Posted by Alex Vanyo – Developer Relations Engineer
TL;DR: Take away pointless function necessities that stop customers from downloading your app on gadgets that don’t assist the options. Automate monitoring function necessities and maximize app availability with badging!
Required options cut back app availability
<uses-feature> is an app manifest aspect that specifies whether or not your app will depend on a {hardware} or software program function. By default, <uses-feature> specifies {that a} function is required. To point that the function is elective, you have to add the android:required=”false” attribute.
Google Play filters which apps can be found to obtain based mostly on required options. If the person’s machine doesn’t assist some {hardware} or software program function, then an app that requires that function received’t be accessible for the person to obtain.
<uses-permission>, one other app manifest aspect, complicates issues by implicitly requiring options for permissions reminiscent of CAMERA or BLUETOOTH (see Permissions that suggest function necessities). The preliminary declared orientations to your actions may also implicitly require {hardware} options.
The system determines implicitly required options after merging all modules and dependencies, so it might not be clear to you which ones options your app finally requires. You may not even remember when the record of required options has modified. For instance, integrating a brand new dependency into your app would possibly introduce a brand new required function. Or the combination would possibly request extra permissions, and the permissions may introduce new, implicitly required options.
This conduct has been round for some time, however Android has modified quite a bit over time. Android apps now run on telephones, foldables, tablets, laptops, automobiles, TVs and watches, and these gadgets are extra diverse than ever. Some gadgets don’t have telephony companies, some don’t have touchscreens, some don’t have cameras.
Expectations based mostly on permissions have additionally modified. With runtime permissions, a <uses-permission> declaration within the manifest now not ensures that your app can be granted that permission. Customers can select to disclaim entry to {hardware} in favor of different methods to work together with the app. For instance, as an alternative of giving an app permission to entry the machine’s location, a person could choose to at all times seek for a specific location as an alternative.
Banking apps shouldn’t require the machine to have an autofocusing digicam for verify scanning. They shouldn’t specify that the digicam should be a entrance or rear digicam or that the machine has a digicam in any respect! It needs to be sufficient to permit the person to add an image of a verify from one other supply.
Apps ought to assist keyboard navigation and mouse enter for accessibility and value causes, so strictly requiring a {hardware} touchscreen shouldn’t be essential.
Apps ought to assist each panorama and portrait orientations, so that they shouldn’t require that the display may very well be landscape-oriented or may very well be portrait-oriented. For instance, screens inbuilt to automobiles could also be in a set panorama orientation. Even when the app helps each panorama and portrait, the app may very well be unnecessarily requiring that the machine helps being utilized in portrait, which might exclude these automobiles.
Decide your app’s required options
You should utilize aapt2 to output info about your APK, together with the explicitly and implicitly required options. The logic matches how the Play Retailer filters app availability.
aapt2 dump badging <path_to_.apk>
Within the Play Console, it’s also possible to verify which gadgets are being excluded from accessing your app.
Improve app availability by making options elective
Most apps shouldn’t strictly require {hardware} and software program options. There are few ensures that the person will permit utilizing that function within the first place, and customers anticipate to have the ability to use all components of your app in the best way they see match. To extend your app’s availability throughout kind components:
- Present alternate options in case the function will not be accessible, guaranteeing your app doesn’t want the function to operate.
- Add android:required=”false” to present <uses-feature> tags to mark the function as not required (or take away the tag solely if the app now not makes use of a function).
- Add the <uses-feature> tag with android:required=”false” for implicitly required function because of declaring permissions that suggest function necessities.
Forestall regressions with CI and badging
To protect towards regressions brought on by inadvertently including a brand new function requirement that reduces machine availability, automate the duty of figuring out your app’s options as a part of your construct system. By storing the badging output of the aapt2 software in a textual content file and checking the file into model management, you possibly can monitor all declared permissions and explicitly and implicitly required options out of your closing common apk. This contains all options and permissions included by transitive dependencies, along with your personal.
You may automate badging as a part of your steady integration setup by organising three Gradle duties for every variant of your app you need to validate. Utilizing launch for example, create these three duties:
- generateReleaseBadging – Generates the badging file from the common APK utilizing the aapt2 executable. The output of this process (the badging info) is used for the next two duties.
- updateReleaseBadging – Copies the generated badging file into the principle challenge listing. The file is checked into supply management as a golden badging file.
- checkReleaseBadging – Validates the generated badging file towards the golden badging file.
CI ought to run checkReleaseBadging to confirm that the checked-in golden badging file nonetheless matches the generated badging file for the present code. If code adjustments or dependency updates have induced the badging file to alter in any approach, CI fails.
