Work is consistently altering. Initiatives multiply throughout the enterprise and grow to be applications. Applications get grouped into portfolios, and administration practices grow to be more and more complicated as organizations develop and start to function at scale. Even one thing so simple as an workplace presence is now not a given.
Mission managers are routinely tasked with dealing with uncertainty, to the purpose that adaptability is a core competency for the occupation. All through all of this complexity, Kanban has remained a keystone of the administration world for greater than 60 years, enabling undertaking professionals to keep up a transparent, high-level view of processes.
It’s simple to see why Kanban has grow to be a vital undertaking administration software. As a light-weight and adaptable workflow technique, it presents fit-for-purpose options that I’ve utilized on initiatives throughout various industries, starting from finance to power to shopper markets. Kanban is able to dealing with workflows by itself, however is especially suited to being hybridized with different frameworks, scaling to an enterprise stage, and even serving because the bridge to take organizations from Waterfall to Agile processes.
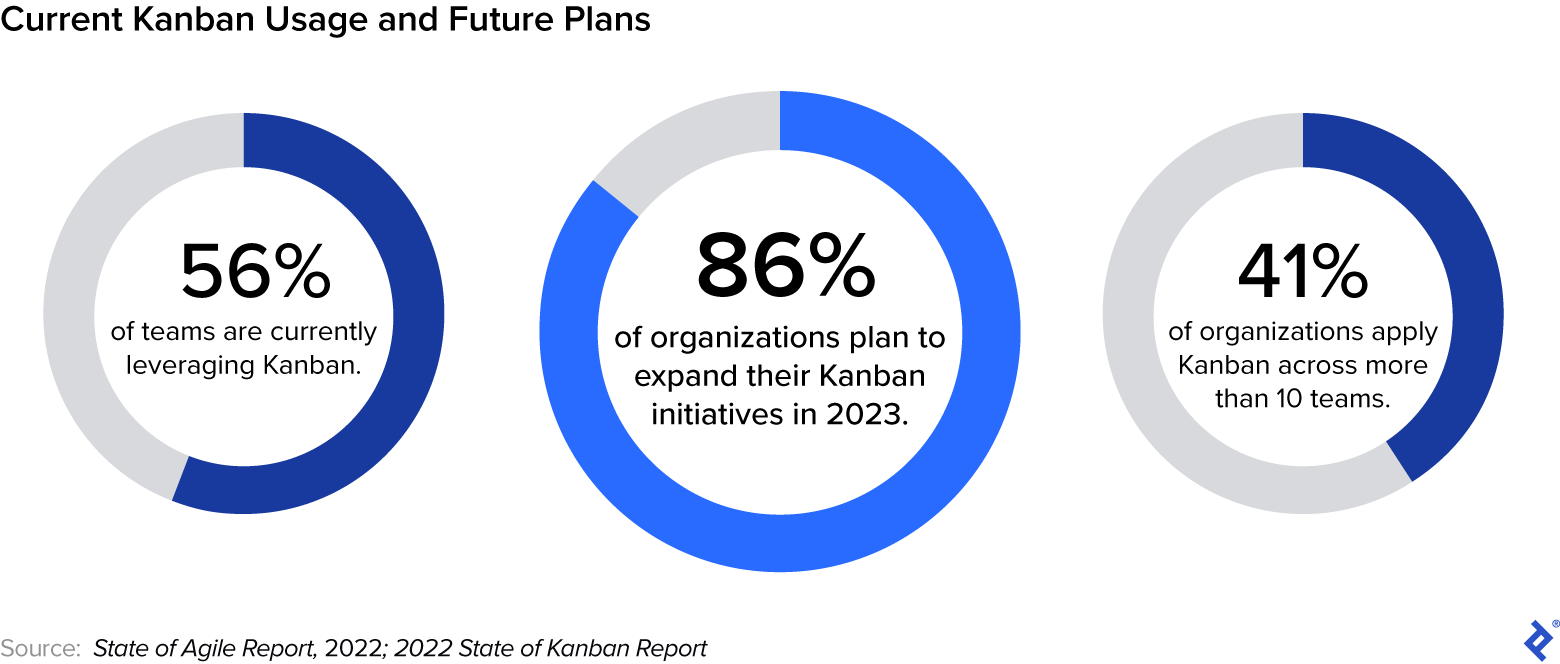
The 2022 State of Agile Report reveals an explosive progress in using Kanban—up from 7% of respondents in 2020 to 56% in 2022. Contemplating the worldwide shift to distant work that occurred in 2020, a part of that improve is little doubt attributable to Kanban use by distant groups.
That mentioned, even with many companies going hybrid or returning to the workplace, Kanban continues to be growing in reputation. In response to the most up-to-date State of Kanban Report, 41% of organizations are making use of Kanban throughout greater than 10 groups, with 86% of respondents planning to broaden their Kanban initiatives in 2023.
