MongoDB is the hottest NoSQL database right this moment, by some measures, even taking up conventional SQL databases like MySQL, which have been the de facto customary for a few years. MongoDB’s doc mannequin and versatile schemas enable for fast iteration in functions. MongoDB is designed to scale out to huge datasets and workloads, so builders know they won’t be restricted by their database. MongoDB helps a wide range of indexes, which speed up selective queries in a lot the identical approach as a SQL database.
Nonetheless, there comes a degree within the lifetime of an software when a secondary index or reproduction of the manufacturing database is required. As a NoSQL database, MongoDB shouldn’t be constructed to carry out for JOINs, and can’t run SQL queries. If you wish to run analytical queries that combination a considerable amount of information, operating them on the first manufacturing database dangers interrupting the efficiency of that database for software serving queries. A secondary database, designed for serving massive analytic queries, can obviate that danger.
Exterior Indexing Utilizing Rockset
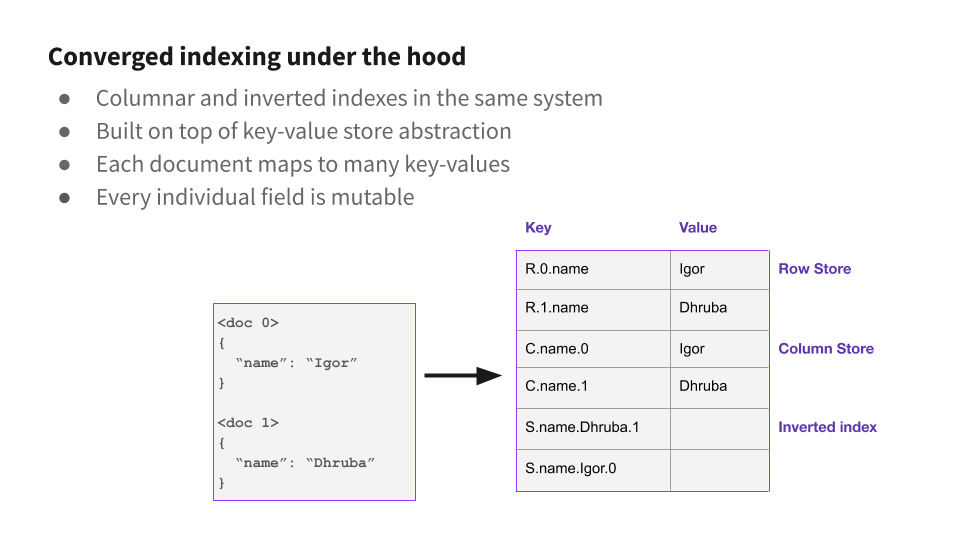
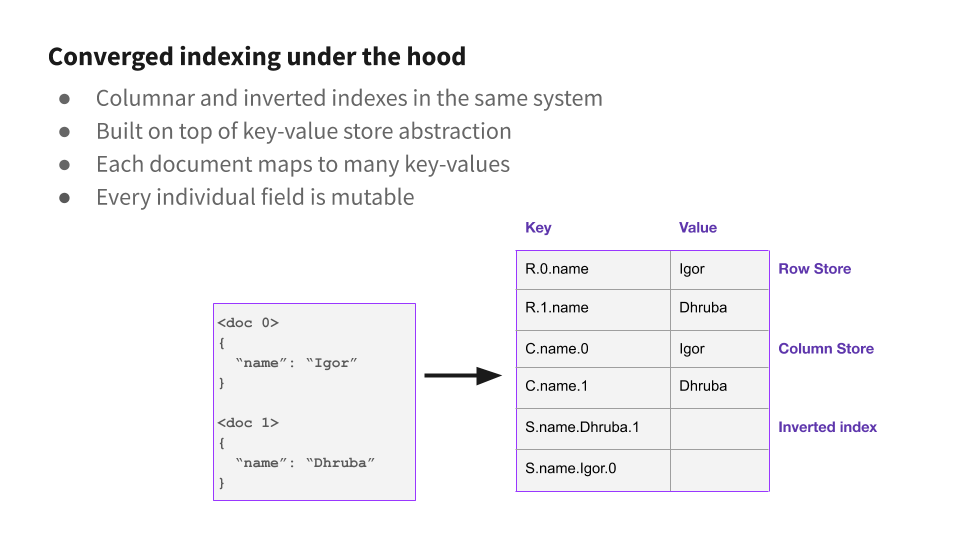
Rockset lately partnered with MongoDB to construct an integration that permits Rockset for use as an exterior indexing layer. Rockset makes use of Converged Indexing to speed up queries with minimal configuration. Each doc is listed on each subject, even nested fields inside arrays or objects. Rockset indexes each subject mechanically so customers don’t must construct indexes to make queries quick — queries are listed by default. There isn’t any restrict to the variety of fields which could be ingested and listed. Rockset’s Converged Index™ is probably the most environment friendly technique to set up your information and permits queries to be obtainable nearly immediately and carry out extremely quick. It’s designed to scale properly for paperwork with hundreds of fields or extra.
