C++ – the must-known and all-time favourite programming language of coders. It’s nonetheless related because it was within the mid-80s. As a general-purpose and object-oriented programming language is extensively employed principally each time throughout coding. In consequence, some job roles demand people to be fluent in C++.
C++ is utilized by prime IT firms reminiscent of Evernote, LinkedIn, Microsoft, Opera, NASA, and Fb due to its dependability, efficiency, and wide selection of settings by which it might be used.
Now it’s of utmost significance to have an inkling of what sort of C++ interview questions might be requested in an interview should you’re making use of for a job place the place C++ is used. To face the interviewer with confidence, you’ll want to be thorough with the language with a view to ace the technical spherical.
To make you interview-ready, we have now introduced the High 50 C++ interview questions for newbie, intermediate and skilled which you need to undoubtedly undergo with a view to get your self positioned at prime MNCs.
Newbie Stage Query
Q-1. What’s C++? What are the benefits of C++?
C++ is an object-oriented programming language that was launched to beat the jurisdictions the place C was missing. By object-oriented we imply that it really works with the idea of polymorphism, inheritance, abstraction, encapsulation, object, and sophistication.
Benefits of C++:
- C++ is an OOPs language which means the information is taken into account as objects.
- C++ is a multi-paradigm language; In easy phrases, it implies that we will program the logic, construction, and process of this system.
- Reminiscence administration is a key characteristic in C++ because it permits dynamic reminiscence allocation
- It’s a Mid-Stage programming language which suggests it might develop video games, desktop purposes, drivers, and kernels
To learn extra, check with the article – What are the benefits of C++?
Q- 2. What are the completely different knowledge sorts current in C++?

Various kinds of knowledge sorts in C++
For extra info, check with C++ knowledge sorts
Q-3. Outline ‘std’?
‘std’ is also referred to as Commonplace or it may be interpreted as a namespace. The command “utilizing namespace std” informs the compiler so as to add all the things underneath the std namespace and inculcate them within the international namespace. This all inculcation of world namespace advantages us to make use of “cout” and “cin” with out utilizing “std::_operator_”.
For extra info, check with namespace and std.
Q-4. What are references in C++?
When a variable is described as a reference it turns into an alias of the already present variable. In easy phrases, a referenced variable is one other named variable of an present variable maintaining in thoughts that modifications made within the reference variable shall be mirrored within the already present variable. A reference variable is preceded with a ‘&’ image.
Syntax:
int GFG = 10; // reference variable int& ref = GFG;
For extra info, check with references in C++
Q-5. What do you imply by Name by Worth and Name by Reference?
On this programming language to name a perform we have now 2 strategies: Name by Worth and Name by Reference
|
Name by Worth |
Name by Reference |
|---|---|
| A duplicate of a variable is handed. | A variable itself is handed basically. |
| Calling a perform by sending the values by copying variables. | Calling a perform by sending the deal with of the handed variable. |
| The modifications made within the perform are by no means mirrored outdoors the perform on the variable. In brief, the unique worth isn’t altered in Name by Worth. | The modifications made within the features might be seen outdoors the perform on the handed perform. In brief, the unique worth is altered in Name by reference. |
| Handed precise and formal parameters are saved in numerous reminiscence areas. Due to this fact, making Name by Worth a bit reminiscence inadequate | Handed precise and formal parameters are saved in the identical reminiscence location. Due to this fact, making Name by Reference a bit extra reminiscence environment friendly. |
For info, check with the distinction between name by worth and name by reference
Q-6. Outline token in C++
A token is the smallest particular person aspect of a program that’s understood by a compiler. A token includes the next:
- Key phrases – That include a particular which means to the compiler
- Identifiers – That maintain a novel worth/identification
- Constants – That by no means change their worth all through this system
- Strings – That accommodates the homogenous sequence of information
- Particular Symbols – They’ve some particular which means and can’t be used for one more objective; eg: [] () {}, ; * = #
- Operators – Who carry out operations on the operand
For extra info, check with Tokens in C++
Q-7. What’s the distinction between C and C++?
|
C |
C++ |
|---|---|
| It’s a procedural programming language. In easy phrases, it doesn’t help courses and objects | It’s a combination of each procedural and object-oriented programming languages. In easy phrases, it helps courses and objects. |
| It doesn’t help any OOPs ideas like polymorphism, knowledge abstraction, encapsulation, courses, and objects. | It helps all ideas of information |
| It doesn’t help Operate and Operator Overloading | It helps Operate and Operator Overloading respectively |
| It’s a function-driven language | It’s an object-driven language |
For extra info, check with Distinction between C and C++
Q-8. What’s the distinction between struct and sophistication?
|
Struct |
Class |
|---|---|
| Members of the struct are all the time by default public mode | Members of the category might be in personal, protected, and public modes. |
| Construction doesn’t help inheritance. | Lessons do help the idea of inheritance. |
| Buildings are of the worth sort. They solely maintain worth in reminiscence. | Lessons are of reference sort. It holds a reference of an object in reminiscence. |
| The reminiscence in buildings is saved as stacks | The reminiscence in courses is saved as heaps. |
For extra info, check with the Distinction between struct and sophistication.