Kanban’s Beginnings
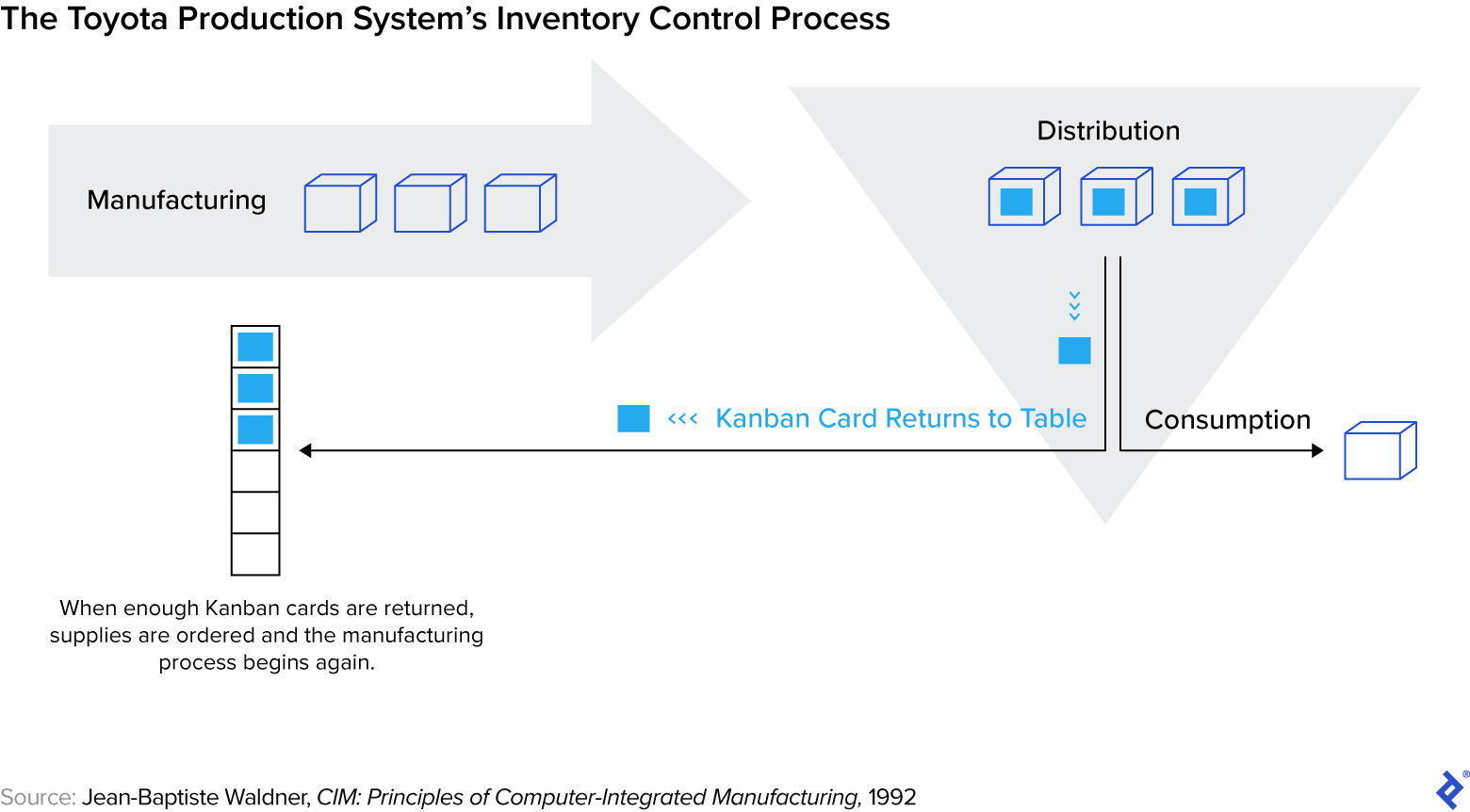
Kanban has its origins within the Toyota Manufacturing System (TPS) invented by Taiichi Ono. A director who had come up by way of the machine store, Ono sought to eradicate waste on the manufacturing line. Two of the areas he recognized have been overproduction and stock: It was wasteful to make too many vehicles, but in addition wasteful to have unused uncooked supplies sitting on the manufacturing facility flooring. His answer drew inspiration from grocery store operations, the place meals is stocked in accordance with demand.
Making use of this precept to manufacturing facility manufacturing proved comparatively easy: For every new automotive, a card containing directions and provide info could be connected to the product throughout meeting, and transfer with it all through the manufacturing course of. As soon as the automotive was bought, the cardboard could be returned to the beginning of the chain. When a predetermined variety of playing cards have been ready to be reassigned to a product, this could sign the necessity for brand spanking new vehicles to enter manufacturing, triggering an order of supplies from the warehouse. The playing cards, named kanbans after the Japanese phrase for signboard, offered a visible support to trace a job from begin to end. By 1963, Kanban was in use in any respect Toyota vegetation. The manufacturing trade at massive would take discover of the strategy and many years later, these rules could be utilized to software program improvement.
