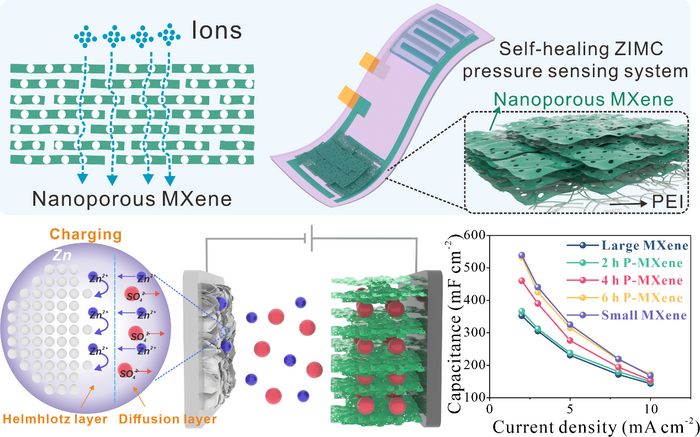
Two-dimensional transition-metal carbides (MXenes) are extraordinarily aggressive in electrochemical vitality storage as a result of their extremely hydrophilic surfaces and excellent metallic conductivity. Nonetheless, the simple stacking-up inclination of interlayers would lead to decreased ion accessibility and accessible transport paths inside MXenes, limiting their electrochemical efficiency.
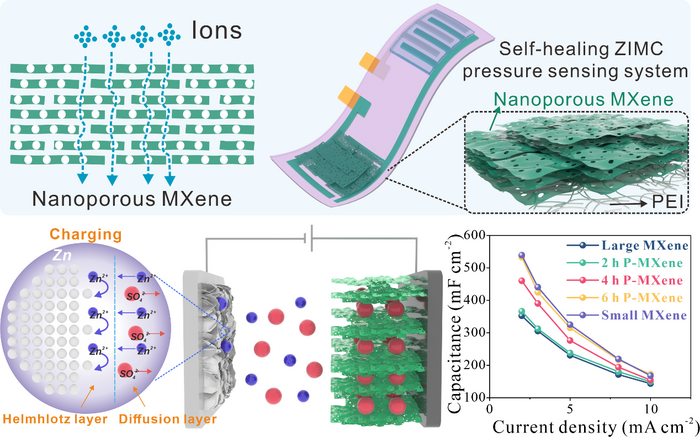
Primarily based on the design of nanoscale ion channels, MXene electrodes with maximized ion accessibility and excessive mechanical power are constructed and used for high-capacity Zinc-ion vitality storage. The design of in-plane ion channels offers a easy, environment friendly, and scalable strategy to enhance the electrochemical vitality storage capability of MXenes and different 2D supplies. Picture Credit score: Science China Press
Quite a few methods have been developed to totally make the most of MXenes’ benefits in electrochemical vitality storage and forestall self-stacking habits. Gap etching is among the methods employed to enhance transport effectivity and ion accessibility, which could be utilized to assemble high-performance vitality storage units.
Notably, chemical etching’s capability to provide nanoscale ion-channel electrodes gives promising utility potential. Controlling the extent of chemical etching for efficient manipulation of electrochemical vitality storage nonetheless poses vital difficulties.
On this examine printed by Science Bulletin, MXene nanosheets with in-plane ion channels are created by chemical oxidation and used as electrodes to create self-healing Zinc-ion micro-capacitors (ZIMC) with distinctive anti-self-discharge performances.
This work relies on the design idea of nanoscale in-plane ion channels. Whereas sustaining the superior mechanical power and electrical conductivity of large-sized MXene nanosheets, the in-plane ion-channel geared up MXene nanosheets can cut back the ions’ transit distance and enhance the electrochemical efficiency of ZIMC.
The self-healing MXene-based Zinc-ion micro-capacitor that was created has excessive areal particular capacitance (532.8 mF cm–2) at present densities of two mA cm–2, a low self-discharge fee of 4.4 mV h–1, and a excessive vitality density of 145.1 μWh cm–2 at energy densities of 2800 μW cm–2.
The developed ZIMC has vital promise to be used in versatile electronics as a result of its superior anti-self-discharge and self-healing traits, which might assist microelectronic units for an prolonged interval.
MXene electrodes with optimum ion accessibility and glorious mechanical power are created and employed for high-capacity zinc-ion vitality storage based mostly on the development of nanoscale ion channels.
An in-plane ion channel design offers a simplified, sensible, and scalable technique to considerably enhance the electrochemical vitality storage functionality of MXenes and different 2D supplies.
Journal Reference
Cheng, Y. et al. (2022) Maximizing the ion accessibility and excessive mechanical power in nanoscale ion channel MXene electrodes for high-capacity zinc-ion vitality storage. Science Bulletin. doi:10.1016/j.scib.2022.10.003
Supply: http://www.scichina.com/english/