Q-9. What’s the distinction between reference and pointer?
|
Reference |
Pointer |
|---|---|
| The worth of a reference can’t be reassigned | The worth of a pointer might be reassigned |
| It might by no means maintain a null worth because it wants an present worth to turn out to be an alias of | It might maintain or level at a null worth and be termed as a nullptr or null pointer |
| It can’t work with arrays | It might work with arrays |
| To entry the members of sophistication/struct it makes use of a ‘ . ‘ | To entry the members of sophistication/struct it makes use of a ‘ -> ‘ |
| The reminiscence location of reference might be accessed simply or it may be used instantly | The reminiscence location of a pointer can’t be accessed simply as we have now to make use of a dereference ‘ * ‘ |
For extra info, check with the Distinction between reference and pointer
Q-10. What’s the distinction between perform overloading and operator overloading?
|
Operate Overloading |
Operator Overloading |
|---|---|
| It’s mainly defining a perform in quite a few methods such that there are lots of methods to name it or in easy phrases you have got a number of variations of the identical perform | It’s mainly giving apply of giving a particular which means to the present which means of an operator or in easy phrases redefining the pre-redefined which means |
| Parameterized Features are a very good instance of Operate Overloading as simply by altering the argument or parameter of a perform you make it helpful for various functions | Polymorphism is an effective instance of an operator overloading as an object of allocations class can be utilized and known as by completely different courses for various functions |
|
Instance of Operate Overloading:
|
Instance of Operator Overloading:
|
For extra info, check with Operator Overloading and Operate Overloading
Q-11. What’s the distinction between an array and an inventory?
|
Arrays |
Lists |
|---|---|
| Array are contiguous reminiscence areas of homogenous knowledge sorts saved in a hard and fast location or dimension. | Lists are traditional particular person components which can be linked or related to one another with the assistance of pointers and shouldn’t have a hard and fast dimension. |
| Arrays are static in nature. | Lists are dynamic in nature |
| Makes use of much less reminiscence than linked lists. | Makes use of extra reminiscence because it has to retailer the worth and the pointer reminiscence location |
For extra info, check with Arrays Vs Record
Q-12: What’s the distinction between some time loop and a do-while loop?
|
Whereas Loop |
do-while Loop |
|---|---|
| Whereas loop can also be termed an entry-controlled loop | The do-while loop is termed an exit management loop |
| If the situation just isn’t happy the statements contained in the loop is not going to execute | Even when the situation just isn’t happy the statements contained in the loop will execute for no less than one time |
|
Instance of some time loop: whereas(situation) {statements to be executed;}; |
Instance of a do-while loop: do { statements to be executed; } whereas(situation or expression); |
For extra info, check with the Distinction between whereas and do-while loop
Q-13. Talk about the distinction between prefix and postfix?
|
prefix |
postfix |
|---|---|
| It merely means placing the operator earlier than the operand | It merely means placing the operator after the operand |
| It executes itself earlier than ‘; ‘ | It executes itself after ‘; ‘ |
| Associativity of prefix ++ is true to left | Associativity of postfix ++ is left to proper |
For extra info, check with the Distinction between prefix and postfix
Q-14. What’s the distinction between new and malloc()?
|
new |
malloc() |
|---|---|
| new is an operator which performs an operation | malloc is a perform that returns and accepts values |
| new calls the constructors | malloc can’t name a constructor |
| new is quicker than malloc as it’s an operator | malloc is slower than new as it’s a perform |
| new returns the precise knowledge sort | malloc returns void* |
For extra info, check with Distinction between new and malloc()
Q-15. What’s the distinction between digital features and pure digital features?
|
Digital Operate |
Pure Digital Operate |
|---|---|
| A Digital Operate is a member perform of a base class that may be redefined in one other derived class. | A Pure Digital Operate is a member perform of a base class that’s solely declared in a base class and outlined in a derived class to forestall it from changing into an summary class. |
| A digital Operate has its definition in its respective base class. | There isn’t a definition in Pure Digital Operate and is initialized with a pure specifier (= 0). |
| The bottom class has a digital perform that may be represented or instanced; In easy phrases, its object might be made. | A base class having pure digital perform turns into summary that can not be represented or instanced; In easy phrases, it means its object can’t be made. |
For extra info, check with the Distinction between digital features and pure digital features
Q-16. What are courses and objects in C++?
