Posted by Gurupreet Singh, Developer Advocate; Android
At the moment marks the primary secure launch of Compose Materials 3. The library means that you can construct Jetpack Compose UIs with Materials Design 3, the subsequent evolution of Materials Design. You can begin utilizing Materials Design 3 in your apps at present!
Notice: The phrases “Materials Design 3”, “Materials 3”, and “M3” are used interchangeably.
Materials 3 consists of up to date theming and parts, unique options like dynamic colour, and is designed to be aligned with the most recent Android visible model and system UI.
 |
| A number of apps utilizing Materials Design 3 theming |
You can begin utilizing Materials Design 3 in your apps by including the Compose Materials 3 dependency to your construct.gradle recordsdata:
Notice: See the most recent M3 variations on the Compose Materials 3 releases web page.
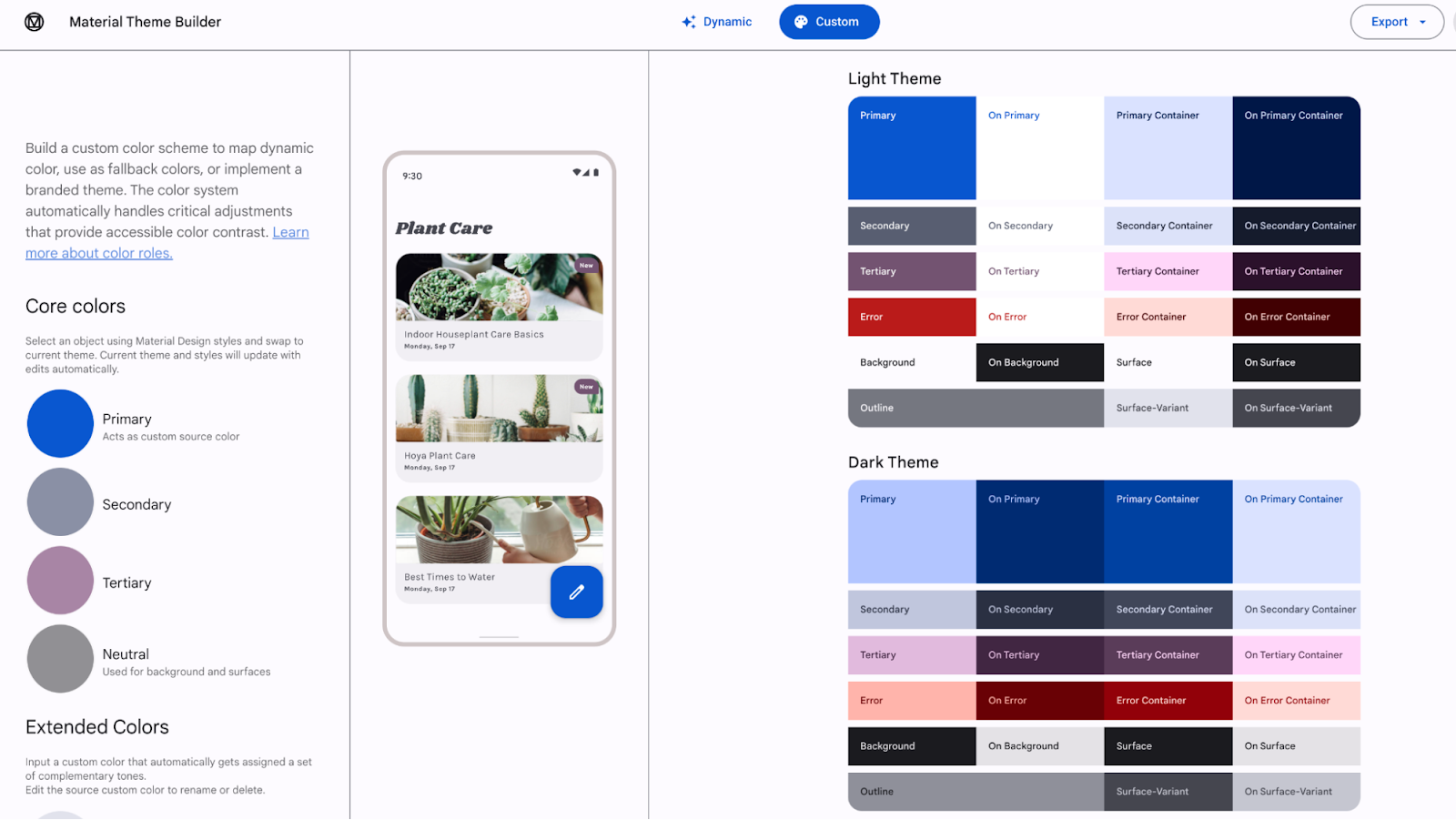 |
| Materials Theme Builder to export Materials 3 colour schemes |
Dynamic colour derives from the person’s wallpaper. The colours might be utilized to apps and the system UI.
