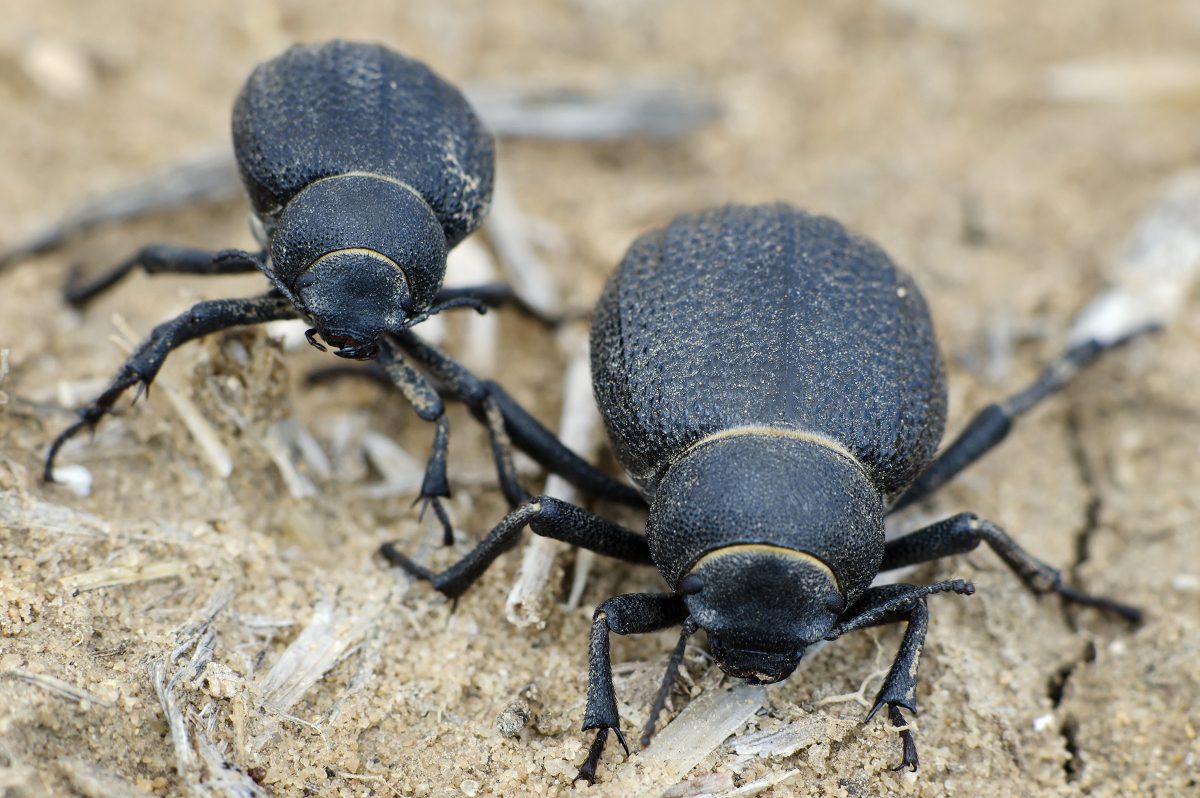

A novel strategy to capturing water vapour from the air makes an attempt to imitate spider’s webs and the our bodies of Namib desert beetles.
The group has developed sponges or membranes with a big floor space that regularly seize moisture from their surrounding setting.
“A spider’s internet is an engineering marvel,” mentioned College of Waterloo professor Michael Tam, a Analysis Chair within the discipline of purposeful colloids and sustainable nanomaterials. “Water is effectively captured by the net. The spider doesn’t must go to the river to drink, because it traps moisture from the air.”
Equally, Namib desert beetles haven’t any easy accessibility to water however purchase water from skinny air by leaning into the wind to seize droplets of water from the fog with their textured physique armour. This permits the moisture to build up and drip into their mouths.
Tam is engaged on the challenge with PhD college students Yi Wang and Weinan Zhao.
The group are engaged in biomimetic floor engineering for sustainable water harvesting. One know-how known as atmospheric water harvesting. To imitate the beetle’s distinctive floor construction, the analysis group is designing the same floor construction utilizing a cellulose-stabilized wax emulsion to manufacture surfaces that entice tiny water droplets whereas swiftly releasing bigger ones.
The group group is creating applied sciences that seize and repel water droplets by harnessing the facility of interfacial science and nanotechnology. Tam has efficiently developed superhydrophobic and waterproof paper. He’s additionally engineering a sensible and tunable floor that captures water from the air and dehumidifies it with seemingly minimal power consumption. The following step is to develop a scalable course of to engineer such surfaces.
Photo voltaic evaporation methods immediately harvest photo voltaic power, absorbing water and producing contemporary collectible vapour via evaporation. Distinctive mushroom buildings impressed the good biomimetic structural designs for photo voltaic evaporation.
The proposed freshwater technology methods may very well be cheap, energy-efficient, and environmentally pleasant.
In a latest publication in Nature Water, the group focus on a number of promising new water assortment and purification applied sciences.
Extra data on the analysis is on the market within the video under.

