| Nov 03, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) There are a lot of creatures on our planet with extra superior senses than people. Turtles can sense Earth’s magnetic area. Mantis shrimp can detect polarized gentle. Elephants can hear a lot decrease frequencies than people can. Butterflies can understand a broader vary of colours, together with ultraviolet (UV) gentle.
|
|
Impressed by the improved visible system of the Papilio xuthus butterfly, a workforce of researchers have developed an imaging sensor able to “seeing” into the UV vary inaccessible to human eyes. The design of the sensor makes use of stacked photodiodes and perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs) able to imaging totally different wavelengths within the UV vary. Utilizing the spectral signatures of biomedical markers, corresponding to amino acids, this new imaging know-how is even able to differentiating between most cancers cells and regular cells with 99% confidence.
|
|
This new analysis, led by College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign electrical and laptop engineering professor Viktor Gruev and bioengineering professor Shuming Nie, was lately printed within the journal Science Advances (“Bioinspired, vertically stacked, and perovskite nanocrystal–enhanced CMOS imaging sensors for resolving UV spectral signatures”). Each Gruev and Nie are associates of the Most cancers Middle at Illinois.
|
Key Takeaways
|
|
The sensor makes use of perovskite nanocrystals and a layered photodiode design to seize the nuances within the UV spectrum, much like how butterflies understand delicate variations.
This know-how has the potential to considerably advance medical diagnostics by figuring out most cancers cells with a excessive diploma of accuracy based mostly on their UV spectral signatures.
The novel sensor could possibly be instrumental throughout surgical procedures to make sure full removing of cancerous tissues by detecting variations in autofluorescence between wholesome and cancerous cells.
Past healthcare, the sensor affords new analysis potentialities in biology, enabling the research of animal conduct and environmental understanding via UV notion.
|
 |
| Creative depiction of a butterfly above the bioinspired imaging sensor. (Picture: College of Illinois)
|
The Analysis
|
|
“We have taken inspiration from the visible system of butterflies, who’re capable of understand a number of areas within the UV spectrum, and designed a digital camera that replicates that performance,” Gruev says. “We did this by utilizing novel perovskite nanocrystals, mixed with silicon imaging know-how, and this new digital camera know-how can detect a number of UV areas.”
|
|
UV gentle is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than that of seen gentle (however longer than x-rays). We’re most accustomed to UV radiation from the solar and the hazards it poses to human well being. UV gentle is categorized into three totally different areas—UVA, UVB and UVC— based mostly on totally different wavelength ranges. As a result of people can’t see UV gentle, it’s difficult to seize UV info, particularly discerning the small variations between every area.
|
|
Butterflies, nevertheless, can see these small variations within the UV spectrum, like people can see shades of blue and inexperienced. Gruev notes, “It’s intriguing to me how they’re able to see these small variations. UV gentle is extremely troublesome to seize, it simply will get absorbed by every part, and butterflies have managed to do it extraordinarily properly.”
|
The Imitation Sport
|
|
People have trichromatic imaginative and prescient with three photoreceptors, the place each colour perceived could be produced from a mix of pink, inexperienced and blue. Butterflies, nevertheless, have compound eyes, with six (or extra) photoreceptor courses with distinct spectral sensitivities. Specifically, the Papilio xuthus, a yellow, Asian swallowtail butterfly, has not solely blue, inexperienced and pink, but additionally violet, ultraviolet and broadband receptors. Additional, butterflies have fluorescent pigments that enable them to transform UV gentle into seen gentle which might then be simply sensed by their photoreceptors. This permits them to understand a broader vary of colours and particulars of their surroundings.
|
|
Past the elevated variety of photoreceptors, butterflies additionally exhibit a novel tiered construction of their photoreceptors. To copy the UV sensing mechanism of the Papilio xuthus butterfly, the UIUC workforce has emulated the method by combining a skinny layer of PNCs with a tiered array of silicon photodiodes.
|
|
PNCs are a category of semiconductor nanocrystals that show distinctive properties much like that of quantum dots—altering the scale and composition of the particle modifications the absorption and emission properties of the fabric. In the previous couple of years, PNCs have emerged as an fascinating materials for various sensing purposes, corresponding to photo voltaic cells and LEDs.
|
|
PNCs are extraordinarily good at detecting UV (and even decrease) wavelengths that conventional silicon detectors aren’t. Within the new imaging sensor, the PNC layer is ready to take up UV photons and re-emit gentle within the seen (inexperienced) spectrum which is then detected by the tiered silicon photodiodes. Processing of those indicators permits for mapping and identification of UV signatures.
