
Intel
Intel introduced technical particulars about its next-generation Core CPUs a number of months in the past. Codenamed Meteor Lake, the chips are good and unhealthy information for Intel’s chip manufacturing ambitions—they’re concurrently the primary chips to make use of the brand-new Intel 4 course of and the primary of Intel’s mass-market client processors to make use of silicon manufactured by somebody apart from Intel (on this case, TSMC). They’re additionally a showcase for Intel’s Foveros packaging know-how, which welds collectively a number of items of silicon (“tiles,” in Intel’s phrases) somewhat than integrating every part right into a single monolithic die.
In the present day, Intel is asserting the primary wave of precise Meteor Lake processors, which Intel says shall be obtainable in some PCs beginning as we speak—count on to see fairly a number of of those PC designs introduced this week, and much more of them at CES subsequent month.
The lineup contains 11 chips throughout two totally different product households: H-series processors for thin-and-light workstation and gaming laptops and U-series chips that may find yourself in Ultrabooks. Eight of those are launching as we speak, and three extra are anticipated in Q1 of 2024. The 2 households share many similarities, together with Intel’s first built-in neural processing unit (NPU) for accelerating machine studying and AI workloads, however briefly, the H-series chips use extra energy and embrace extra P-cores and GPU cores.
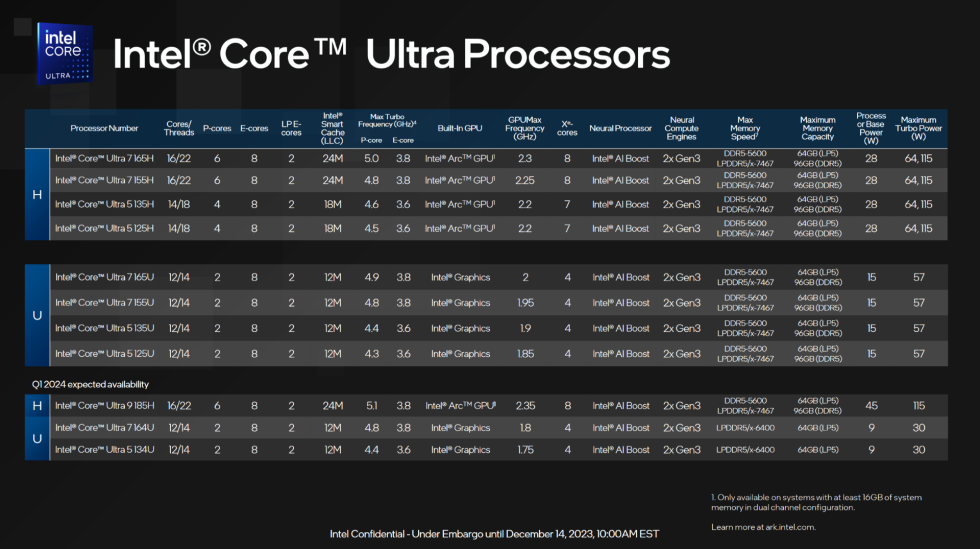
Intel
The slide above has all the important thing specs, however at a excessive stage: the H-series chips embrace both six or 4 Redwood Cove P-cores, eight Crestmont E-cores, and two Crestmont LP E-cores. (Meteor Lake features a pair of even lower-power E-cores in its SoC tile, permitting the principle CPU tile to be shut off solely when CPU utilization is low.) In addition they embrace Intel Arc-branded, TSMC-manufactured GPU tiles with both eight or seven Xe cores, base CPU energy limits of 28 W, and most Turbo Increase energy limits of both 64 or 115 W (seemingly relying on the particular laptop computer you purchase).
The U-series chips are in the reduction of significantly to suit inside a decrease energy funds. All of them embrace simply two P-cores plus eight E-cores and two LP E-cores, and built-in GPUs with solely 4 Xe cores; the Arc branding has been dropped for these regardless of their use of the identical GPU structure, one thing Intel was already doing with the Iris GPU branding in earlier generations. Their base energy restrict is 15 W, and their turbo energy restrict is 57 W, although the 2 further fashions coming in early 2024 have decrease base and Turbo limits of 9 and 30 W, respectively.
Not one of the chips introduced as we speak use the top-tier Core Extremely 9 branding, however the Core Extremely 9 185H will launch early subsequent 12 months with a slightly elevated 5.1 GHz peak clock velocity, greater base and turbo energy utilization, and a lot of the similar fundamental specs because the Core Extremely 7 165H. Intel has introduced non-Extremely Core 7, Core 5, and Core 3 branding for slower and cheaper CPUs, however none of those are being introduced as we speak.
-
Core Extremely’s platform options.
Intel -
The Arc-branded GPU contains a lot of the similar options as desktop Arc playing cards, together with AV1 video encoding.
Intel