Our distinctive method to indexing typically leaves individuals with questions. How will we preserve indexes on each subject when paperwork can preserve hundreds and even hundreds of thousands of fields? What kind of queries can make the most of these indexes? By design, it isn’t essential to know Rockset’s indexing engine as a way to use Rockset. Nonetheless, it may be useful to know how Rockset indexes information, and the way Rockset indexes examine to different methods, particularly indexing in MongoDB, when transitioning to Rockset.
Single Discipline Indexes
In MongoDB, you may create a single subject index on a subject to rapidly choose all paperwork with a selected worth of a subject, or a contiguous vary of values.
Rockset indexes are very related, however they’re created mechanically for each subject, and there’s no restrict to the variety of indexes you may have. When Rockset ingests a doc, each scalar subject is mechanically added to an inverted index. This contains fields inside arrays or objects. For every subject, we retailer a map from every worth to the set of paperwork which comprise that worth. To guage a question with an equality predicate (say SELECT * FROM individuals WHERE identify="Ben"), Rockset finds the inverted index entry for desired worth (Ben), finds the paperwork which match and appears up the entire different fields for that doc.
Compound Indexes
You should use compound indexes in MongoDB if you wish to search a group with constraints on two subject concurrently. Compound indexes are nice for equality predicates and sure vary predicates, however don’t help all mixtures of predicates and kind orders.
Rockset makes use of a extra versatile method just like MongoDB’s index intersection. For each subject, we retailer the checklist of paperwork which comprise every distinct worth. When you have predicates on a number of fields, we retrieve the set of paperwork which match every predicate from the index, and take the intersection (AND) or the union (OR). Whereas this method requires minimal configuration and is quick for many queries, in some circumstances a real compound index can outperform index intersection. If Rockset customers need the performance of a compound index, they will specify a subject mapping to mix the fields they wish to index on to create a brand new subject, and use an index on that mixed subject.
Rockset can intersect the end result units of various indexes effectively as a result of inside every worth, the paperwork are all sorted in the identical order. Subsequently we will intersect two units in streaming vogue, which is each quick and reminiscence environment friendly. For evaluating vary predicates, we use a knowledge construction referred to as a static vary tree. We group numeric values and timestamps into buckets at numerous ranges of granularity so we will discover paperwork with a variety of values by combing a small variety of distinct units.
Multikey Indexes
MongoDB multikey indexes enable customers to index values within arrays. This accelerates a question to search out all paperwork the place an array comprises a worth. As an example, if every person has an inventory of pursuits, you should utilize a multikey index to search out all customers who’re considering a given matter rapidly.
Rockset mechanically indexes each factor of each array, so queries like SELECT * FROM individuals WHERE ARRAY_CONTAINS(pursuits, 'databases') are accelerated by an index with no configuration.
Textual content Indexes
Textual content indexes are helpful for textual content search – discovering all paperwork the place a string comprises a time period or set of phrases. MongoDB textual content index and Rockset textual content indexes are very related. Strings are first damaged down into tokens and normalized to the basis phrase based mostly on the language locale. then you may rating strings based mostly on what number of search phrases they comprise.
Rockset textual content indexes are somewhat totally different from different indexes in that the person should do some work to create them explicitly. Rockset textual content search operates on an array of strings (phrases) moderately than a single string. Rockset will mechanically carry out this tokenization at ingest time when you arrange an applicable subject mapping. As soon as your information is ingested, you should utilize the SEARCH operate to make use of Rockset textual content search. This question will discover all candidates whose resumes comprise both the time period “rockset” or “sql”, and present those who comprise extra matches first:
SELECT
*
FROM
candidates
WHERE
search(
has_term(resume, 'rockset'),
has_term(resume, 'sql')
)
ORDER BY
rating() DESC
Wildcard Indexes
In MongoDB, a wildcard index creates an index on all nested paths inside an object. That is helpful if the schema of the thing is dynamic, and also you wish to mechanically index new fields, or the thing has many fields and also you wish to index all of them. Customers create a wildcard index by operating the next command:
db.assortment.createIndex( { "subject.$**" : 1 } )
At Rockset, we expect indexing information mechanically is a good concept, so we construct indexes mechanically on each subject, even deeply nested fields inside objects. Rockset primarily has a wildcard index on the complete doc. Not like wildcard indexes in MongoDB, even nested geographical fields are listed. Whereas MongoDB restricts customers to a complete of 64 indexes, Rockset permits collections to have a limiteless variety of indexes.