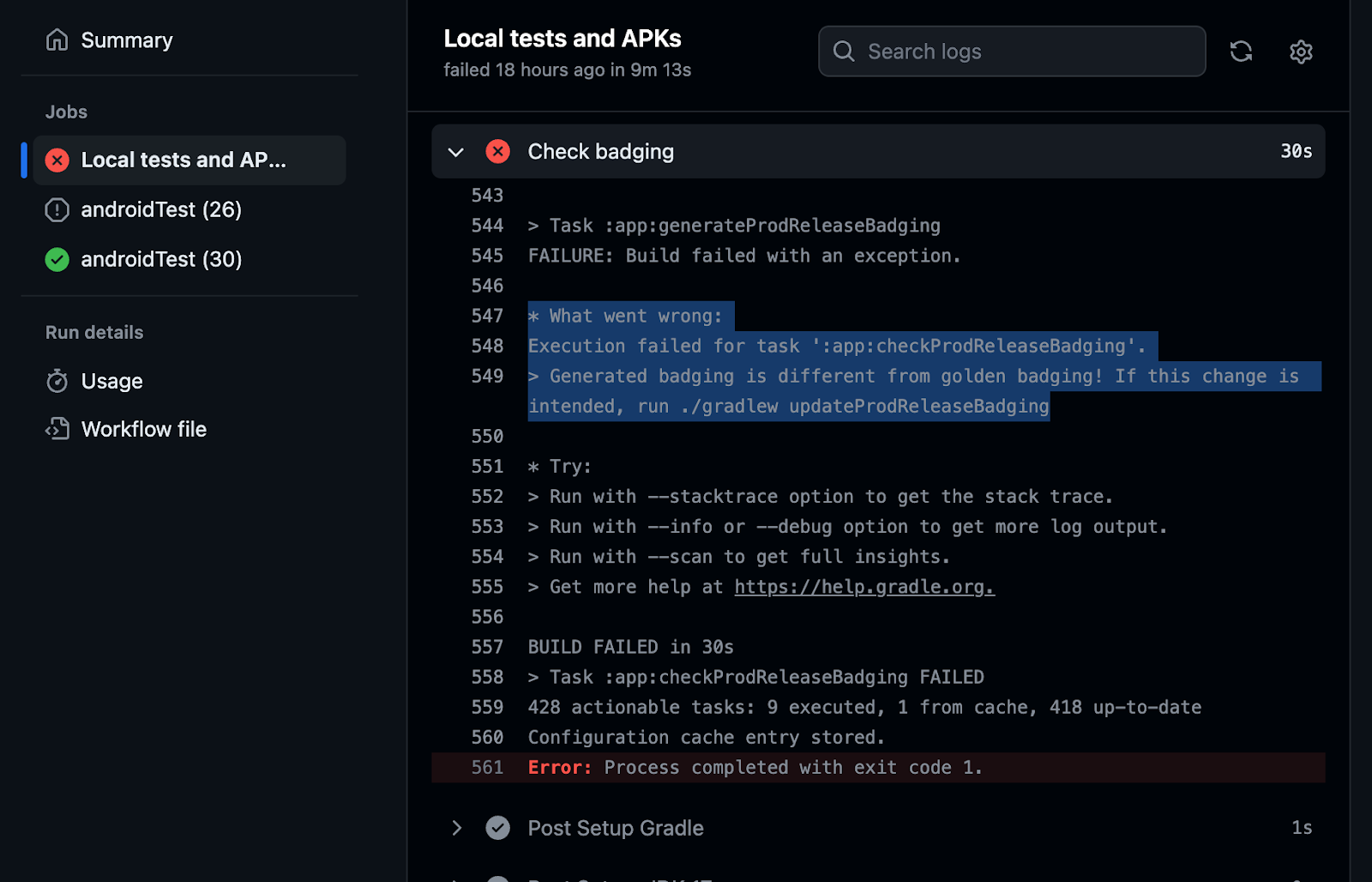
When adjustments are intentional, run updateReleaseBadging to replace the golden badging file and recheck it into supply management. Then, this transformation will floor in code overview to be validated by reviewers that the badging adjustments are anticipated.