From the Manufacturing unit Ground to the Dev Crew’s Whiteboard
In 2010, Microsoft engineer David J. Anderson revealed Kanban: Profitable Evolutionary Change for Your Expertise Enterprise, which constructed on the work of Ono and others to use the rules of Kanban to software program improvement. Central to this framework was using the Kanban board: This visible illustration of a job’s journey by way of the manufacturing course of reenvisioned the manufacturing mannequin for software program improvement. As a substitute of attaching the cardboard to a bodily object, the cardboard is moved between one in all a number of columns representing the duty’s progress.
Anderson additionally laid out (and later expanded) core practices for Kanban:
- Visualize the stream of labor. That is the place the Kanban board is utilized in follow; it really works from the premise {that a} seen workflow is extra manageable and extra simply tracked amongst customers.
- Restrict work in progress (WIP). By limiting the variety of duties a workforce or particular person can deal with directly, Kanban seeks to stability workloads and forestall burnout.
- Handle stream. Kanban permits duties to maneuver by way of every stage within the workflow with pace and effectivity.
- Make insurance policies specific. Kanban empowers groups with transparency; it helps people and groups perceive how, why, and when work is completed.
- Implement suggestions loops. A Kanban workforce makes common course of and coverage changes based mostly on the outcomes of assessment classes.
- Enhance collaboratively, evolve experimentally. The mixed results of elevated transparency from a visualized workflow and the common self-assessment of suggestions loops create an setting by which groups work collectively to enhance efficiency.
These practices type the premise for adaptive functionality; collectively, they create a system by which anybody on the workforce can see and perceive the workflow, assess what’s working and what isn’t, and alter priorities accordingly.
Kanban Distant Groups within the Age of Digital Transformation
In the period of distant work, Kanban has developed once more from bodily playing cards to undertaking administration software program, comparable to Kanbanize, Jira, SwiftKanban, Azure DevOps, and Trello. A digital board supplies distributed groups with a collaborative area by which to handle duties, observe exercise, and preserve priorities from any geographical location. And WIP limits enable groups to handle their time and duties extra effectively, inserting the human contact on the heart of productiveness.
Jidoka, or “automation with human intelligence,” was a core idea of TPS and Lean manufacturing; it refers to successfully stopping work when an issue first emerges, in order that processes can instantly be improved. Whereas automation is valued, human intervention and innovation stay key. Thus, Kanban’s emphasis on suggestions and enchancment is very invaluable in corporations which are new to distant tradition and nonetheless working to solidify efficient distant work or hybrid insurance policies.
Kanban has additionally been tailored past undertaking work to help in reaching organizational agility as distant groups and firms start to scale. Recognizing the position Kanban may play in enterprisewide operations, Anderson and co-author Teodora Bozheva launched the Kanban Maturity Mannequin in 2018. The mannequin is designed to allow corporations to gauge organizational well being as they scale and is an element adoption roadmap, half finest practices tips. It lays out seven maturity ranges to evaluate a company’s capability to fulfill challenges comparable to buyer satisfaction, workforce cohesion, and resilience within the face of sudden market circumstances. Different scaled Agile frameworks and toolkits, comparable to SAFe and Disciplined Agile, have already got strategies of their very own for integrating Kanban at an enterprise stage.
The Way forward for Kanban
Whereas Kanban’s pre-software and pre-Agile period origins are seemingly far faraway from at this time’s more and more distant undertaking environments, its rules of visualizing workflows, limiting work in progress, and regularly enhancing processes are rapidly evolving to include AI-powered analytics and machine studying algorithms to drive undertaking success.
Synthetic intelligence guarantees to allow undertaking administration software program to supply high-quality studies and insights, improve the accuracy of effort estimation, and automate routine undertaking administration duties. A number of Kanban platforms comparable to Atlassian and Trello have already begun to advance the framework utilizing AI, proving as soon as once more its adaptability as new productiveness instruments and applied sciences are launched.
Given how Kanban has progressed by way of new industries and methods of working over the course of 60 years, it shouldn’t be stunning that Anderson compares the adjustments it promotes to evolution. Its foundational precept, “Begin with what you do now,” empowers undertaking managers utilizing Kanban strategies to enact change, making certain that the success of initiatives and firms is predicated on their health inside their setting.
As we face more and more risky instances, undertaking managers can proceed to rely on Kanban’s workflow technique, which prompts responsiveness to vary when mandatory, meets issues the place they’re, and adapts throughout industries and many years in an evolutionary arc that retains tempo with advancing applied sciences and methods of working. If you happen to haven’t adopted Kanban’s rules, strategies, and practices into your undertaking work, now’s the time to begin.