|
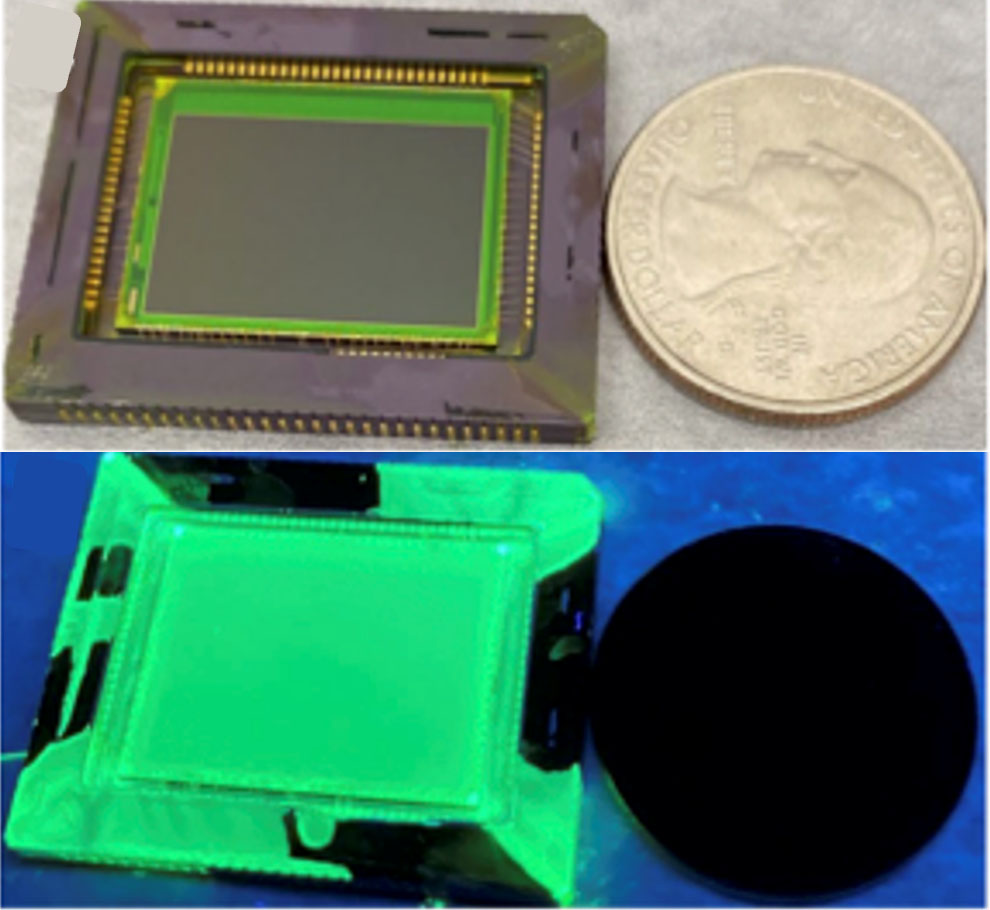 |
| UV imaging sensor in comparison with a US quarter underneath white gentle (prime) and underneath UV gentle (backside), inexperienced look attributed to PNC layer fluorescence. (Picture: College of Illinois)
|
Healthcare and Past
|
|
There are numerous biomedical markers current in cancerous tissues at increased concentrations than in wholesome tissues—amino acids (constructing blocks of proteins), proteins, and enzymes. When excited with UV gentle, these markers gentle up and fluoresce within the UV and a part of the seen spectrum, in a course of referred to as autofluorescence. “Imaging within the UV area has been restricted and I might say that has been the most important roadblock for making scientific progress,” explains Nie. “Now we’ve give you this know-how the place we are able to picture UV gentle with excessive sensitivity and may distinguish small wavelength variations.”
|
|
As a result of most cancers and wholesome cells have totally different concentrations of markers and subsequently totally different spectral signatures, the 2 courses of cells could be differentiated based mostly on their fluorescence within the UV spectrum. The workforce evaluated their imaging gadget on its means to discriminate cancer-related markers and located that’s able to differentiating between most cancers and wholesome cells with 99% confidence.
|
|
Gruev, Nie and their collaborative analysis workforce envision with the ability to use this sensor throughout surgical procedure. One of many greatest challenges is understanding how a lot tissue to take away to make sure clear margins and such a sensor may help facilitate the decision-making course of when a surgeon is eradicating a cancerous tumor.
|
|
“This new imaging know-how is enabling us to distinguish cancerous versus wholesome cells and is opening up new and thrilling purposes past simply well being,” Nie says. There are a lot of different species apart from butterflies able to seeing within the UV, and having a technique to detect that gentle will present fascinating alternatives for biologists to study extra about these species, corresponding to their looking and mating habits. Bringing the sensor underwater may help carry a better understanding of that surroundings as properly. Whereas plenty of UV is absorbed by water, there may be nonetheless sufficient that makes it via to have an effect and there are a lot of animals underwater that additionally see and use UV gentle.
|



