As units get smaller and extra highly effective, the danger of them overheating and burning out will increase considerably. Regardless of developments in cooling options, the interface between an digital chip and its cooling system has remained a barrier for thermal transport as a result of supplies’ intrinsic roughness.
Sheng Shen, Professor within the Division of Mechanical Engineering at Carnegie Mellon College has fabricated a versatile, highly effective, and extremely dependable materials to effectively fill the hole.
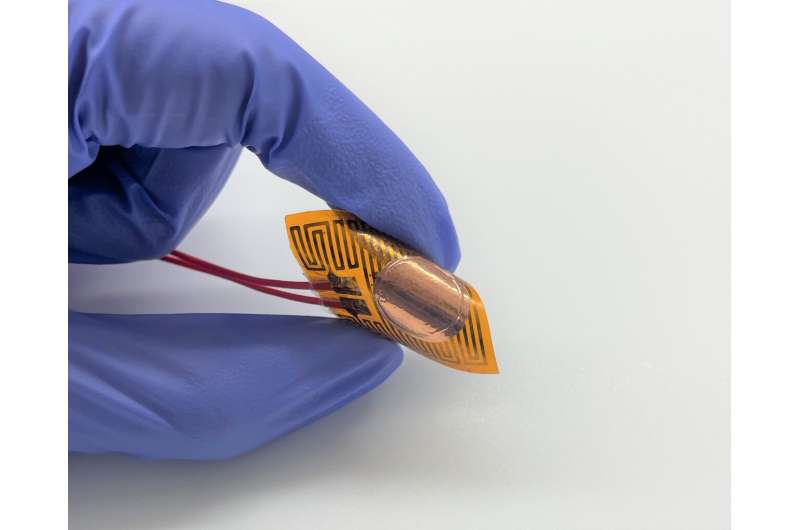
“At first look, our answer seems to be like every odd copper movie, however below a microscope the novelty of our materials turns into clear,” defined Lin Jing, PhD scholar.
The fabric, composed of two skinny copper movies with a graphene-coated copper nanowire array sandwiched between, is extraordinarily user-friendly.
“Different nanowires have to be in-situ grown the place the warmth is designed to be dissipated in order that their utility threshold and value is excessive,” stated Rui Cheng, postdoctoral researcher in Shen’s lab. “Our movie is not depending on any substrate, it’s a free standing movie that may be lower to any measurement or form to fill the hole between numerous electrical elements.”
The “sandwich” builds out of Shen’s “supersolder,” a thermal interface materials (TIM) that may be used equally as standard solders, however with twice the thermal conductance of present state-of-the-art TIMs.
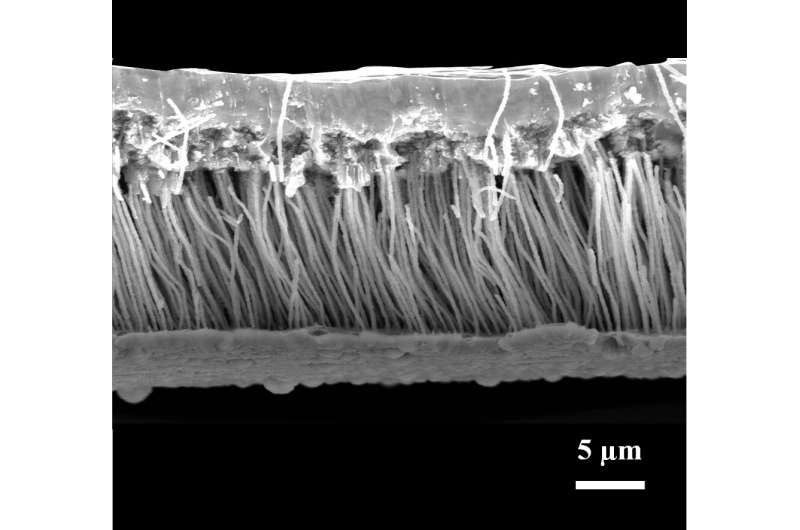
By coating the “supersolder” in graphene, Shen’s workforce enhanced its thermal transport capabilities and prevented the danger of oxidation, making certain an extended service life. The “sandwich,” in comparison with the thermal pastes/adhesives at present in the marketplace, can scale back thermal resistance by greater than 90% when contemplating the identical thickness.
Due to its extremely excessive mechanical flexibility, the “sandwich” can allow a variety of purposes in versatile electronics and microelectronics, together with versatile LEDs and lasers for lighting and show, wearable sensors for communication, implantable electronics for monitoring well being and imaging, and tender robotics.
Transferring ahead, Shen’s workforce will discover methods to scale the fabric at an industrial stage, decrease its price, whereas persevering with to hunt methods to enhance it.
“We’re very enthusiastic about this materials’s potential,” Shen shared. “We consider that all kinds of digital techniques can profit from it by permitting them to function at a decrease temperature with larger efficiency.”
The analysis is revealed within the journal ACS Nano.
Extra info:
Lin Jing et al, 3D Graphene-Nanowire “Sandwich” Thermal Interface with Ultralow Resistance and Stiffness, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c10525
Quotation:
How a thin-film copper sandwich is remodeling electronics (2023, February 14)
retrieved 14 February 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-02-thin-film-copper-sandwich-electronics.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.


