Greater than 5 years after area title registrars began redacting private knowledge from all public area registration information, the non-profit group overseeing the area business has launched a centralized on-line service designed to make it simpler for researchers, regulation enforcement and others to request the knowledge straight from registrars.

In Could 2018, the Web Company for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) — the nonprofit entity that manages the worldwide area title system — instructed all registrars to redact the shopper’s title, handle, cellphone quantity and electronic mail from WHOIS, the system for querying databases that retailer the registered customers of domains and blocks of Web handle ranges.
ICANN made the coverage change in response to the Basic Information Safety Regulation (GDPR), a regulation enacted by the European Parliament that requires firms to achieve affirmative consent for any private info they accumulate on individuals inside the European Union. Within the meantime, registrars had been to proceed accumulating the info however not publish it, and ICANN promised it will develop a system that facilitates entry to this info.
On the finish of November 2023, ICANN launched the Registration Information Request Service (RDRS), which is designed as a one-stop store to submit registration knowledge requests to taking part registrars. This video from ICANN walks by way of how the system works.
Accredited registrars don’t must take part, however ICANN is asking all registrars to hitch and says individuals can choose out or cease utilizing it at any time. ICANN contends that using a standardized request type makes it simpler for the right info and supporting paperwork to be offered to guage a request.
ICANN says the RDRS doesn’t assure entry to requested registration knowledge, and that every one communication and knowledge disclosure between the registrars and requestors takes place outdoors of the system. The service can’t be used to request WHOIS knowledge tied to country-code high stage domains (CCTLDs), akin to these ending in .de (Germany) or .nz (New Zealand), for instance.
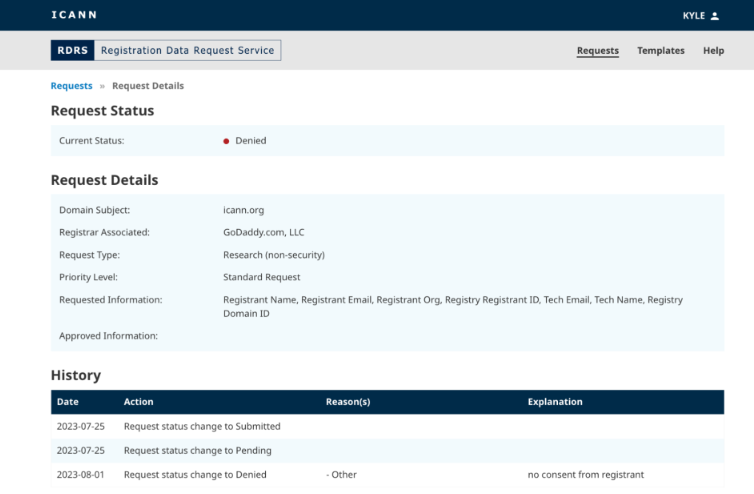
The RDRS portal.
As Catalin Cimpanu writes for Dangerous Enterprise Information, at present investigators can file authorized requests or abuse studies with every particular person registrar, however the thought behind the RDRS is to create a spot the place requests from “verified” events could be honored sooner and with a better diploma of belief.
The registrar group usually views public WHOIS knowledge as a nuisance difficulty for his or her area prospects and an unwelcome cost-center. Privateness advocates preserve that cybercriminals don’t present their actual info in registration information anyway, and that requiring WHOIS knowledge to be public merely causes area registrants to be pestered by spammers, scammers and stalkers.
In the meantime, safety consultants argue that even in instances the place on-line abusers present deliberately deceptive or false info in WHOIS information, that info continues to be extraordinarily helpful in mapping the extent of their malware, phishing and scamming operations. What’s extra, the overwhelming majority of phishing is carried out with the assistance of compromised domains, and the first technique for cleansing up these compromises is utilizing WHOIS knowledge to contact the sufferer and/or their internet hosting supplier.
Anybody searching for copious examples of each want solely to search this Site for the time period “WHOIS,” which yields dozens of tales and investigations that merely wouldn’t have been potential with out the info obtainable within the international WHOIS information.
KrebsOnSecurity stays uncertain that taking part registrars shall be any extra prone to share WHOIS knowledge with researchers simply because the request comes by way of ICANN. However I look ahead to being improper on this one, and will definitely point out it in my reporting if the RDRS proves helpful.
No matter whether or not the RDRS succeeds or fails, there may be one other European regulation that takes impact in 2024 which is prone to place extra strain on registrars to answer reputable WHOIS knowledge requests. The brand new Community and Data Safety Directive (NIS2), which EU member states have till October 2024 to implement, requires registrars to maintain rather more correct WHOIS information, and to reply inside as little as 24 hours to WHOIS knowledge requests tied every little thing from phishing, malware and spam to copyright and model enforcement.