A category is a user-defined knowledge sort the place all of the member features and knowledge members are tailored in line with calls for and necessities along with which these all might be accessed with the assistance of an object. To declare a user-defined knowledge sort we use a key phrase class.
An object is an occasion of a category and an entity with worth and state; In easy phrases, it’s used as a catalyst or to characterize a category member. It might include completely different parameters or none.
Be aware: A category is a blueprint thaty defines features that are utilized by an object.
For extra info, check with this What are courses and objects
Q-17. What’s Operate Overriding?
When a perform of the identical title, identical arguments or parameters, and identical return sort already current/declared within the base class is utilized in a derived class is named Operate Overriding. It’s an instance of Runtime Polymorphism or Late Binding which suggests the overridden perform shall be executed on the run time of the execution.
For extra info, check with Operate Overriding in C++
Q-18. What are the varied OOPs ideas in C++?
- Lessons: It’s a user-defined datatype
- Objects: It’s an occasion of a category
- Abstraction: It’s a strategy of displaying solely needed particulars
- Encapsulation: Wrapping of information in a single unit
- Inheritance: The aptitude of a category to derive properties and traits from one other class
- Polymorphism: Polymorphism is named many types of the identical factor
For extra info, check with Varied OOPs ideas in C++
Q-19. Clarify inheritance
The aptitude or skill of a category to derive properties and traits from one other class is named inheritance. In easy phrases, it’s a system or strategy of reusing and increasing present courses with out modifying them.
For extra info, check with Inheritance
Q-20. When ought to we use a number of inheritance?
A number of inheritances imply {that a} derived class can inherit two or extra base/guardian courses. It’s helpful when a derived class wants to mix quite a few attributes/contracts and inherit some, or all, of the implementation from these attributes/contracts. To take a real-life instance think about your Dad and mom the place Mum or dad A is your DAD Mum or dad B is your MOM and Chid C is you.

A number of Inheritances
For extra info, check with A number of Inheritance.
Q-21. What’s digital inheritance?
Digital inheritance is a way that ensures just one copy of a base class’s member variables is inherited by grandchild-derived courses. Or in easy phrases, digital inheritance is used after we are coping with a state of affairs of a number of inheritances however need to stop a number of situations of the identical class from showing within the inheritance hierarchy.
Q-22. What’s polymorphism in C++?
Polymorphism is named many types of the identical factor. In easy phrases, we will say that Polymorphism is the power to show a member perform in a number of types relying on the kind of object that calls them.
In different phrases, we will additionally say {that a} man might be an worker to somebody, a son of somebody, a father of somebody, and a husband of somebody; that is how polymorphism might be projected in actual life.
There’s 2 sort of polymorphism:
- Compile Time Polymorphism
- Operate Overloading
- Operator Overloading
- Run Time Polymorphism
- Operate Overriding
- Digital Operate
To know extra about it, check with Polymorphism
Q-23. What are the various kinds of polymorphism in C++?
There’s 2 sort of polymorphism
Compile Time Polymorphism or Static Binding
Any such polymorphism is achieved through the compile time of this system which ends up in it making a bit quicker than Run time. Additionally, Inheritance just isn’t concerned in it. It’s comprised of 2 additional strategies:
Operate Overloading: When there are a number of features with the identical title however completely different parameters then this is named perform overloading.
C++
|
|
Operator Overloading: It’s mainly giving apply of giving a particular which means to the present which means of an operator or in easy phrases redefining the pre-redefined which means
C++
|
|
Run-Time Polymorphism or Late Binding
Run-time polymorphism takes place when features are invoked throughout run time.
Operate Overriding: Operate overriding happens when a base class member perform is redefined in a derived class with the identical arguments and return sort.
