workforce for a plant is basically constrained to a area. However if you happen to mix digital 100% operational transparency, low latency networks, and superior robotics, may somebody in Atlanta work in a Detroit manufacturing facility as if she have been there? The choice to supply distant bodily work may take a regionally concentrated spike of job demand and re-distribute it throughout the nation to raised match provide. And if bodily work will be carried out just about, we may open up bodily work to new populations just like the bodily disabled.”
Salim Awad, president and CEO of SPINNER North America, says an engaged and expert workforce are elementary parts to the way forward for manufacturing, and metaverse will play a job in creating an engaged, expert workforce, in addition to creating different useful alternatives. “The metaverse, though nonetheless in its infancy, presents significant alternatives for superior manufacturing, the place it may be utilized for coaching, simulations, and course of growth,” Awad says.
Collaboration in manufacturing can even profit from metaverse applied sciences. For example, Awad describes how older and soon-to-be-retired staff possess immense data that have to be transferred to the incoming workforce. “A good way to make this switch of information and expertise is to construct multigenerational groups the place an alternate of concepts, in addition to mentoring and training, can happen in a wholesome ecosystem,” he provides. “Manufacturing leaders should create the circumstances for this alternate and deliberately construct the groups that enable a profitable and collaborative transition.”
MIT’s Liu agrees the commercial metaverse has far-reaching implications for collaboration in manufacturing and past. “Colleagues from around the globe will now be capable of work in the identical digital world, troubleshooting the identical real-world downside or attempting out completely different concepts collectively,” he explains. “And knowledge that’s not usually accessible to the bare eye is now readily visualized, so teams can extra simply extract probably the most helpful insights from complicated knowledge and make higher choices.”
However whereas the metaverse demonstrates thrilling potential and a few early successes, Liu factors out the gathering of applied sciences that compose it are nonetheless nascent, and nobody is aware of what it can actually turn into. “As a complete, we people have a spotty document in the direction of making correct predictions,” Liu says. “It’s simpler to debate potential and tougher to precisely predict what the metaverse will turn into and the best methods it can truly affect the trade.”
CESMII’s Leiva says there’s no want to attend for a metaverse to appreciate a number of worth with digital transformation and good manufacturing applied sciences. “It’s straightforward to get fascinated with the potential of future applied sciences, however we don’t need to neglect that proper now there are a number of alternatives to implement good manufacturing applied sciences which might be accessible at this time,” he says. “It extra sensible than ever for small- to medium-sized producers to modernize their practices and turn into extra digital-ready for at this time’s related digital provide chain. I get excited too about (the) future, however there may be a number of stuff to do proper now and a number of know-how accessible that’s serving to producers at this time.”
Hyperlinks for Additional Studying:
Need to tweet about this text? Use hashtags #IoT #sustainability #AI #5G #cloud #edge #digitaltransformation #machinelearning #futureofwork #cybersecurity #metaverse #manufacturing #supplychain #tendencies #AR #VR #automation #digitaltwin #industry40 #skillsgap #industrialmetaverse #Molex #SME #MxD #CESMII #SPINNNER


