The event of a high-conductivity materials by a crew of researchers in China may considerably decrease contact resistance and Schottky barrier peak in essential areas of digital and optoelectronic microchips, opening the door for pc and digital imaging components that use much less energy in relation to their efficiency than present chipsets.
The Bi2Te3 nanosheets with excessive conductivity have been grown on MoS2 as van der Waals contacts, resulting in a high-performance MoS2 FET. Picture Credit score: Nano Analysis, Tsinghua College Press
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is a fabric that’s so skinny it’s categorized as two-dimensional. In different phrases, the fabric is grown in sheets that reach within the X and Y instructions however are primarily immeasurable on the Z axis as a result of the fabric is often just one molecule or atom tall.
On December 5th, 2022, the crew at Hunan College’s Faculty of Supplies Science and Engineering, led by professors Dong Li and Anlian Pan, printed its findings within the journal Nano Analysis.
The authors of the examine “Epitaxial van der Waals Contacts for Low Schottky Barrier MoS2 Area Impact Transistors” spotlight how 2D supplies have drawn a number of curiosity as a consequence of their quite a few and tunable digital states and quite a lot of optical, digital, and mechanical properties.
These qualities make them promising constructing blocks for upcoming high-performance digital and optoelectronic gadgets, comparable to transistors, photodetectors, and light-emitting diodes.
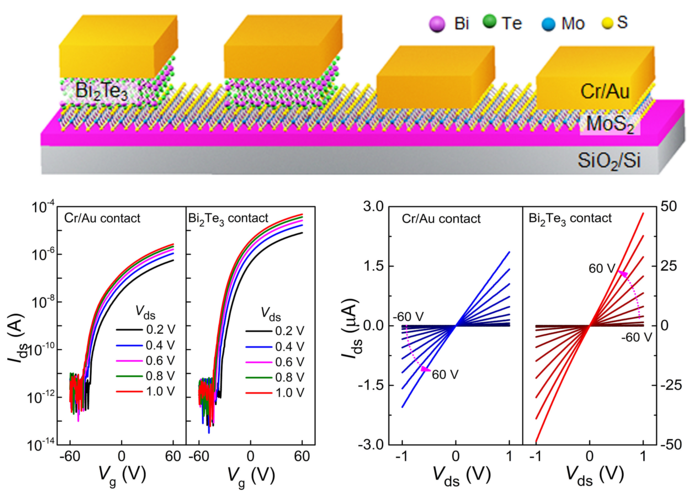
The efficiency of a 2D semiconductor transistor primarily depends on the microscopic connections amongst parts inside a chip, and the standard of these connections relies upon finally on the fabric utilized in these contact factors, that are at all times metals achieved by thermal evaporation, limiting the efficiency of 2D materials-based transistors.
Dong Li, Professor, Faculty of Supplies Science and Engineering, Hunan College
Li’s crew mixed semiconducting MoS2 with the extremely conductive metalloid and semimetal Bismuth Telluride (Bi2Te3) to create a better-performing contact level. The hybrid development of those metalloid nanosheet crystals confirmed initially promising outcomes.
Li additional said, “Makes an attempt in recent times to attain epitaxially grown semiconductor contacts have succeeded in laboratory settings, however weren’t probably candidates for being scaled as much as the extent that might be wanted to fabricate chips and different gadgets.”
“Most of those strategies put ahead strict necessities for materials preparation and strict fabrication and are hardly appropriate with additional manufacturing processes in built-in circuits. The conclusion of high-quality semiconducting 2D supplies and glorious contact on the similar time is important for dependable machine functions,” he continued.
Vertical stacking of MoS2 and Bi2Te3 in a two-step synthesis process was required to create this experimental van der Waals contact.
A chunk of silicon dioxide (SiO2) substrate was positioned downstream of a quartz tube, and molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) and sulfur powder have been added to the middle and higher streams of the furnace, respectively, to function the expansion medium for the monolayer of MoS2.
Bi2Te3 powder and MoS2 nanosheets that had already grown have been positioned within the heart and on the base of the quartz tube, respectively, for the second step development of the Bi2Te3 nanosheet.
MoS2/Bi2Te3 heterostructures have been produced following a 5-minute development interval. Bi2Te3 nanosheet thickness and nucleation websites could also be affected by the expansion temperature and gasoline movement fee, in line with the examine’s findings.
The crew used quite a lot of electrical and imaging strategies to look at the looks and conductive efficiency of the hybrid nanosheets, and so they found that the brand new contact technique carried out considerably higher than gold contacts, that are helpful as a baseline measurement as a result of gold is so often utilized in chip manufacturing.
A vital step towards making the MoS2/Bi2Te3 semiconducting contact technique a powerful candidate for future industrial viability, the brand new contact technique was examined at numerous ambient temperatures and maintained good efficiency at room temperature.
Li said, “Combining the a number of benefits, the epitaxial van der Waals Bi2Te3 contacts present a brand new technique for the appliance of 2D MoS2 in future optoelectronic gadgets. Now that we now have established the performance of Bi2Te3 contacts in a managed laboratory setting, the subsequent steps will likely be to proceed to research and optimize this technique, with the hope that this new expertise can ultimately be adopted for widespread use in additional highly effective, decrease power consumption electronics.”
Journal Reference
Liu, H., et al. (2022) Epitaxial van der Waals contacts for low schottky barrier MoS2 discipline impact transistors. Nano Analysis. doi:10.1007/s12274-022-5229-y.