Dynamic colour is obtainable on Android 12 (API stage 31) and above. If dynamic colour is obtainable, you possibly can arrange a dynamic ColorScheme. If not, you must fall again to utilizing a customized gentle or darkish ColorScheme.
Reply Dynamic theming from wallpaper(Left) and Default app theming (Proper)
The ColorScheme class gives builder features to create each dynamic and customized gentle and darkish colour schemes:
Theme.kt
The M3 Swap element has a model new UI refresh with accessibility-compliant minimal contact goal measurement help, colour mappings, and non-compulsory icon help within the swap thumb. The contact goal is larger, and the thumb measurement will increase on person interplay, offering suggestions to the person that the thumb is being interacted with.
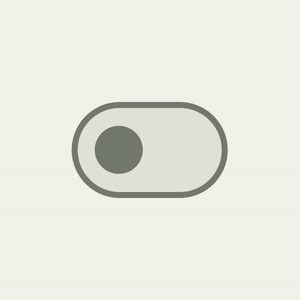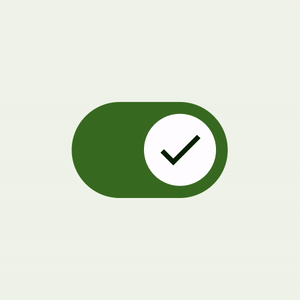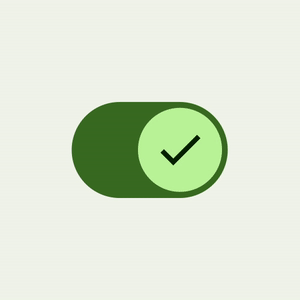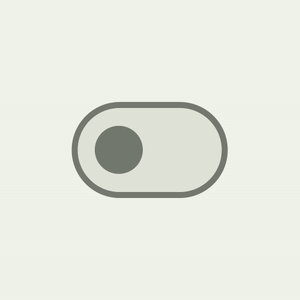 |
| Materials 3 Swap thumb interplay |
Navigation drawer parts now present wrapper sheets for content material to vary colours, shapes, and elevation independently.
 |
| ModalNavigationDrawer with content material wrapped in ModalDrawerSheet |
We now have a model new CenterAlignedTopAppBar along with already current app bars. This can be utilized for the principle root web page in an app: you possibly can show the app identify or web page headline with dwelling and motion icons.
 |
| Materials CenterAlignedTopAppBar with dwelling and motion objects. |
See the most recent M3 parts and layouts on the Compose Materials 3 API reference overview. Control the releases web page for brand new and up to date APIs.
Materials 3 simplified the naming and grouping of typography to:
- Show
- Headline
- Title
- Physique
- Label
There are massive, medium, and small sizes for every, offering a complete of 15 textual content model variations.
The
Typography constructor provides defaults for every model, so you possibly can omit any parameters that you simply don’t wish to customise:
There are completely different sizes of shapes:
- Additional small
- Small
- Medium
- Massive
- Additional massive
 |
| Materials Design 3 shapes utilized in varied parts as default worth. |
Every form has a default worth however you possibly can override it:
You possibly can learn extra about making use of form.
Jetpack Compose and Materials 3 present window measurement artifacts that may assist make your apps adaptive. You can begin by including the Compose Materials 3 window measurement class dependency to your construct.gradle recordsdata:
Window measurement courses group sizes into customary measurement buckets, that are breakpoints which can be designed to optimize your app for most original circumstances.
 |
| WindowWidthSize Class for grouping gadgets in numerous measurement buckets |
See the Reply Compose pattern to be taught extra about adaptive apps and the window measurement courses implementation.
M3 parts, like high app bars, navigation drawers, bar, and rail, embody built-in help for window insets. These parts, when used independently or with Scaffold, will robotically deal with insets decided by the standing bar, navigation bar, and different components of the system UI.
Scaffold now helps the contentWindowInsets parameter which will help to specify insets for the scaffold content material.
Scaffold insets are solely considered when a topBar or bottomBar will not be current in Scaffold, as these parts deal with insets on the element stage.