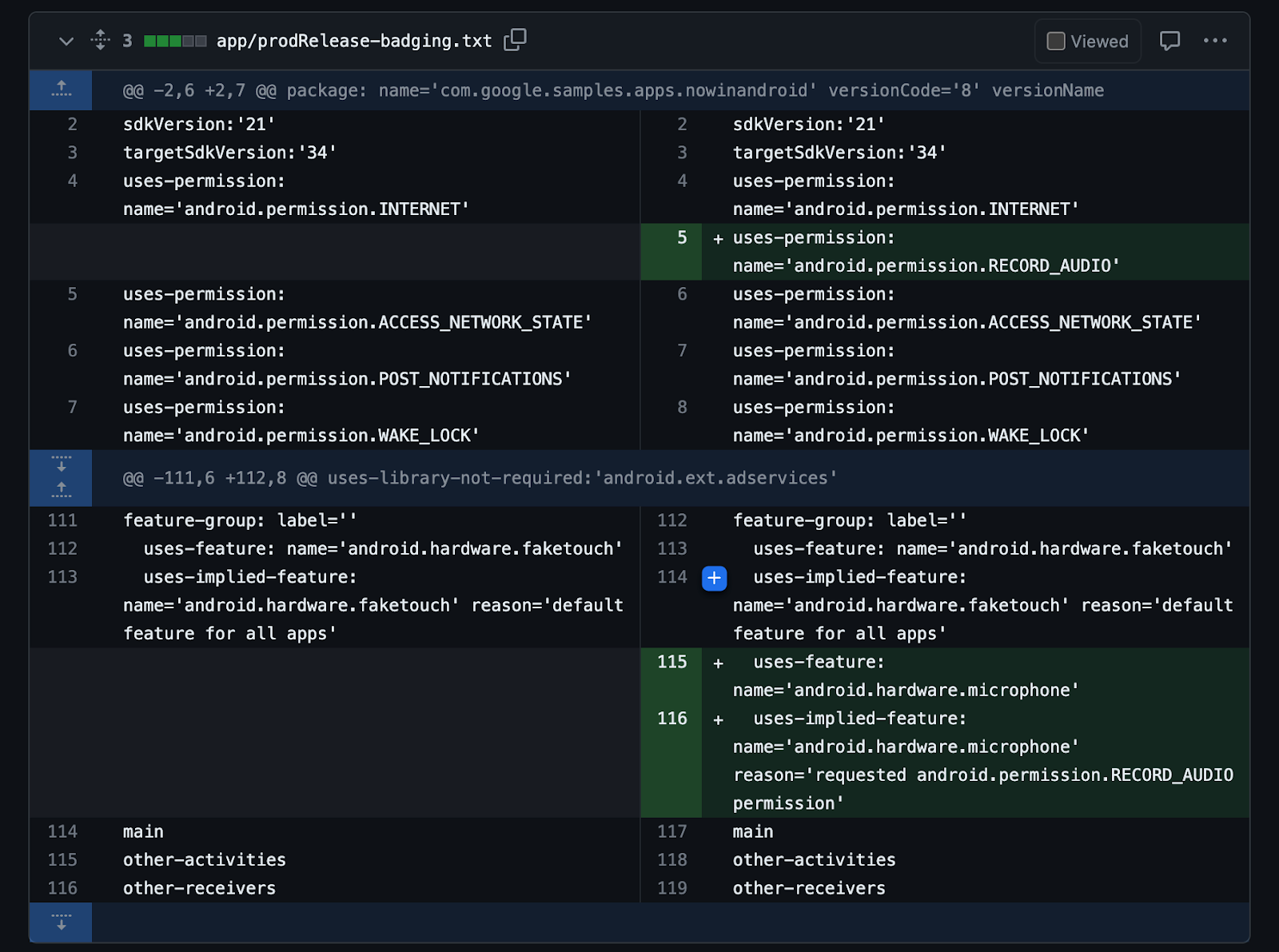
CI-automated badging guards towards adjustments inadvertently inflicting a brand new function to be required, which would cut back availability of the app.
For a whole working instance of a CI system verifying the badging file, try the setup within the Now in Android app.
Hold options elective
Android gadgets are regularly turning into extra diverse, with customers anticipating an ideal expertise out of your Android app no matter the kind of machine they’re utilizing. Whereas some software program or {hardware} options is perhaps important to your app’s operate, in lots of circumstances they shouldn’t be strictly required, needlessly stopping some customers from downloading your app.
Use the badging output from aapt2 to verify which options your app requires, and use the Play Console to confirm which gadgets the necessities are stopping from downloading your app. You may routinely verify your app’s badging in CI and catch regressions.
Backside line: When you don’t completely want a function to your whole app to operate, make the function elective to make sure your app’s availability to the best variety of gadgets and customers.
Study extra by trying out our developer information.

.png)