C++
|
|
Output:
Operate of derived class
For extra info, check with Various kinds of Polymorphism
Q-24. Examine compile-time polymorphism and Runtime polymorphism
|
Compile-Time Polymorphism |
Runtime Polymorphism |
|---|---|
| It is usually termed static binding and early binding. | It is usually termed Dynamic binding and Late binding. |
| It’s quick as a result of execution is understood early at compile time. | It’s gradual as in comparison with compile-time as a result of execution is understood at runtime. |
| It’s achieved by perform overloading and operator overloading. | It’s achieved by digital features and performance overriding. |
For extra info, check with Compile-time polymorphism and Runtime polymorphism
Q-25. Clarify the constructor in C++.
A constructor is a particular sort of member perform of a category, whose title is similar as that of the category by whom it’s invoked and initializes worth to the thing of a category.
There are 3 kinds of constructors:
A. Default constructor: It’s the most simple sort of constructor which accepts no arguments or parameters. Even when it isn’t known as the compiler calls it robotically when an object is created.
Instance:
C++
|
|
B. Parameterized constructor: It’s a sort of constructor which accepts arguments or parameters. It needs to be known as explicitly by passing values within the arguments as these arguments assist initialize an object when it’s created. It additionally has the identical title as that of the category.
Additionally, It’s used to overload constructors.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Output
G.x = 10, G.y = 15
C. Copy Constructor: A duplicate constructor is a member perform that initializes an object utilizing one other object of the identical class. Additionally, the Copy constructor takes a reference to an object of the identical class as an argument.
Instance:
C++
|
|
For extra info, check with Constructors
Q-26. What are destructors in C++?
Destructors are members of features in a category that delete an object when an object of the category goes out of scope. Destructors have the identical title as the category preceded by a tilde (~) signal. Additionally, destructors comply with a down-to-top strategy, in contrast to constructors which comply with a top-to-down.
Syntax:
~constructor_name(); // tilde signal signifies that it's a destructor
For extra info, check with Destructor.
Q-27. What’s a digital destructor?
When destroying situations or objects of a derived class utilizing a base class pointer object, a digital destructor is invoked to unlock reminiscence house allotted by the derived class object or occasion.
Digital destructor ensures that first the derived class’ destructor known as. Then the bottom class’s destructor known as to launch the house occupied by each destructors within the inheritance class which saves us from the reminiscence leak. It’s suggested to make your destructor digital every time your class is polymorphic.
For extra info, check with Digital Destructor
Q-28. Is destructor overloading doable? If sure then clarify and if no then why?
The easy reply is NO we can’t overload a destructor. It’s obligatory to solely destructor per class in C++. Additionally to say, Destructor neither take arguments nor they’ve a parameter which may assist to overload.
Intermediate Stage Query
Q-29. Which operations are permitted on pointers?
Pointers are the variables which can be used to retailer the deal with location of one other variable. Operations which can be permitted to a pointer are:
- Increment/Decrement of a Pointer
- Addition and Subtraction of integer to a pointer
- Comparability of pointers of the identical sort
Q-30. What’s the objective of the “delete” operator?
The delete operator is used to delete/take away all of the traits/properties from an object by deallocating its reminiscence; moreover, it returns true or false ultimately. In easy phrases, it destroys or deallocates array and non-array(pointer) objects that are created by new expressions.
C++
|
|
For extra info, check with Delete operator
Q-31. How delete [] is completely different from delete?
|
delete[] |
delete |
|---|---|
| It’s used for deleting an entire array | It’s used to delete just one single pointer |
| It’s used for deleting the objects of new[]; By this, we will say that delete[] is used to delete an array of objects | It’s used for deleting the objects of new; By this, we will say that delete is used to delete a single object |
| It might name as many destructors it desires | It might solely name the destructor of a category as soon as |
Q-32. What are you aware about good friend class and good friend perform?
A good friend class is a category that may entry each the protected and personal variables of the courses the place it’s declared as a good friend.
Instance of good friend class:
C++
|
|
A good friend perform is a perform used to entry the personal, protected, and public knowledge members or member features of different courses. It’s declared with a good friend key phrase. The benefit of a good friend perform is that it isn’t sure to the scope of the category and as soon as it’s declared in a category, moreover to that, it can’t be known as by an object of the category; due to this fact it may be known as by different features. Contemplating all of the talked about factors we will say {that a} good friend perform is a worldwide perform.
Instance of good friend perform:
C++
|
|
For extra info, check with the good friend perform and good friend class
Q-33. What’s an Overflow Error?
Overflow Error happens when the quantity is simply too giant for the information sort to deal with. In easy phrases, it’s a sort of error that’s legitimate for the outlined however exceeds used the outlined vary the place it ought to coincide/lie.
For instance, the vary of int knowledge sort is –2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 and if we declare a variable of dimension 2,247,483,648 it would generate a overflow error.
Q-34. What does the Scope Decision operator do?
A scope decision operator is denoted by a ‘::‘ image. Identical to its title this operator resolves the barrier of scope in a program. A scope decision operator is used to reference a member perform or a worldwide variable out of their scope moreover to which it might additionally entry the hid variable or perform in a program.
Scope Decision is used for quite a few quantities of duties:
- To entry a worldwide variable when there’s a native variable with the identical title
- To outline the perform outdoors the category
- In case of a number of inheritances
- For namespace
For extra info, check with Scope decision operator
Q-35. What are the C++ entry modifiers?
The entry restriction specified to the category members( whether or not it’s member perform or knowledge member) is named entry modifiers/specifiers.
Entry Modifiers are of three sorts:
- Non-public – It might neither be accessed nor be seen from outdoors the category
- Protected – It may be accessed if and provided that the accessor is the derived class
- Public – It may be accessed or be seen from outdoors the category
For extra info, check with Entry Modifiers
Q-36. Are you able to compile a program with out the primary perform?
Sure, it’s completely doable to compile a program and not using a major(). For instance Use Macros that defines the primary
C++
|
|
For extra info, check with Are you able to compile a program with out the primary perform
Q-37. What’s STL?
STL is named Commonplace Template Library, it’s a library that gives 4 parts like container, algorithms, and iterators.

C++ STL
For extra info, check with STL in C++
Q-38. Outline inline perform. Can we have now a recursive inline perform in C++?
An inline perform is a type of request not an order to a compiler which ends up in the inlining of our perform to the primary perform physique. An inline perform can turn out to be overhead if the execution time of the perform is lower than the switching time from the caller perform to known as perform. To make a perform inline use the key phrase inline earlier than and outline the perform earlier than any calls are made to the perform.
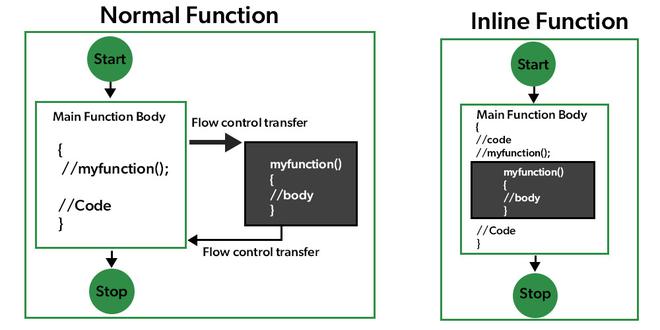
Inline Operate Rationalization
Syntax:
inline data_type function_name()
{
Physique;
}
The reply is No; It can’t be recursive.
An inline perform can’t be recursive as a result of within the case of an inline perform the code is merely positioned into the place from the place it’s known as and doesn’t preserve a chunk of knowledge on the stack which is critical for recursion.
Plus, should you write an inline key phrase in entrance of a recursive perform, the compiler will robotically ignore it as a result of the inline is just taken as a suggestion by the compiler.
For extra info, check with Inline Operate
Q-39. What’s an summary class and when do you utilize it?
An summary class is a category that’s particularly designed for use as a base class. An summary class accommodates no less than one pure digital perform. You declare a pure digital perform by utilizing a pure specifier(= 0) within the declaration of a digital member perform within the class declaration
You can not use an summary class as a parameter sort, a perform return sort, or the kind of an express conversion, nor are you able to declare an object of an summary class. Nevertheless, it may be used to declare pointers and references to an summary class.
An summary class is used if you wish to present a standard, carried out performance amongst all of the implementations of the part. Summary courses will assist you to partially implement your class, whereas interfaces would haven’t any implementation for any members in anyway. In easy phrases, Summary Lessons are a very good match if you wish to present implementation particulars to your kids however don’t need to enable an occasion of your class to be instantly instantiated.
Q-40. What are the static knowledge members and static member features?
The static knowledge member of a category is a standard knowledge member however preceded with a static key phrase. It executes earlier than major() in a program and is initialized to 0 when the primary object of the category is created. It is just seen to an outlined class however its scope is of a lifetime.
Syntax:
static Data_Type Data_Member;
The static member perform is the member perform that’s used to entry different static knowledge members or different static member features. It is usually outlined with a static key phrase. We will entry the static member perform utilizing the category title or class objects.
Syntax:
classname::perform title(parameter);
Knowledgeable Stage Query
Q-41. What’s the major use of the key phrase “Risky”?
Identical to its title, issues can change all of a sudden and unexpectantly; So it’s used to tell the compiler that the worth might change anytime. Additionally, the unstable key phrase prevents the compiler from performing optimization on the code. It was meant for use when interfacing with memory-mapped {hardware}, sign handlers, and machine code instruction.
For extra info, check with this Risky
Q-42. Outline storage class in C++ and title some
Storage class is used to outline the options(lifetime and visibility) of a variable or perform. These options normally assist in tracing the existence of a variable through the runtime of a program.
Syntax:
storage_class var_data_type var_name;
Some kinds of storage courses:

Examples of storage class
For extra info, check with Storage Class
Q-43. What’s a mutable storage class specifier? How can they be used?
Identical to its title, the mutable storage class specifier is used solely on a category knowledge member to make it modifiable though the member is a part of an object declared as const. Static or const, or reference members can’t use the mutable specifier. After we declare a perform as const, this pointer handed to the perform turns into const.
Q-44. Outline the Block scope variable.
So the scope of a variable is a area the place a variable is accessible. There are two scope areas, A world and block or native.
A block scope variable is also referred to as a neighborhood scope variable. A variable that’s outlined inside a perform (like major) or inside a block (like loops and if blocks) is a neighborhood variable. It may be used ONLY inside that exact perform/block by which it’s declared. a block-scoped variable is not going to be accessible outdoors the block even when the block is inside a perform.
For extra info, check with Scope of a variable
Q-45. What’s the perform of the key phrase “Auto”?
The auto key phrase could also be used to declare a variable with a posh sort in a simple vogue. You should use auto to declare a variable if the initialization phrase accommodates templates, tips that could features, references to members, and so on. With sort inference capabilities, we will spend much less time having to jot down out issues the compiler already is aware of. As all the categories are deduced within the compiler section solely, the time for compilation will increase barely however it doesn’t have an effect on the runtime of this system.
For extra info, check with Auto in C++
Q-46. Outline namespace in C++.
Namespaces allow us to arrange named objects that might in any other case have international scope into smaller scopes, permitting us to present them namespace scope. This allows program components to be organized into distinct logical scopes with names. The namespace offers a spot to outline or declare identifiers reminiscent of variables, strategies, and courses.
Or lets say that A namespace is a declarative zone that offers the identifiers (names of sorts, features, variables, and so forth) inside it a scope. Namespaces are used to rearrange code into logical classes and to keep away from title clashes, which could occur when you have got many libraries in your code base.
For extra info, check with Namespace in C++
Q-47. When is void() return sort used?
The void key phrase, when used as a perform return sort, signifies that the perform doesn’t return a worth. When used as a parameter listing for a perform, void signifies that the perform takes no parameters. Non-Worth Returning features are also referred to as void features. They’re known as “void” since they’re not designed to return something. True, however solely partially. We will’t return values from void features, however we will definitely return one thing. Though void features haven’t any return sort, they’ll return values.
For extra info, check with Void return sort.
Q-48. What’s the distinction between shallow copy and deep copy?
|
Shallow Copy |
Deep Copy |
|---|---|
| In Shallow copy, a replica of the unique object is saved and solely the reference deal with is lastly copied. In easy phrases, Shallow copy duplicates as little as doable | In Deep copy, the copy of the unique object and the repetitive copies each are saved. In easy phrases, Deep copy duplicates all the things |
| A shallow copy of a set is a replica of the gathering construction, not the weather. With a shallow copy, two collections now share particular person components. | A deep copy of a set is 2 collections with all the components within the authentic assortment duplicated. |
| A shallow copy is quicker | Deep copy is relatively slower. |
For extra info, check with Shallow copy VS Deep Copy
Q-49. Can we name a digital perform from a constructor?
Sure, we will name a digital perform from a constructor. However it might throw an exception of overriding.
Q-50. What are void pointers?
Identical to its title a void pointer is a pointer that isn’t related to something or with any knowledge sort. However, a void pointer can maintain the deal with worth of any sort and might be transformed from one knowledge sort to a different.
For extra, info refers to Void Pointer in C++
Bonus Query:
Q-1. What’s ‘this‘ pointer in C++?
this pointer permits each object to have entry to its personal deal with by means of an important pointer. All member features take this pointer as an implicit argument. this pointer could also be used to check with the calling object inside a member perform.
- this pointer is used to go an object as a parameter to a different technique.
- Every object will get its personal copy of the information member.
- this pointer is used to declare indexers.
For extra info, check with this pointer in C++