2dsphere Indexes
MongoDB and Rockset each help quick queries for geographical shapes – close by factors, factors inside a polygon, and so on. Any information which comprises latitudes and longitudes can doubtless profit from a geospatial index. In reality, each MongoDB and Rockset use the Google S2 library for storing and manipulating geographical objects. All it’s essential to do to start out utilizing Rockset’s geospatial index is to ingest geographically typed information. For study extra about how Rockset geospatial indexes work and the way you should utilize them, take a look at Exterior Lands, Airbnb Costs, and Rockset’s Geospatial Queries.
2nd and geoHaystack Indexes
MongoDB has 2dsphere indexes for indexing spherical geometry (i.e. the floor of the Earth) and 2nd and geoHaystack indexes for indexing objects in flat, Euclidean geometry.
Sadly, Rockset doesn’t help 2nd indexes in Euclidean area. As a workaround, you may specify the 2 coordinates as separate fields, and write a question which makes use of each fields. As an example, if you wish to discover all (x, y) factors close to (1, 1), you possibly can run the next question, and it could intersect the set of factors with x in (0, 2) and y in (0, 2):
SELECT * FROM factors WHERE x > 0 AND x < 2 AND y > 0 AND y < 2
An alternative choice is to transform your factors into latitude/longitude coordinates in a small vary (say -1 to 1), and use Rockset’s geospatial index. Whereas outcomes received’t be actual because of the curvature of a sphere, inside a small vary the floor of a sphere approximates a aircraft.
Hashed Indexes
In case you create a hashed index on a subject x in MongoDB, it creates a mapping from the hash of x to all of the paperwork which comprise that worth of x (a posting checklist). Hashed indexes are helpful for equality predicates. Rockset’s inverted index is analogous, in that we retailer a posting checklist for each distinct worth, so it may be used to speed up an equality predicate. The Rockset inverted index doesn’t hash the values although, so it will also be used to speed up vary predicates by merging the posting lists for all values in a variety.
Hashed indexes in MongoDB will also be used to shard a group based mostly on a given hash key. Rockset doesn’t enable customers to manage sharding. As an alternative, paperwork are mechanically sharded evenly to make sure writes and reads are balanced throughout all replicas. This maximizes parallelism and efficiency.
Getting the Most Out of Rockset’s Indexes
Rockset is designed to reduce the quantity of person configuration to get quick queries, however there are nonetheless steps you may take to make your queries sooner. You possibly can run EXPLAIN on the question in query to see how the question is being executed. In case you see index filter, the question is being accelerated by a number of indexes.
api.rs2.usw2.rockset.com> EXPLAIN SELECT * from individuals WHERE age > 18;
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| EXPLAIN |
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| choose *:$2 |
| reshuffle on_final |
| index filter on commons.individuals: fields($2=*, $1=age), question($1:float(18,inf], int(18,9223372036854775807]) |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Listed here are a number of widespread causes your question might not use an index:
- In case you’re looking by a LIKE sample or common expression with a wildcard initially (i.e.,
WHERE haystack LIKE %needle%), we can not use an index. In case you are trying to find a selected phrase or token, it is best to strive making a textual content index with a subject mapping, and use textual content search as a substitute of LIKE. - A question which selects paperwork based mostly on the output of a operate (i.e.
WHERE DATE_PARSE(creation_date, '%Y/%m/%d') = DATE(2020, 7, 13)) Rockset can not apply the index. You possibly can both rewrite the predicate to use on to a subject (WHERE creation_date="2020/07/13") or create a subject mapping with the output of the operate, then apply a predicate on that. - The place attainable, categorical predicates as ranges. As an example, if you wish to discover all strings which begin with an higher case letter, use
WHERE my_string >= 'A' AND my_string <= '['moderately thanWHERE UPPER(SUBSTR(my_string, 1, 1)) = SUBSTR(my_string, 1, 1).
You’ll find extra recommendation on accelerating your queries within the question efficiency information.
Different MongoDB assets: